Difference Between Real Diamonds and Fake Diamonds
A confusion is increasing between the recognition of a fake and a real diamond. Diamond is a lucrative natural metal hence its counterfeit are increasingly prevalent in markets the world over. There is an emergence of imitations such as moissanite, white sapphire, cubic zirconium, and topaz. However, advanced technological detections can separate a fake diamond from a real one. This article highlights these tests.
What is a Real Diamond?
This is a diamond made of strong and durable natural resources with distinct brilliance, sparkle, fire properties. A real diamond is used for many purposes and it is a very lucrative product. It has unparalleled light reflectivity and refractivity properties. If one reads the newspaper by laying the diamond on it, the prints will not be visible due to the light refractivity of diamond. It scatters light in different directions.
The internal crystal structure of a diamond is also distinct. A loupe (a scientific magnifying glass) can be used to see the internal structure. X-rays machines are also used for this purpose. Looking at the structure, it shows some imperfections as compared to a counterfeit diamond which, oftentimes, looks very perfect. The edges of the real diamond are sharp while fake diamond display rounded edges.
Diamond has a large density. It therefore sinks in a class of water whereas a fake counterpart would float either on the top or at the surface. A real diamond is well-known for its thermal and electrical conductivity. It disperses heat quickly. Also, it is not destroyed by higher temperatures. If it is heated and immediately inserted in a class of cold water, it will not break.
What is a Fake Diamond?
There are varieties of counterfeit diamonds on the market. Some exhibit similar thermal and durability properties like diamond. However, not all features can precisely mimic the real diamond. White sapphire, for instance, is blue but also available in white and is often misrepresented as a real diamond. Unfortunately, it lacks the sparkle and brilliance of a real diamond. It is similar to a white topaz which is available in a variety of colors such as yellow, brown, and gray. The topaz scratches easily whereas the diamond does not.
Some counterfeits such as the moissanite possess most similar properties like a real diamond. Moissanite is harder than topaz, sapphire and cubic zirconium. It is resistant to scratches. As thus, it can be confusing to test the legitimacy of a real diamond versus the moissanite using the scratch test. Furthermore, moissanite can also conduct heat but not electricity. This property disqualifies thermal conductivity tests in differentiating a real diamond from a moissanite.
Cubic zirconium, too, is a counterfeit of a real diamond. Rainbow colors are visible in the stone whereas with the real diamond there are visible outside. There are also lab manufactured diamond which exhibit similar chemical and physical properties to real diamonds. Nonetheless, they still do not possess all the features of a real diamond. Some of these counterfeit diamonds are not easily detectable with the naked eye. A gemologist is armed with skills to professionally detect a real diamond from a broad range of fake diamonds on the market.
Key differences between a real diamond and a fake diamond
Water test for Real vs. Fake Diamond
Inserting a fake diamond in water, it may float. Depending on the composition of the fake diamond, they will float differently with some sinking but not firmly touching the bottom. A real diamond has a large density and thus it will sink to the bottom.
Loupe test for Real vs. Fake Diamond
Loupe is a magnifying glass found at many jewelry stores. The glass can look closely at the structure of the diamond to detect if it is fake or a real one. A real diamond will show some imperfections in the carbon whereas counterfeit ones will show a perfect structure. But, the edges of a real diamond are often sharper whereas the fake diamonds have rounded edges.
Light refractivity of Real vs. Fake Diamond
A real diamond refract and bend light in a unique way that most counterfeit products may not. When light strikes the surface of a real diamond, it bounces hence reading through a diamond is not possible. A newspaper could be the ideal test. No matter how bright is, prints will not be visible through a real diamond. If one reads through a “diamond”, then that is probably a fake diamond with less light refractivity. A real diamond refract the light in various directions not linearly.
A fog test for Real vs. Fake Diamond
When inhaling air onto a diamond, a real one will disperse the heat quickly. A fake one will take time to disperse the fog. This is yet another DIY test to detect the identity of a diamond.
Thermal conductivity
Heating a diamond and inserting it in cold water will not break it. It is strong and resistant to high heat. But, moissanite can also withstand higher temperatures. This, therefore, makes it challenging to spot a real diamond from a moissanite. Other counterfeits do not survive higher temperatures and subsequent immersion into cold water without breaking.
Light reflectivity
Like light refractivity, light reflectivity is also effective in detecting a real diamond from a fake one. This feature refers to the quality of light reflected when it strikes the surface of the diamond. A sparkle test is ideal in this case. For instance, holding the diamond closer to the lamp will show some colorful reflections with some bright white light bouncing off perfectly.
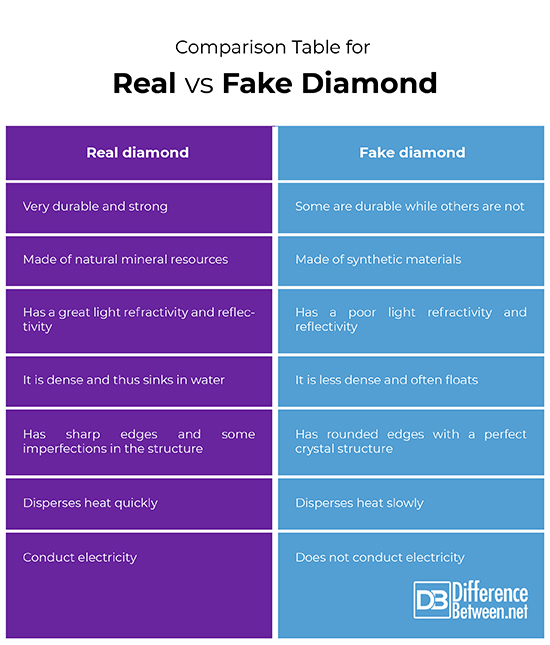
Comparison Table for Real Vs. Fake Diamond
Summary of Real vs. Fake Diamond
- A real diamond is natural whereas a fake diamond is synthetic
- A real diamond refracts and reflects light extremely well whereas a fake diamond does not excel in that
- A real diamond is scratch resistant whereas most fake diamonds are not except a few mimics such as moissanite
- A real diamond conducts heat and electricity whereas a fake diamond does not. Moissanite is an exception with regard to thermal conductivity
- A fake diamond has perfect structures with rounded edges
- A real diamond has sharper edgesD
- Difference Between CBD and Indica - April 22, 2019
- Difference Between Unilateral Contract and Bilateral Contract - February 8, 2019
- Difference Between Polki and Kundan - December 15, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/61093791@N04/33331706871
[1]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/jewellery-diamond-jewelry-diamonds-1203951/
[2]Nonyelu Anyichie (16 October 2015). The Fake Crystal Diamond. AuthorHouse
[3]Megan Willett (16 January 2015). How to tell if a diamond is fake or real? Accessed at: https://www.businessinsider.com/how-to-tell-if-a-diamond-is-fake-or-real-2015-1?IR=T. Accessed on: 25 August 2018.