Difference Between DNS and DHCP
DNS vs DHCP
DNS and DHCP are the two most essential IT Services and the cornerstones of how the internet operates. Without them, you’d be stuck remembering an array of numbers or IP addresses to access anything over the internet. DHCP makes sure no two hosts can have the same IP addresses. So, simply put, the internet connection ceases to exist without either of them. We break down some key differences between DNS and DHCP to avoid any confusion, if any.
What is DNS?
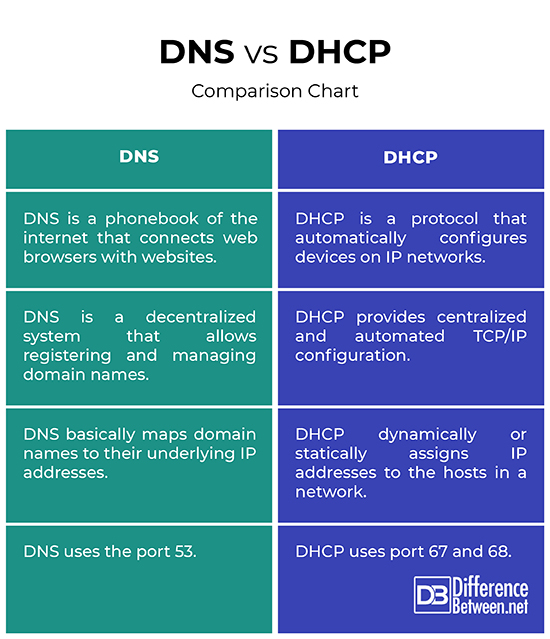
The Domain Name System, or simply called DNS, is like a phonebook of the internet that connects web browsers with websites. It is hierarchical naming system that identifies computers, services, or any other resources connected to the internet. It links a website to its matching human-readable domain name. When you look for something on the internet, if it’s registered with the DNS server you can query that server and it can tell you where the site is. It maintains a database of names of websites with their underlying IP addresses, which computers use to communicate with each other. Simply put, it is like a contacts app for the entire Internet.
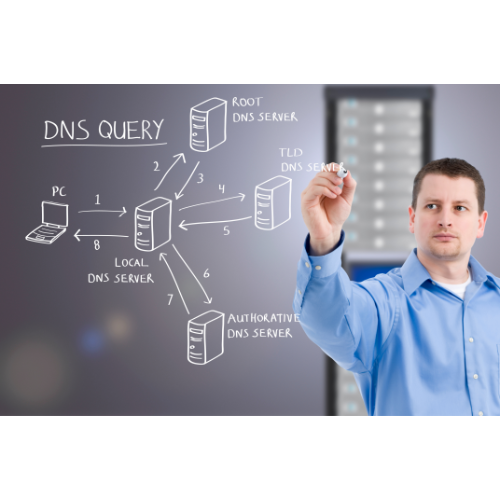

What is DHCP?
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and is a client-server protocol that automatically configures devices on IP networks. It has been an excellent time saver for IP network administrators. It is basically a network management protocol used to dynamically assign IP addresses and other information to fixed and mobile hosts that are either connected wirelessly or wired to the internet. DHCP enable a device to request for an IP address, and have one or more DHCP servers within the IP network service the request without any user intervention. It also allows efficient use of IP addresses to be reused among several devices within dynamically allocated address pools.
Difference between DNS and DHCP
- Definition – DNS is a hierarchical naming system that identifies, locates, and translated internet domain names into IP addresses, similar to a phone’s contacts list. DNS is like a phonebook, but for the entire internet that connects web browsers with websites. DHCP is a client-server protocol that dynamically assigns IP addresses and other information to fixed and mobile hosts that are either connected wirelessly or wired to the internet.
- Methodology – DNS is a decentralized system that allows registering, managing, and resolving domain names. Web browsing and most of the other internet activities rely on DNS to instantly locate an IP address in order to connect and access the content you’re looking for in the internet. DHCP provides centralized and automated TCP/IP configuration, allowing the network administrator to configure the network from a centralized area.
- Purpose – DNS is a database that located and translates internet domain names into IP addresses. It links a website to its matching human-readable domain name. So, DNS basically maps domain names to their underlying IP addresses. DHCP, on the other hand, is a network protocol that dynamically or statically assigns IP addresses to the hosts in a network. DNS eliminates the need to remember so many IP addresses, while DHCP reduces network administration by making everything fast and reliable.
DNS vs. DHCP: Comparison Chart
Summary
In a nutshell, without the DNS, the internet as we know it today would cease to exist. The computers that make up the internet are a system of large networks that communicate with each other and are identified using strings of numbers called IP addresses. It is not practical for any of us to remember such a huge array of numbers. DNS translates an actual name into these numbers. DHCP, on the other hand, is the protocol used for assigning IP addresses to the host in a network either dynamically or statically.

Is DNS the same as DHCP?
DNS and DHCP are entirely different things and each one has its own purpose. DNS is like a phonebook of the internet that maps domain names to their underlying IP addresses while DHCP is the protocol that dynamically or statically assigns IPs to the host in a network.
How do DHCP and DNS work together?
DHCP servers provide devices with IP addresses which can be registered against the DNS server so that the other devices on the internet can easily locate them and communicate with them.
Which comes first DNS or DHCP?
Both work across the client-server architecture, but DNS maps domain names to the IP addresses whereas DHCP assigns an IP to a requesting client. So, DHCP comes first.
What is DNS Example?
When you type a URL into the web browser, the DNS server returns the IP address associated with that name. For example, DNS translates domain names such as www.google.com into machine readable IPs such as 192.0.2.168.
Is DHCP better than static IP?
DHCP is the more popular option because as it’s cheaper and easier to deploy. Besides, DHCP is better for dynamic environments while static are better for static environments. DHCP basically eliminates the headache of assigning multiple IPs to each device on a network.
What is the purpose of DHCP?
DHCP is a network protocol that dynamically or statically assigns IP addresses to the hosts in a network, thereby reducing network administration.
Which port is DNS?
DNS uses the port 53.
- Difference Between HTML and Text - April 19, 2024
- Difference Between FTP and SFTP - April 16, 2024
- Difference Between El Nino and La Nina - April 13, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
2 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Rooney, Timothy and Michael Dooley. IP Address Management. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2020. Print
[1]Rooney, Timothy. IP Address Management: Principles and Practice. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. Print


sir, i would like to make a LAN for small office complex. which may i make DHCP or DNS server.
hi..
sir i have to make DHCP server
plz guide me for this project…
if u have any suggection then plz ut it on my email address
thnx in advance….