Difference between Asthma and Upper Respiratory Infection
What is Asthma?
Definition of Asthma:
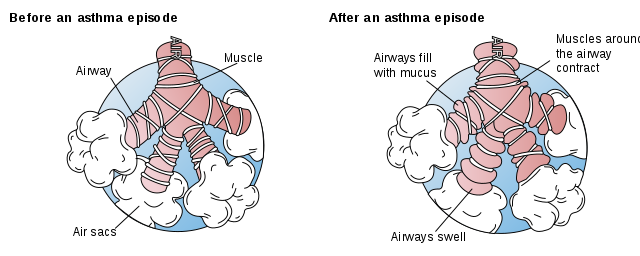
Asthma is a condition in which the airways become inflamed causing the bronchial tubes to constrict. Excess mucus is also often produced and the person struggles to breathe. Asthma should be taken seriously as it can kill a person if not controlled.
Symptoms of Asthma:
Symptoms of asthma include a feeling of tightness in the chest, cough, and difficulty breathing. Patients often have wheezing and a slight drop in systolic blood pressure when breathing in (usually the decrease in blood pressure is about 10 mmHg). Breathing rate and heart rate often speed up. Some patients have worse asthma symptoms at night.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis is made based on both a physical exam and tests of lung function. The lung function tests include spirometry to see if airflow is restricted. Provocative testing is also sometimes done in which patients inhale a substance like histamine, and the amount of bronchoconstriction is then noted. In addition, diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco) tests and allergy tests may also be done.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Asthma can be caused by an immune system response to allergens such as mold, dander, or pet dander. Other irritants such as cigarette smoke or perfumes can also worsen asthma. In some people asthma is triggered by exercise. Respiratory infections and some medicines such as aspirin or ibuprofen can also trigger an asthmatic attack in some people. Asthma occurs more often in boys and is more prevalent in cities than in rural areas, and it is more common in developed nations. More than 50% of first time attacks occur in childhood. Individuals who are prone to asthmatic attacks are more likely to have worse symptoms if they contract a respiratory infection.
Prevention and Treatment:
Asthma attacks can be prevented by knowing what factors trigger the attacks for a person, and avoiding these triggers. Using HEPA filters in houses can help reduce the number of airborne irritants that may cause an allergic response and an asthma attack. Inhalers that contain beta-2 antagonists can help to relax and open up the airways. Corticosteroids, mast cell stabilizers and leukotriene modifiers can help with the inflammation as well.
What is Upper Respiratory Infection?
Definition of Upper Respiratory Infection:
An upper respiratory infection is usually a contagious condition in which bacteria or viruses affect the upper parts of the human respiratory system which includes the throat, the sinuses and the nose.
Symptoms of Upper Respiratory Infection:
Symptoms of upper respiratory infection vary but usually include a runny or congested nose, fever, sneezing, coughing, and often a sore throat.
Diagnosis:
Physical exam along with symptoms is how the infection is diagnosed. Depending on what part of the system is infected, a person may be diagnosed with rhinitis (when the nose is affected), sinusitis (sinus infection) or pharyngitis (when the pharynx in the throat region is affected). Laryngitis is diagnosed when the voice box, the larynx, is affected.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The cause of upper respiratory infections is most often viral. These infections can be caused by viruses such as those that cause the common cold or influenza. Viruses implicated in such upper respiratory tract infections include respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza, influenza, rhinovirus and adenovirus. People who have a compromised immune system are also at higher risk of catching these viruses and becoming ill.
Prevention and Treatment:
One way to help reduce the chances of catching a virus or bacteria is to wash your hands often and avoid contact with people who are ill. Being vaccinated against the flu virus can help prevent upper respiratory tract infections that occur due to influenza. Treatment of infections, particularly if viral, is symptomatic and aimed at relieving symptoms. Patients can be given medicines to reduce fever and pain, expectorants, cough suppressants, and antihistamines.
Difference Between Asthma and Upper Respiratory Infection
Definition
Asthma is an inflammatory condition in which the bronchial tubes become constricted making breathing difficult. Upper respiratory infections are infections of the nose, throat and sinuses that are caused by contagious bacteria and viruses.
Symptoms
Symptoms of asthma include difficulty in breathing, wheezing, coughing, fast heart rate and breathing rate, and often, a slight drop in blood pressure when breathing in. Symptoms of upper respiratory infections include coughing, runny or congested nose, sore throat, and fever.
