Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Meiosis and Mitosis describe cell division in eukaryotic cells when the chromosome separates.
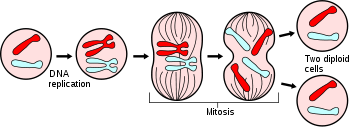
In mitosis chromosomes separates and form into two identical sets of daughter nuclei, and it is followed by cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm). Basically, in mitosis the mother cell divides into two daughter cells which are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell.
Phases of mitosis include:
1. Interface -where cell prepares for cell division and it also includes three other phases such as G1 (growth), S (synthesis), and G2 (second gap)
2. Prophase ‘“ formation of centrosomes, condensation of chromatin
3. Prometaphase- degradation of the nuclear membrane, attachment of microtubules to kinetochores
4. Metaphase- alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate
5. Early anaphase- shortening of kinetochore microtubules
6. Telophase- de-condensation of chromosomes and surrounded by nuclear membranes, formation of cleavage furrow.
7. Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm
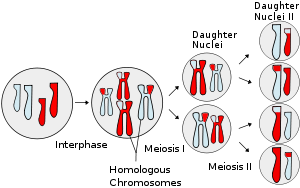
Meiosis is a reductional cell division where the number of chromosomes is divided into half. Gametes formations occur in animal cell and meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction which occurs in eukaryotes. Meiosis influence stable sexual reproduction by halving of ploidy or chromosome count. Without meiosis the fertilization would result in zygote with twice the number of the parent.
Phases of meiosis include:
1. Meiosis I ‘“ separation of homologous chromosomes and production of two haploid cells (23 chromosomes, N in humans)
2. Prophase I ‘“ pairing of homologous chromosome pair and recombination (crossing over) occurs
3. Metaphase I – Homologous pairs move along the metaphase plate, kinetochore microtubules from both centrioles attach to the homologous chromosomes align along an equatorial plane.
4. Anaphase I – shortening of microtubules, pulling of chromosomes toward opposing poles, forming two haploid sets
5. Telophase I – arrival of chromosomes to the poles with each daughter cell containing half the number of chromosomes
6. Meiosis II – second part of the meiotic process with the production of four haploid cells from the two haploid cells
Summary:
Mitosis ‘“ separation of chromosomes into two identical sets of daughter cells
Meiosis- reductional cell division and the number of chromosomes is divided into half; it is essential for sexual reproduction, and therefore it occurs in eukaryotes
Find more information on Mitosis and Meiosis.
- Difference Between CA and CMA - February 1, 2010
- Difference Between CGA and CMA - January 30, 2010
- Difference Between Molds and Yeast - January 27, 2010
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
20 Comments
Trackbacks
- Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes | Difference Between
- Difference Between Cytokinesis and Mitosis | Difference Between | Cytokinesis vs Mitosis
- Difference Between Gymnosperms and Ferns | Difference Between | Gymnosperms vs Ferns

what happen to anaphase when reacting
right
I still don’t get it 😛
I REALLY GOT A LOT OF HELP AFTER READING THIS INFORMATION.BEFORE THIS I AM NOT ABLE TO MAKE DIFFRENCE B/W CELL DIVISION
Yeah me tooo
I like It!… Its a big help for a student like me, thanks a lot!
I agree with you, Its a big help
it was cool but too long cuz i don;t like to read
I’m korean but it’s easy to understand!! Thanks!
this website is really very good for all students like me,which is helpful to make d/ff . its like awesome…………..
Great post.
THANK YOU
thanks ****
Tank you better if side by side definition would have been given
this was really helpful am so appreciative
It’s not my first time to visit this web page, i am browsing this site
dailly and take pleasant facts from here every day.
It is best for study