Difference Between Tumor and Cyst
Introduction
Both tumors and cysts are growths found in the body. They have distinct characteristics. A cyst is, like a sac structure that can contain substances such as air, fluid or other materials. They can develop in areas of the body including bones organs and soft tissues. While most cysts are harmless (not cancerous) there are cases where a cyst might be associated with cancer. On the hand a tumor refers to a mass or growth of tissue that can appear anywhere in the body. Like cysts tumors can develop in parts of the body. Tumors are classified into two types; noncancerous) and malignant (cancerous).
What is a Tumor?
Definition
A tumor is a mass of tissue that occurs due, to uncontrolled cell division. It can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors remain confined to one area without spreading whereas malignant tumors have the ability to invade tissues and spread to parts of the body (metastasis).
Risk Factors
The causes of tumors can vary. They often arise from a combination of factors and external influences, like exposure to environmental toxins, radiation and certain lifestyle choices such as smoking. In addition, specific viruses and chronic inflammation can also increase the risk.
Diagnosis
Tumors are identified through methods, including imaging tests like X rays CT scans, MRI scans and PET scans. Biopsies play a role in determining the nature of the tumor by examining a sample under a microscope.
Symptoms
The symptoms a person might experience from a tumor largely depend on its size and where it’s located. Common signs can include noticeable swelling or lumps, a sense of pain or discomfort, general fatigue, unexpected weight loss, and alterations in bodily functions. It’s also crucial to understand that many tumors don’t initially cause any noticeable symptoms, making them hard to detect in their early stages. This can sometimes lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Complications
Malignant tumors can pose life threatening risks; therefore, early detection is essential for care givers to manage and prevent complications. Benign tumors can also lead to complications by exerting pressure, on organs or nerves.
Some complications associated with tumors include;
- Invasion of neighboring tissues resulting in pain and dysfunction.
- Metastasis which involves cancer cells spreading to parts of the body.
- Obstruction of vital organ function potentially leading to organ failure.
Side effects that can arise from cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation therapy are nausea, fatigue and a weakened immune system.
Treatment
Treating tumors involves a range of options, each tailored to the tumor’s type, stage, and the patient’s health and preferences. Key treatments include:
- Surgery: removing the tumor physically.
- Radiotherapy: using radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: employing drugs to target cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: focusing on specific cancer characteristics and boosting the immune response.
The choice of treatment is a collaborative decision between the patient and their healthcare team, considering both medical and personal factors.

What is a Cyst?
Definition
A cyst refers to a sac structure that is usually benign in nature. It can contain fluids, air or semi solid material and may appear within the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cysts can develop due to reasons such as infections, genetic conditions, blockages in ducts or passageways within the body chronic inflammatory conditions or as a result of foreign bodies.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves making use of imaging techniques like ultrasound scans, CT. MRIs. In some cases where necessary for confirmation purposes or further investigation, into findings related to cysts; a biopsy may be performed.
Symptoms
The symptoms associated with cysts vary depending on their location and size. They often manifest as lumps. Sometimes cause discomfort or pain.
Complications
Possible complications that may arise from cysts include rupture (bursting) infection or interference with organ function if the cyst grows large enough.
Treatment options
Treatment options for cysts can vary depending on the size, type, site and associated symptoms. It can range from monitoring to surgical removal.
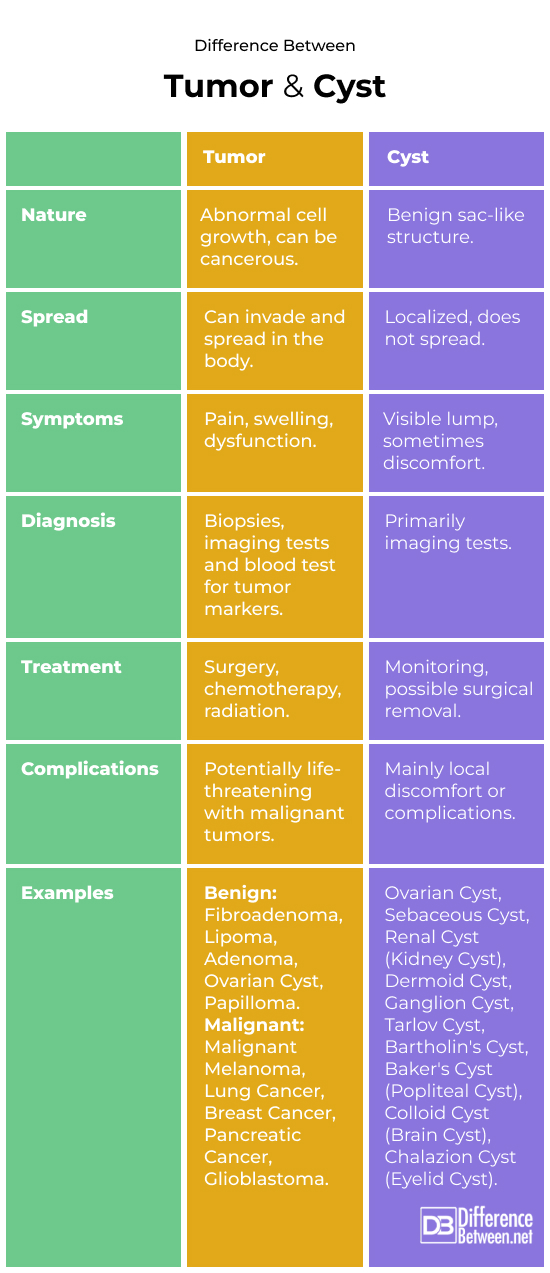
Differentiating between tumors and cysts
- Tumors refer to cell growth. Have the potential to be cancerous. On the hand cysts are sacs filled with fluid, air or semi solid material and are usually benign.
