Difference Between IQ and EQ
Introduction
The difference between Intelligence Quotient (IQ) and Emotional Quotient (EQ) is very important when trying to understand human potential. EQ measures the depth of emotional intelligence, which is important for empathy, resilience, and getting along with others. IQ measures cognitive skills that are important for doing well in school and solving problems. This study tries to break down their similarities and differences in order to show how they shape our personal and professional lives, both individually and as a group. By talking about these parts of human intelligence, we hope to add to the conversation about how to help people improve both their cognitive and emotional skills in a way that is balanced and necessary for a happy life.

What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
Definition and Origin
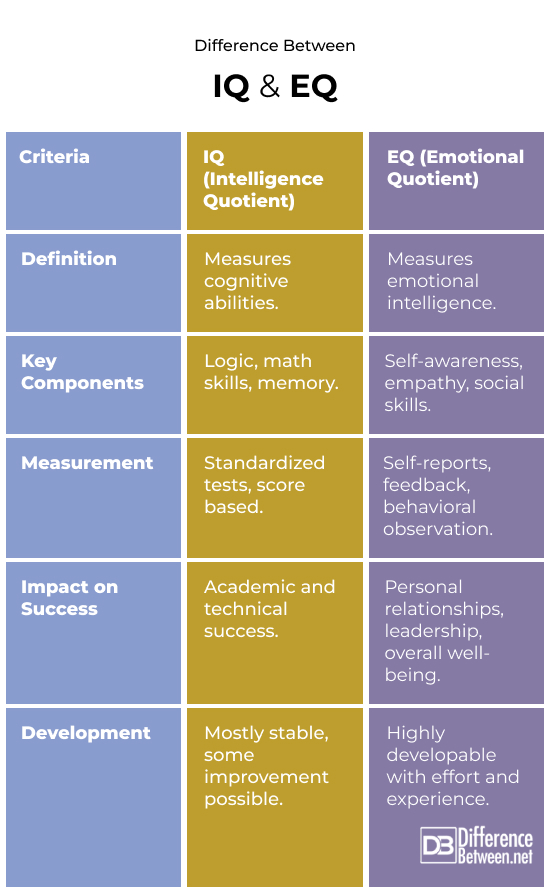
IQ is a typical intelligence test. It is based on a set of tests that measure cognitive skills. IQ was first discussed by French psychologist Alfred Binet and Théodore Simon in the early 1900s. The Binet-Simon exam identified students who needed more help in school. German psychologist William Stern coined “IQ” to represent the gap between mental and physical age.
How It’s Measured
Many IQ tests are standard. These tests assess many cognitive abilities. These assessments assess a person’s ability to think broadly, solve problems, understand complex ideas, and learn quickly. The test findings determine the IQ score, which is usually 100. Scores above 100 indicate wiser than average, while scores below 100 indicate less smart. Few people have very high or very low IQ scores. Most have normal scores. This is a bell curve.
Key Components
There are a few important parts of cognitive skill that IQ tests measure:
- Mathematical proficiency.
- Memory
- Logical reasoning: the skill of looking at problems, finding patterns, and drawing conclusions from them.
- Spatial Recognition: Being able to see and change forms and how they fit together in space.
- Understanding analogies is the ability to see how different ideas or things are related to each other.

