Difference Between Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephron
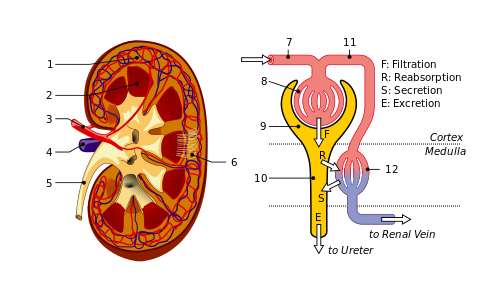
Each kidney consists of two parts: outer, 5-10 mm thick, called the cortex, and inner, called medulla.
The basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys is the nephron. Each human kidney contains 800 000 to 15 000 000 nephrons.
Each nephron consists of:
- Renal (Malpighian) corpuscle:
o Glomerulus;
o Bowman’s capsule.
- Renal tubule:
o Proximal convoluted tubule;
o Proximal straight tubule;
o Distal convoluted tubule;
o Distal straight tubule;
o Connecting tubule;
o Loop of Henle.
Depending on the location of the Malpighian corpuscles and the length of the loop of Henle, the following types of nephrons are distinguished:
- Cortical nephrons – short loop of Henle, Malpighian corpuscles located in the outer cortex;
- Intermedium nephrons – medium loop of Henle, Malpighian corpuscles located in the middle of the cortex;
- Juxtamedullary nephrons – long loop of Henle, Malpighian corpuscles located under the base of the pyramids.
What is Cortical Nephron?
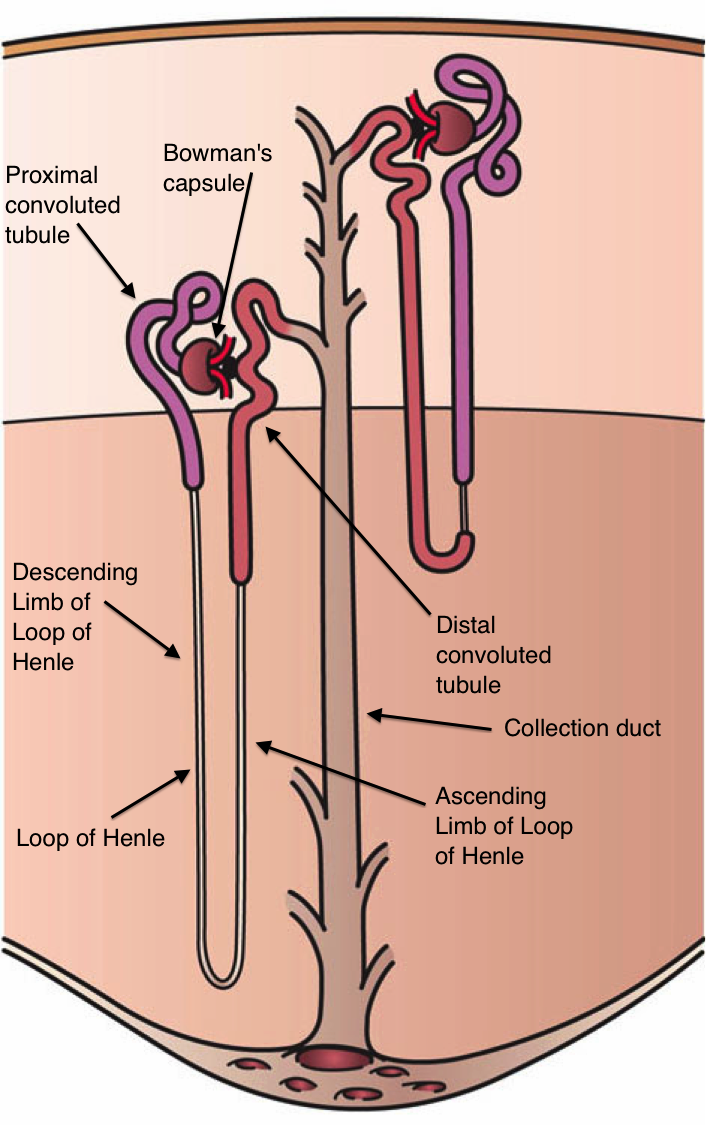
Cortical nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a short loop of Henle, which penetrates only the outer renal medulla. The Malpighian corpuscles of these nephrons are located in the outer part of the renal cortex.
Cortical nephrons occur in all vertebrates. About 85% of all nephrons in the human kidney are cortical. The major part of the regulatory and excretory functions of the human body is carried out by them.
At the beginning of each cortical nephron, in the outer renal cortex, is located a small network of capillaries called glomerulus. The main function of the glomerulus is to filter the blood, coming from an afferent arteriole of the renal arterial circulation. During the filtration water, ions, amino acids, glucose, and other small molecules are filtered into the Bowman’s space of the nephrons. From there the filtrate enters the renal tubule and follows a U-shaped path to the collecting ducts. Then it flows into the renal calyx as urine. Platelets, red and white blood cells, and large proteins remain inside the glomerulus. In the renal tubules of the cortical nephrons occurs reabsorption. Most of the water, ions, amino acids and glucose are reabsorbed through a vascular network situated around the loop of Henle, called vasa recta. As a result of the short loop of Henle, the vasa recta in the cortical nephrons is also small.
What is Juxtamedullary Nephron?
Juxtamedullary nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a long loop of Henle extending deep into the renal medulla. The renal corpuscles of these nephrons are situated close to the renal medulla.