- Tumors can invade tissues. Spread throughout the body whereas cysts remain localized and do not spread.
- Symptoms of tumors may include pain, swelling or dysfunction depending on their location. Cysts present as a lump that might cause some discomfort.
- Tumors are diagnosed through biopsies and imaging tests. Cysts are often identified through imaging techniques.
- Treatment for tumors may involve surgery, chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In contrast cysts usually require monitoring over time or surgical removal if they become problematic.
- While tumors can be life threatening, in cases cysts generally cause discomfort or local complications.
- The severity and expected outcomes differ significantly between tumors and cysts:
- Tumors: The severity depends on whether the tumor’s benign or malignant. Benign tumors are typically not life threatening. Can often be successfully removed through surgery with results. However malignant tumors (cancers) pose a health risk that could lead to death if not effectively treated. The differences in outcomes depend on the type of growth the stage at which it is diagnosed and how well it responds to treatment.
- Cysts: Generally speaking, cysts are less severe compared to tumors. Most cysts are non-cancerous. Do not lead to health complications. In many cases they can be left untreated unless they cause discomfort or affect the functioning of organs. If necessary surgical removal of cysts usually results in outcomes with risk of recurrence.
Summary
Tumors and cysts are types of growths that can occur in the body. Tumors consist of cells that can be either benign or malignant. They have the potential to invade surrounding tissues and spread throughout the body. On the other hand, cysts are sacs filled with fluid, air or semi solid material that typically remain localized. The diagnosis, treatment methods and outcomes differ significantly between these two conditions. Tumors generally pose a health risk. Require more aggressive treatments compared to cysts which are often less severe and managed through less invasive approaches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How can you distinguish between a cyst and a tumor?
Cysts typically have a round appearance as they contain fluid (such, as cysts). They also tend to be movable when touched. Tumors however may have a shape. Feel harder (like breast cancer).
Can a cyst develop into a tumor?
Most cysts are non-cancerous. Do not develop into tumors. However, there are types of cysts that have the potential to become cancerous. For example, certain ovarian cysts can progress into cancer.
Are tumors usually firm or soft?
Tumors can vary in texture depending on their type and location. Soft tumors, like lipomas, which’re fatty growths have a different consistency compared to hard tumors like bone tumors.
Do cancerous cysts contain pus?
No, the presence of pus is commonly associated with abscesses than cancerous cysts.
Do tumors cause pain upon pressing?
Some tumors may cause discomfort when pressed especially if they are inflamed or located near nerves. Inflamed lipomas serve as an example.
What does a cancerous cyst look like?
Cancerous cysts can exhibit appearances but they often appear irregular in shape and feel firm to the touch.
How can you differentiate between a lump being a cyst or something else?
If a lump feels smooth, round and movable similar to cysts it is more likely to be a cyst. However, an accurate diagnosis requires evaluation.
Do tumors move when touched?
Certain benign tumors such as fibroadenomas in the breast may exhibit movement upon touching. On the hand malignant (cancerous) tumors tend to remain fixed in place.
Can cysts become hard over time?
Yes, if filled with substances, like keratin cysts have the potential to harden over time. Epidermoid cysts serve as an example of this occurrence.
- Difference Between Psychopath and Sociopath - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between IQ and EQ - April 2, 2024
- Difference Between Good Carbs and Bad Carbs - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
3 Comments
Trackbacks
Leave a Response
References :
[0](1) Neoplasia. In M. S. Delbridge & W. Al-Jundi (Eds.), Basic science for the MRCS: A revision guide for surgical trainees (4th ed., pp. 317-330). Elsevier Limited.
[1](2) Neoplasia. In M. S. Delbridge & W. Al-Jundi (Eds.), Basic science for the MRCS: A revision guide for surgical trainees (4th ed., pp. 317-330). Elsevier Limited.
[2](3) Neoplasia. In M. S. Delbridge & W. Al-Jundi (Eds.), Basic science for the MRCS: A revision guide for surgical trainees (4th ed., pp. 317-330). Elsevier Limited.
[3](4) Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Tumor: What does it mean? Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/expert-answers/tumor/faq-20057829
[4](5) Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Tumor: What does it mean? Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/expert-answers/tumor/faq-20057829
[5]Neoplasia. In Schneider, A. S., & Szanto, P. A. (2014). Pathology (5th ed., pp. 87-103). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
[6]Micalizzi, D. S. (2023, February 7). What’s the Difference Between a Tumor and a Cyst? Mass General Brigham. Retrieved [date of access], from https://www.massgeneralbrigham.org/en/about/newsroom/articles/difference-between-cyst-and-tumor
[7]Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Tumor: What does it mean? Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/expert-answers/tumor/faq-20057829
[8]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADDOa784sA-stomach-tumor-caused-by-h-pylori/
[9]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADB6MUOfjw-cyst/


Very nice, informative.
My husband’s mother had breast cancer. After removing the breast and treatment she survived for tenyears. After she had bone cancer and survived only for eight months. Now there is cyst in my daughter’s scalp. Do i have to go for cancer diagnosis. Kindly advice us.