Difference Between Cannabis and Alcohol
Cannabis is a drug that is named for the plant genus that it is extracted from. Alcohol is a chemical substance that consists of an alkyl group attached to at least one hydroxyl group.

What is Cannabis?
Definition:
Cannabis is the name given to marijuana which is a chemical substance extracted from leaves and buds of the plant of the same genus, Cannabis.
Properties:
Cannabis plants contain chemical substances known as cannabinoids, which are secondary metabolites produced by the plant. The main two cannabinoids of interest to people are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol); the two main chemicals found in marijuana.
Formation:
The cannabis drug is extracted from the Cannabis plants that are grown either outdoors or inside. The most important species of cannabis plants used to extract the cannabinoids and make cannabis are Cannabis sativa, C. indica, and C. ruderalis.
Effects on the brain:
The cannabinoid chemicals found in cannabis bind to various receptors in the brain, causing changes in how the brain works. The THC binds to both the CB1 and CB2 receptors on nerve cells in the brain while the CBD binds to the 5-HT1a receptor of nerve cells. The THC chemical found in cannabis does have a psychoactive impact on the brain and it in fact causes the “high” associated with smoking marijuana, and it can cause people to feel paranoid or to hallucinate. The CBD seems to have an anti-convulsant effect on the brain.
Uses:
The CBD in cannabis does seem to help reduce seizure activity in children who have severe seizure disorders such as Dravet syndrome. This chemical, CBD or cannabidiol also has useful antispasmodic properties.

What is Alcohol?
Definition:
Alcohol is a chemical substance that is comprised of at least one hydroxyl group which is bonded to an alkyl group. This bond is formed at the carbon atom of the alkyl group. A small percentage of the alcohol, ethanol, is also used to make alcoholic beverages which people drink.
Properties:
Alcoholic substances are liquids which have no color and a smell that can be described as like a fruit. There are different types of alcohols, each with their own properties, but they do all have a greater boiling point than alkane molecules.
Formation:
Alcohols can be made in the laboratory through artificial means, but the type of alcohol known as ethanol is formed naturally by organisms such as plants and yeasts, that are undergoing fermentation reactions. Synthetically, alcohols can be formed by reduction reactions involving carbonyl groups and hydrogen atoms.
Effects on the brain:
When alcohol is consumed the chemical passes through the blood-brain barrier and binds to receptors on the nerve cells. The ethanol adversely affects short-term memory because it influences the hippocampus region of the brain. The molecules of alcohol actually bind to GABA receptors and glutamate receptors. Alcohol influences mood because it impacts the neurotransmitters dopamine and serotonin, causing feelings of relaxation and pleasure. The cumulative effect of alcohol in the brain is that it can cause intoxication symptoms depending on how much and how quickly alcohol is consumed.
Uses:
The many different types of alcohol are used in industry for various applications, for instance, methanol is used in the formation of fuels and as part of antifreeze substances. The ethanol is used to make up alcoholic beverages which people drink for relaxation and in social settings.
Difference between Cannabis and Alcohol?
Definition
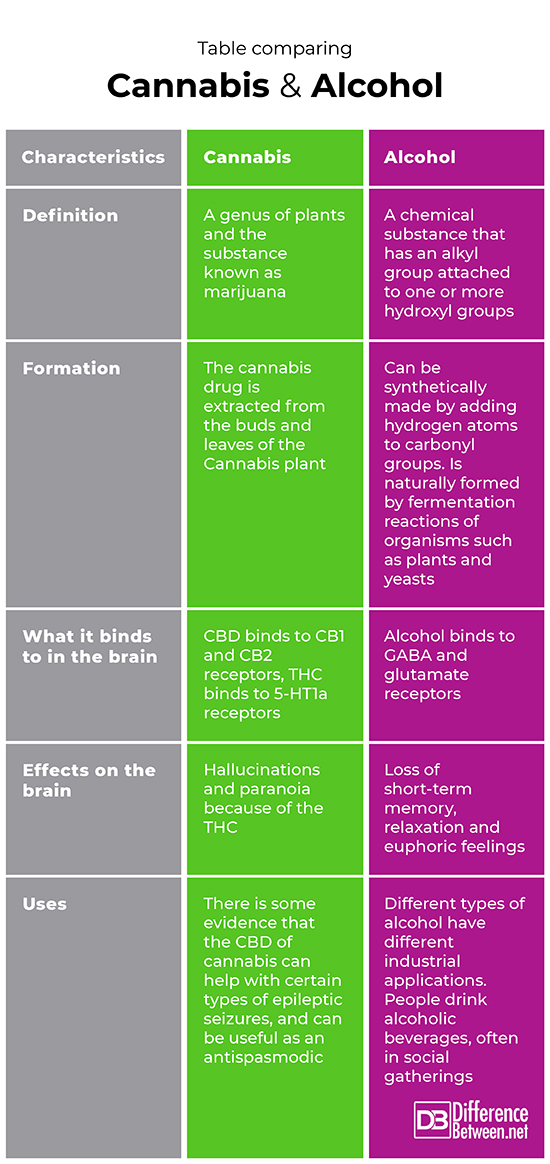
Cannabis is the name for a genus of plants and for a drug that is made from cannabinoid extracts of the plant. Alcohol is a chemical substance that consists of an alkyl group that is bonded to one or more hydroxyl groups.
Formation
The cannabis drug is extracted from the leaves and buds of the marijuana, Cannabis, plant. Alcohol can be synthesized by a reduction reaction involving hydrogen atoms and carbonyl groups and can be made naturally during fermentation in plants or yeasts.
What it binds to in the brain
The CBD of cannabis binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors while the THC binds to 5-HT1a receptors. The alcohol binds to both glutamate and GABA receptors in the brain.
Effects on the brain
Cannabis does have psychoactive effects because the THC can cause paranoia and hallucinations in people, and the CBD acts as an anti-convulsant. Alcohol as a beverage affects short-term memory and it also causes a feeling of euphoria and relaxation.
Uses
There is scientific evidence that CBD, a component in cannabis can help with certain epileptic seizures, and can be useful as an antispasmodic. There are various industrial applications for alcohol and people drink alcoholic beverages, often in social gatherings.
Table comparing Cannabis and Alcohol
Summary of Cannabis Vs. Alcohol
- Cannabis is the marijuana drug extracted from the marijuana plant which is called Cannabis.
- Alcohol is a chemical substance and is found in several different forms such as methanol or ethanol.
- Cannabis contains cannabinoid chemicals which can have psychoactive effects and some beneficial effects, such as helping to treat certain seizure disorders.
- Alcohol is often made into a beverage that people drink in social settings.
- Difference Between Constipation and Bowel Obstruction - April 3, 2024
- Difference Between Constipation and Diarrhea - March 30, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulite and Stretch Marks - March 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Banerjee, Niladri. "Neurotransmitters in alcoholism: A review of neurobiological and genetic studies." Indian journal of human genetics 20.1 (2014): 20.
[1]Mechoulam, Raphael, and Lumı́r Hanuš. "Cannabidiol: an overview of some chemical and pharmacological aspects. Part I: chemical aspects." Chemistry and physics of lipids 121.1-2 (2002): 35-43.
[2]Paul, Steven M. "Alcohol-sensitive GABA receptors and alcohol antagonists." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 103.22 (2006): 8307-8308.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cannabis_01_bgiu.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/1464/24060063701_90f43e248d_b.jpg


The following statement appears on your website. It looks incorrect:
The CBD of cannabis binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors while the THC binds to 5-HT1a receptors.