Difference Between EMT and Paramedic
Introduction
Ever wondered who rescues people from automobile accidents and heart attacks like superheroes? Meet EMTs and Paramedics, the emergency world’s dynamic team. Consider EMS a high-speed race against time where every second is a precipice. Though flashing lights and ambulances generate drama, it’s more than that.
EMTs and paramedics are commonly confused, but they’re different. They both act when things go wrong, but there’s more. Like superheroes and super-superheroes, each are amazing but in different ways.
Why care about the difference? Apart from winning your next trivia night, knowing the difference can help you appreciate these unsung heroes. Also, knowing who’s who saves you in a need, so it’s good. Discover what makes these lifesavers special. It’s not just the uniform!

What is an EMT? (Emergency Medical Technician)
Alright, let’s break it down. An EMT, short for Emergency Medical Technician, is basically your first line of defense in a medical emergency. Think of them as the MVPs who jump into the game when someone’s health is on the line. They’re the folks who show up first when you dial 911 for a medical emergency – be it a slip and fall, a fender bender, or something more serious.
Definition and Role
So, what’s in a name? EMTs are trained to provide basic emergency medical care. It’s like they carry a toolkit of life-saving skills. Their main gig? Stabilize you, make you comfortable, and get you to the hospital if needed. They’re the calm in your storm, keeping things under control until you’re in the safe hands of hospital staff.
Training and Certification Requirements
Becoming an EMT isn’t just a walk in the park. These guys go through rigorous training. We’re talking about a course that can take anywhere from three months to a year, depending on where you’re at. They learn the ABCs of emergency care – Airway, Breathing, Circulation – and get hands-on with skills like CPR, using defibrillators, and controlling bleeding. And the grand finale? They’ve got to pass a national or state exam to be certified. No small feat, that.
Key Responsibilities and Skills
Now, when it comes to the nitty-gritty, EMTs are trained to handle the rough stuff. They assess patients, figure out what’s wrong, and jump into action. They’re masters at splinting broken limbs, bandaging wounds, and managing shock. Plus, they’re skilled drivers (ambulance racing, anyone?) and top-notch communicators. They’ve got to relay patient info to the doctors, after all. And let’s not forget the softer skills – like keeping patients (and sometimes their freaked-out families) calm in what’s probably one of their worst days.

What is a Paramedic?
Let’s emphasize paramedics. Paramedics are like EMTs’ older siblings—they’ve been around longer and have more tricks. Like emergency medical special forces, they intervene when things get tough.
Definition and Role
Paramedics are skilled emergency medical professionals. When more than first aid is needed, these pros step in. Need immediate medication? They have. Need more complex lifesaving methods? They’re involved. Paramedics make complex medical decisions in high-pressure situations. They’re like emergency care quarterbacks in rapid fire.
Training and Certification Requirements
Now things get serious. Paramedics train more than EMTs. The program lasts 1,200 to 1,800 hours and may need an associate degree. This instruction goes beyond talent enhancement. It’s intensive, encompassing sophisticated medical techniques, pharmacology, anatomy, and physiology. And certification? Equally tough. For certification, paramedics must pass a demanding national exam.
Key Responsibilities and Skills
Paramedics are turbocharged EMTs. They can now do more sophisticated procedures like intubation, providing a larger spectrum of drugs, and advanced resuscitation. They can handle heart attacks and serious traumas. EKGs and other lifesaving devices are also taught to them.
Possible Similarities Between EMTs and Paramedics
EMTs and paramedics are a dynamic team. Despite their differences, these two share more than an ambulance journey. Similar to different flavors of lifesaving ice cream. Investigate their similarities.
Emergency Medical Care Goals Shared
EMTs and paramedics save lives. They hop into that ambulance when the alarm rings to help the needy immediately. They’re knights in shining armor (or uniforms) for anyone facing the worst day of their life, whether it’s a slight injury or a severe problem. Both strive to stabilize patients, give prompt care, and ensure safe hospital transport.
Skills and Duties Overlap
Now for the details:
- Both EMTs and Paramedics have basic skills.
- Both are skilled in CPR, bleeding control, and shock management.
- They also excel at patient assessment, which is like solving a puzzle in real time.
- They must also communicate well with patients, families, hospital staff, and other first responders.
- Remember, they both must stay calm under pressure, which is difficult when there are emergencies around.
Despite their distinctions, EMTs and Paramedics both provide excellent emergency care. They’re like two sides of the same coin, each protecting us from life’s surprises.
Key Differences Between EMTs and Paramedics
Let’s examine what distinguishes EMTs and Paramedics. Similar to comparing a Swiss Army knife to a multi-tool. Both are handy, but one has more devices. Analyze these distinctions.