Diagnosis
Asthma is diagnosed using a physical exam, along with lung function tests such as spirometry. Diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco) tests and allergy tests may also help to detect asthma. Upper respiratory infections are diagnosed by physical exam and noting the symptoms.
Causes
Asthma is caused most often by a person reacting to airborne allergens and irritants, but it can be induced by exercise in some people. Upper respiratory infections are caused by some bacteria, but mostly by viruses such as influenza, rhinovirus, parainfluenza virus, adenovirus and respiratory syncytial virus.
Prevention
Asthma is best prevented by avoiding the triggers that cause it. Upper respiratory infections can be prevented by washing hands often, avoiding contact with sick people and by obtaining a flu vaccine every year.
Treatment
Asthma is treated by inhalers containing beta-2 antagonists; as well as medicines such as corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers. Upper respiratory infections are most often treated symptomatically with pain and fever reducers, cough suppressants, expectorants and antihistamines.
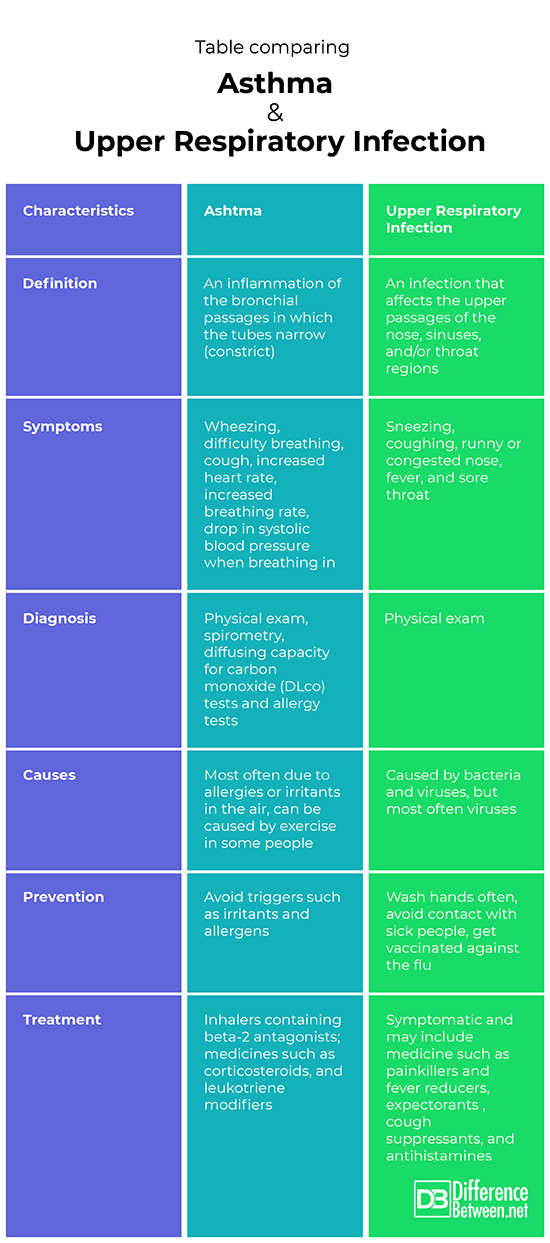
Table Comparing Asthma and Upper Respiratory Infection
Summary of Asthma Vs. Upper Respiratory Infection
- Asthma is an inflammatory condition which can make breathing very difficult.
- Upper respiratory infections are caused most often by viruses and cause symptoms like a congested and runny nose, coughing and sneezing and sore throat.
- Asthma can be made worse by having an upper respiratory infection.
- Asthma can be dangerous and thus needs to be carefully controlled.
- Upper respiratory infections can be prevented by avoiding sick people and getting the flu vaccine each year.
- Difference Between Constipation and Bowel Obstruction - April 3, 2024
- Difference Between Constipation and Diarrhea - March 30, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulite and Stretch Marks - March 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/14/Asthma_before-after-en.svg/640px-Asthma_before-after-en.svg.png
[1]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2012/Mar/05/2000172800/780/780/0/120305-F-JV314-001.JPG
[2]Bijanzadeh, Mahdi, Padukudru Mahesh, and Nallur Ramachandra. "An understanding of the genetic basis of asthma." Indian Journal of Medical Research 134.2 (2011): 149.
[3]Kramer, Laura D. “Types of viral disorders”.Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/viruses/types-of-viral-disorders#v1017628
[4]Ortega, Victor E, and Emily J. Pennington. “Asthma”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2017, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pulmonary-disorders/asthma-and-related-disorders/asthma