Juxtamedullary nephrons occur only in birds and mammals. About 15% of all nephrons in the human kidney are juxtamedullary. At the beginning of each of them is located a large glomerulus. The bigger size of the glomeruli increases the filtration rate of the juxtamedullary nephrons, compared to the cortical ones. The long loop of Henle is surrounded by a large vasa recta network. The generated hyperosmolar gradient leads to the production of concentrated urine.
The juxtamedullary nephrons concentrate or dilute urine. Depending on the quantity of water, absorbed by the vasa recta the produced urine is more concentrated or diluted.
Difference Between Cortical Nephron and Juxtamedullary Nephron
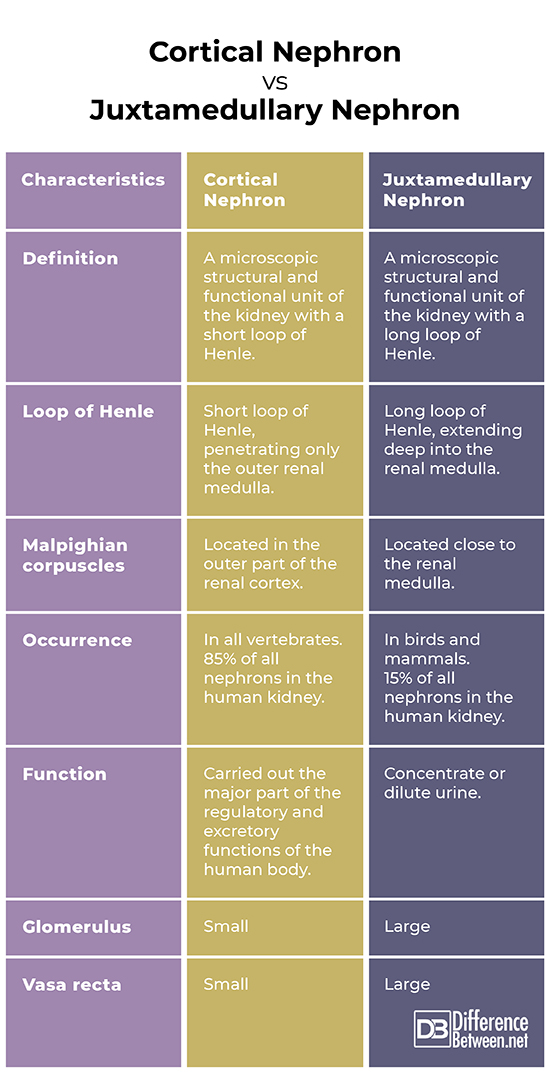
Definition
Cortical Nephron: Cortical nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a short loop of Henle.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: Juxtamedullary nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a long loop of Henle.
Loop of Henle
Cortical Nephron: Cortical nephrons have a short loop of Henle, which penetrates only the outer renal medulla.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: Juxtamedullary nephrons have a long loop of Henle extending deep into the renal medulla.
Malpighian corpuscles
Cortical Nephron: The Malpighian corpuscles of the cortical nephrons are located in the outer part of the renal cortex.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: The Malpighian corpuscles of the juxtamedullary nephrons are situated close to the renal medulla.
Occurrence
Cortical Nephron: Cortical nephrons occur in all vertebrates.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: Juxtamedullary nephrons occur only in birds and mammals.
Function
Cortical Nephron: The major part of the regulatory and excretory functions of the human body is carried out by the cortical nephrons.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: The juxtamedullary nephrons concentrate or dilute urine.
Glomerulus
Cortical Nephron: At the beginning of each cortical nephron, in the outer renal cortex, is located a small glomerulus.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: At the beginning of each juxtamedullary nephron is located a large glomerulus.
Vasa recta
Cortical Nephron: As a result of the short loop of Henle, the vasa recta of the cortical nephrons is also small.
Juxtamedullary Nephron: The long loop of Henle of the juxtamedullary nephrons is surrounded by a large vasa recta network.
Cortical Nephron VS. Juxtamedullary Nephron
Summary:
- The basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys is called nephron. Each human kidney contains 800 000 to 15 000 000 nephrons.
- Cortical nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a short loop of Henle.
- Juxtamedullary nephron is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney with a long loop of Henle.
- Cortical nephrons have a short loop of Henle, which penetrates only the outer renal medulla. Juxtamedullary nephrons have a long loop of Henle extending deep into the renal medulla.
- The Malpighian corpuscles of the cortical nephrons are located in the outer part of the renal cortex and those of the juxtamedullary nephrons – close to the renal medulla.
- Cortical nephrons occur in all vertebrates, while the juxtamedullary nephrons occur only in birds and mammals.
- About 85% of the nephrons in the human kidney are cortical, and about 15% – juxtamedullary.
- The major part of the regulatory and excretory functions of the human body is carried out by the cortical nephrons. The juxtamedullary nephrons concentrate or dilute urine.
- As a result of the short loop of Henle, the vasa recta of the cortical nephrons is small. The long loop of Henle of the juxtamedullary nephrons is surrounded by a large vasa recta network.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/dc/KidneyAndNephron-v4_Antares42.svg/500px-KidneyAndNephron-v4_Antares42.svg.png
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kidney_Nephron.png
[2]Baldzhiev, G., V. Vasilev, A. Baldzhiev. Human Anatomy - a textbook for medical colleges. Sofia: Laks Book. 2015. Print.
[3]Netter, F. Atlas of Human Anatomy. Sixt Edition. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier. 2014. Print.
[4]Taal, M., G. Chertow, P. Marsden, K. Skorecki, A. Yu, B. Brenner. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney E-Book. 9th Edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. 2011. E-book.


NYC information