Difference between education and training
EMT training is like emergency care’s beginning course—important but superficial. A course that lasts a few months to a year.
EM paramedics are like emergency medicine PhDs. Their training is more like a marathon, lasting up to two years and covering more ground. They study sophisticated medical procedures, pharmacology, anatomy, and physiology.
They can do several medical procedures.
The fundamental medical operations EMTs can perform are CPR, bandaging, and helping patients with their prescriptions.
What about paramedics? Their list is longer. They can perform EMT duties and more advanced life-saving treatments like medicine administration, intravenous therapy, and more. Like an ambulance-back emergency room.
Decision-Making Authority vs. Autonomy
EMTs are like trusted sidekicks. They follow procedures and hand the baton to paramedics or doctors when things get tricky.
Paramedics are increasingly independent. They often make vital health care decisions on the spot. They learn to make snap decisions that can change a patient’s care.
Career advancement opportunities vary
Career advancement for EMTs generally requires paramedic training. Leveling up in the game gives you greater skills and responsibilities.
With enhanced training, paramedics have more options. They might become flight paramedics or EMS managers.
Possible Workplace Differences
Usually, EMTs work in ambulances and basic life support. Quick responses and patient stabilization are key.
Given their increased training, paramedics may work in more diverse settings. Consider critical care transport, aviation medical services, or tactical law enforcement.
EMTs Vs Paramedics: Difference between EMTs and Paramedics comparison chart
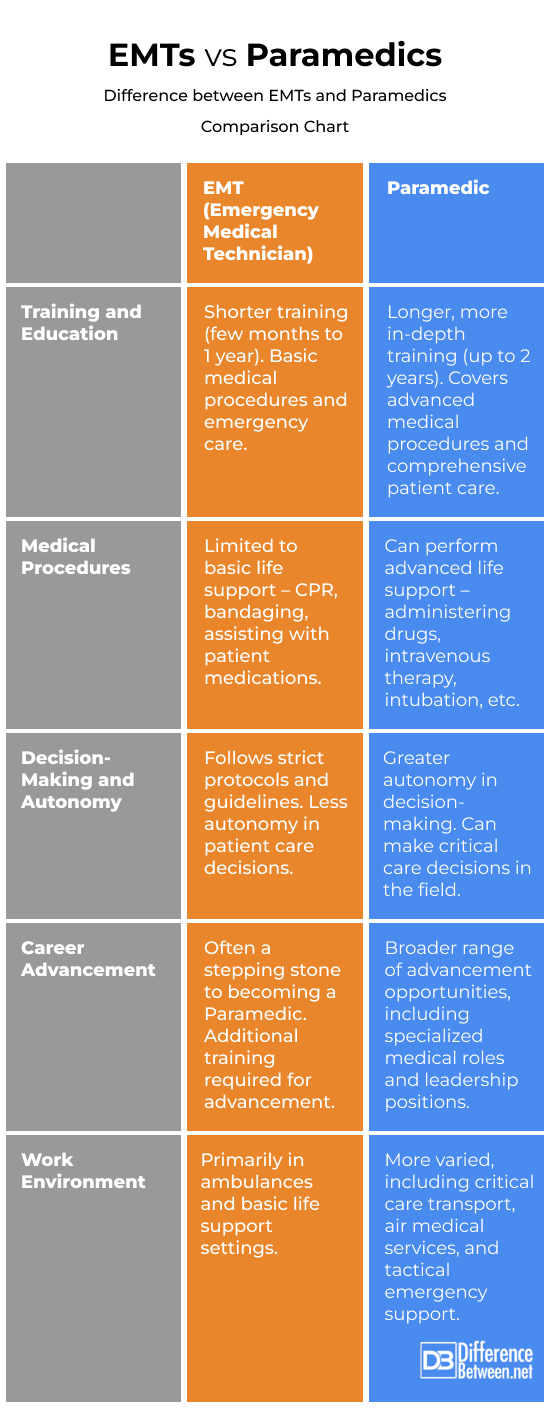
Summary
To conclude, EMTs and paramedics are the unsung heroes of emergency medical care. Basic life support skills prepare EMTs to offer rapid care and stabilization in crises. They prepare patients for advanced care as first responders.
However, paramedics provide more medical experience. They can make quick decisions and perform advanced life-saving techniques with increased training. They can handle complex medical situations in different and difficult settings.
Though different in duties and scope, both jobs are essential to emergency medical care. They collaborate to provide critical care to patients. In emergencies, EMTs and paramedics save lives and provide comfort. Emergency medical services depend on their dedication and abilities, improving communities daily.