What is EQ? (Emotional Quotient)
Definition and origin
Emotional Intelligence (EQ) measures a person’s ability to detect, comprehend, control, and use their emotions to communicate, relate, solve problems, and avoid arguments. The best-selling book “Emotional Intelligence” by psychologist Daniel Goleman stressed the importance of emotional intelligence. EQ gained popularity then. Goleman suggested that EQ may be more significant than IQ for career and life success.
How It’s Measured
Several instruments and methodologies measure EQ by assessing emotional and social skills. These assessments include self-report surveys and 360-degree tests that gather feedback from peers, subordinates, and managers. IQ tests score questions consistently, whereas EQ tests don’t. They assess emotional intelligence and social skills.
Key components
Daniel Goleman found that emotional intelligence is made up of five main parts:
- Being self-aware means being able to see and understand your own feelings, strengths, weaknesses, beliefs, and goals.
- Self-regulation means being able to control or shift your unwanted feelings.
- Drive: A strong desire to work for reasons other than money or fame.
- Empathy: the skill of being able to understand how other people feel and treat them based on their feelings.
Similarities Between IQ and EQ
- Important for Success: Both IQ and EQ are important for success in both personal and work life.
- IQ measures how smart someone is, while EQ measures how emotionally and socially intelligent someone is.
- Potential for Growth: EQ can grow a lot over time, but IQ stays pretty stable overall.
- Important for well-being: both affect how decisions are made, how leaders act, and how happy people are with their own lives.
- Comprehensive ability View: They give a full picture of a person’s ability when put together.
Difference Between IQ and EQ – Comparison of Key Differences
- Problem-solving and reasoning are measured by IQ. EQ addresses emotions and social relationships.
- Success: IQ affects academic and job performance. EQ impacts relationships and happiness.
- Improvement Potential: IQ changes little over time. EQ may be substantially enhanced with practice.
- Workplace: IQ aids technical skills and work completion. People management, teamwork, and conflict resolution require EQ.
- IQ is mostly inherited and stable. Life experiences shape EQ, which can improve over time.
Difference Between IQ and EQ
Summary
Both IQ and EQ are complimentary to personal and professional success: IQ tests cognitive capacities and predicts academic and technical achievement, while EQ measures emotional intelligence, necessary for leadership and well-being. Through effort and experience, EQ may grow despite IQ’s stability and standardization. To live a full and satisfying life, IQ and EQ must be balanced.
FAQs
Is it better to have high IQ or EQ?
Both are important. High IQ can enhance academic and problem-solving skills, while high EQ improves social interactions and emotional well-being. A balance of both is ideal for overall success.
Is EQ more accurate than IQ?
EQ and IQ measure different aspects of intelligence; one is not more accurate than the other. They serve different purposes in assessing cognitive abilities and emotional intelligence.
Why does IQ matter more than EQ?
In some contexts, especially in academic settings or tasks requiring technical skills, IQ might be emphasized. However, for leadership, teamwork, and personal relationships, EQ can be equally or more important.
How do I know my IQ and EQ?
IQ can be determined through standardized testing by professionals. EQ assessments often involve self-reported questionnaires and feedback from others on emotional and social competence.
Do geniuses have high EQ?
Not necessarily. While some geniuses may have high EQ, it varies from person to person. Genius-level IQ does not automatically equate to high emotional intelligence.
What are the 4 types of intelligence?
Howard Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences includes linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, and bodily-kinesthetic, among others. It highlights diverse cognitive abilities beyond traditional IQ.
Why do employers prefer EQ over IQ?
Employers value EQ for its role in teamwork, leadership, and adaptability in the workplace. High EQ individuals tend to have better conflict resolution skills and emotional management.
What is the IQ of a genius?
A genius-level IQ is often considered to be 140 or above on a standard IQ test.
Can you increase EQ?
Yes, EQ can be increased through self-awareness, empathy training, social skills development, and practical experience in managing emotions and relationships.
- Difference Between Psychopath and Sociopath - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between IQ and EQ - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between Good Carbs and Bad Carbs - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
4 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cherniss, C., & Goleman, D. (2000). Emotional intelligence. In Annual Meeting for the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology. New Orleans, LA.
[1]Mackintosh, N. (2011). IQ and human intelligence. American Chemical Society.
[2]Gondal, U. H., & Husain, T. (2013). Research Article A Comparative Study of Intelligence Quotient and Emotional Intelligence: Effect on Employees’ Performance. Asian journal of Business management, 5(1), 153-162.
[3]Mackintosh, N. (2011). IQ and human intelligence. American Chemical Society.
[4]Mackintosh, N. (2011). IQ and human intelligence. American Chemical Society.
[5]Mackintosh, N. (2011). IQ and human intelligence. American Chemical Society.
[6]Cherniss, C., & Goleman, D. (2000). Emotional intelligence. In Annual Meeting for the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology. New Orleans, LA.
[7]Cherniss, C., & Goleman, D. (2000). Emotional intelligence. In Annual Meeting for the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology. New Orleans, LA.
[8]Cherniss, C., & Goleman, D. (2000). Emotional intelligence. In Annual Meeting for the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology. New Orleans, LA.
[9]Gondal, U. H., & Husain, T. (2013). Research Article A Comparative Study of Intelligence Quotient and Emotional Intelligence: Effect on Employees’ Performance. Asian journal of Business management, 5(1), 153-162.
[10]Gondal, U. H., & Husain, T. (2013). Research Article A Comparative Study of Intelligence Quotient and Emotional Intelligence: Effect on Employees’ Performance. Asian journal of Business management, 5(1), 153-162.
[11]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEX7SVRpSU-brain-areas-low-poly-design-intelligence-abstract-geometric-image-iq/
[12]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADerysgJtc-emotional-quotient-and-intelligence-quotient-eq-and-iq-concept-with-human-brain-shape-and-gears/


Really inspiring to know
Thanks a ton for this ! EQ for the win ^^
VERY NICE! Thanks
Is it possible to overcome a lack of EQ? Specifically, I am a partner with a high IQ but a low EQ. His inability to motivate employees causes problems. He is somewhat narcissistic. He seems not to want to change. Can you help me? 619.985.1773 thank you.