FAQ
What is the highest level of paramedic?
The highest level of paramedic is typically known as a Critical Care Paramedic or a Flight Paramedic. These professionals have advanced training in critical care, often including flight physiology and advanced pharmacology.
Is EMT better than EMS?
EMT (Emergency Medical Technician) is a specific role within EMS (Emergency Medical Services). EMS is the broader system that includes various roles like EMTs, Paramedics, and sometimes, first responders. It’s not about one being better; they’re different components of the same emergency response system.
Is an EMT not a doctor?
No, an EMT is not a doctor. EMTs are trained in emergency care and basic life support but do not have the extensive medical training that doctors undergo. They provide critical first response care in emergency situations.
How do I become an EMT in Ontario?
To become an EMT (commonly known as a Primary Care Paramedic) in Ontario, you need to complete a recognized paramedic training program, usually offered at the college level, and pass the provincial certification exam.
What is the difference between EMT and paramedic in Canada?
In Canada, the terms EMT and Paramedic have evolved. The role previously known as EMT is now often referred to as Primary Care Paramedic (PCP), while Paramedic typically refers to Advanced Care Paramedic (ACP). PCPs provide basic life support, while ACPs have more advanced training and scope of practice.
What is the best salary for a paramedic?
The salary for a paramedic can vary widely based on location, experience, and the level of training. In general, paramedics can expect a higher salary with more experience and advanced certifications.
How long is EMT school in Canada?
EMT (or Primary Care Paramedic) programs in Canada typically range from 1 to 2 years, including both classroom instruction and practical experience.
How much are EMTs paid in Canada?
Salaries for EMTs (or Primary Care Paramedics) in Canada vary by province and experience. The starting salary is usually competitive, with potential increases based on experience, additional skills, and geographical location.
How many years does it take to become a paramedic in Ontario?
Becoming a paramedic in Ontario typically requires 2 to 3 years of education, including college programs and practical experience.
Difference between Respiratory Therapist and Paramedic?
A Respiratory Therapist specializes in providing and managing respiratory care and life support to patients with breathing disorders. A Paramedic provides a broader range of emergency medical care, including trauma care, cardiac support, and medication administration. Respiratory Therapists often work in hospital settings, while Paramedics are primarily field-based.
- Difference Between Psychopath and Sociopath - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between IQ and EQ - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between Good Carbs and Bad Carbs - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAETd5YzmcM-emt-wearing-a-blue-jacket/
[1]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAAgMJFd2lY-paramedic-with-oxygen-unit/
[2]Moungey, B. M., Mercer, C. B., Powell, J. R., Cash, R. E., Rivard, M. K., & Panchal, A. R. (2021). Paramedic and EMT program performance on certification examinations varies by program size and geographic location. Prehospital Emergency Care, 26(5), 673-681.
[3]Woollard, M. (2006). The role of the paramedic practitioner in the UK. Australasian Journal of Paramedicine, 4, 1-9.
[4]Franks, P. E., Kocher, N., & Chapman, S. (2004). Emergency medical technicians and paramedics in California. University of California, San Francisco, Center for the Health Professions.
[5]1 Franks, P. E., Kocher, N., & Chapman, S. (2004). Emergency medical technicians and paramedics in California. University of California, San Francisco, Center for the Health Professions.
[6]2 Moungey, B. M., Mercer, C. B., Powell, J. R., Cash, R. E., Rivard, M. K., & Panchal, A. R. (2021). Paramedic and EMT program performance on certification examinations varies by program size and geographic location. Prehospital Emergency Care, 26(5), 673-681.
[7]3 Franks, P. E., Kocher, N., & Chapman, S. (2004). Emergency medical technicians and paramedics in California. University of California, San Francisco, Center for the Health Professions.
[8]4 Woollard, M. (2006). The role of the paramedic practitioner in the UK. Australasian Journal of Paramedicine, 4, 1-9.
[9]5 Moungey, B. M., Mercer, C. B., Powell, J. R., Cash, R. E., Rivard, M. K., & Panchal, A. R. (2021). Paramedic and EMT program performance on certification examinations varies by program size and geographic location. Prehospital Emergency Care, 26(5), 673-681.
[10]6 Woollard, M. (2006). The role of the paramedic practitioner in the UK. Australasian Journal of Paramedicine, 4, 1-9.


Very nice article. EMTs and Medics are quite different, in the types of treatments they perform. Also, an EMTs career outlook is limited to either obtaining a Paramedic cert, or making the jump into management with an EMS Management degree, while a Paramedic has many more options. Many are taking a Paramedic to RN program, or leaving the profession for careers in other types of Public Safety.