Difference Between OLED and AMOLED
Smartphones have dramatically transformed from a luxury possession into a necessity. It’s a necessary evil that has inflicted itself into our daily lives in such a way that it has no longer seen as a device primary designed to make and receive phone calls.
With technological innovation at its peak and burgeoning smartphone market, smartphones have come a long way since the first phone was created in 1973. While smartphones have evolved into a mini-computer much like a personal computer which fits in your pocket, we would like to shift your focus into the most important factor which most of the smartphone users tend to ignore, the display of the smartphone.
Let’s take a look the two display technologies – OLED and AMOLED – in detail.

What is OLED?
OLED stands for “Organic Light Emitting Diodes” and it works in a similar way to conventional diodes and LEDs, but instead of semiconductors it uses a series of thin organic films to produce rich and vibrant colors with much darker blacks.
The organic compounds emit light when current is passed through them which may not seem like a big difference when compared to conventional LED displays. However, unlike LEDs, OLED displays are insanely thin, more flexible, and remarkably small, in fact, so small they can be seen as individual pixels, millions of them which make for exceptional images.
Each tiny pixel creates light of its own based on how much current is passed through it, which is the key to the OLED’s excellent picture quality. As a result, it produces perfect deep blacks to deliver accurate colors and gain infinite contrast ratio.

What is AMOLED?
AMOLED is technically OLED with an additional layer of semiconducting film to activate each pixel more quickly. AMOLED stands for “Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode” and instead of a passive matrix technology, AMOLED uses an active matrix system which attach a thin film transistor (TFT) to control the flow of current to each pixel.
It exerts a high level of control over each pixel to provide an exceptional viewing experience. The TFT backplane technology is the key to the AMOLED’s vivid display. Because of the higher refresh rates, the power consumption is significantly less than other display technologies. AMOLED displays are mainly used in smartphones, laptops, and televisions – basically anything portable to accommodate superb display quality into a much flexible screen for spectacular results.
Basically, it’s a complete package of exceptional picture quality, power efficiency, and incredible performance.
Difference between OLED and AMOLED
Technology of OLED and AMOLED
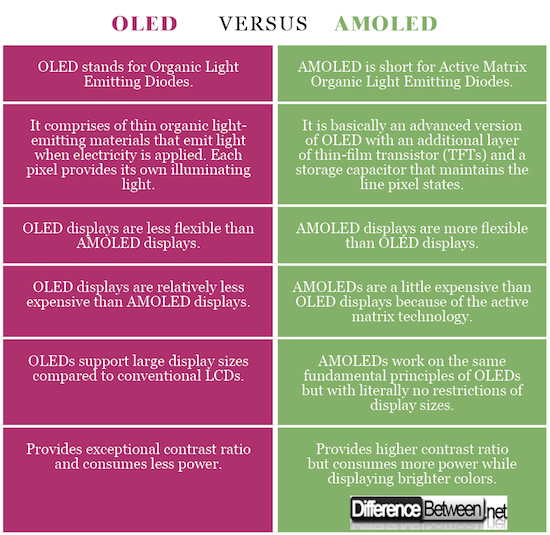
Smartphone displays have come a long way from conventional LCD screens to more vivid and crisp AMOLED panels. OLEDs (short for “Organic Light Emitting Diodes”) are made from thin organic light-emitting materials that emit light when current is passed through them. AMOLED (short for “Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode”), on the other hand, springs from OLEDs itself but with an additional layer of thin-film transistors (TFTs).
Display of OLED and AMOLED
OLED displays deliver much deeper blacks and on the contrary to the conventional LCD panels which are back-lit, OLEDs are “always off” by default unless each pixel is electrified individually. AMOLED displays are not as quite visible in direct sunlight. The TFT backplane technology is the key to AMOLED’s exceptional picture quality.
Working of OLED and AMOLED
OLEDs are simple solid-state devices comprised of a very thin film of organic compounds in an emissive electroluminescent layer where the electricity is produced. The organic compounds are sandwiched between the protective layers of glass or plastic. AMOLED, as the name suggests, consists of a matrix of OLED pixels with an additional layer of TFTs between them, which in turn controls the flow of current to each pixel.
Contrast Ratio for OLED and AMOLED
The light emitters in OLED display technology can be switched off completely which allows for a higher level of control over each pixel, which ultimately results in much deeper blacks and an excellent contrast ratio. Because each pixel emits light in AMOLED displays, the entire display delivers a greater artificial contrast ratio with much darker blacks and deeper brights. AMOLED displays have high refresh rate as well, but they are not well visible in direct sunlight.
Display Size of OLED and AMOLED
OLEDs are significantly thinner than standard LCDs as each pixel provides its own illumination resulting in thin, bright, and efficient displays. AMOLEDs are the newest sensation in the display technology that supports much larger display sizes. AMOLED panels can support literally any display size and can produce faster refresh rate.
OLED vs. AMOLED: Comparison Chart
Summary of OLED vs. AMOLED
While changes on a hardware level are easily recognizable, you may not just realize how much the smartphone displays have evolved as well. Display screens are like the windows to the mobile world which have witnessed a dramatic evolution in terms of innovation and technology. Mobile phones have evolved over the years in terms of shape, size, and features. But one of the most prominent features that always stand out might be the display. From the tiny pixilated screens of good old Nokia phones to the enormous retina HD displays of the much sophisticated iPhone to the high-tech super AMOLED displays of the Samsung phones, it’s easier to see how smartphone displays have evolved over time. This article explains the difference between the two popular display technologies – OLED and AMOLED.
- Difference Between Serif and Sans Serif - April 22, 2024
- Difference Between HTML and Text - April 19, 2024
- Difference Between FTP and SFTP - April 16, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
 Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
Email This Post
: If you like this article or our site. Please spread the word. Share it with your friends/family.
2 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Castellano, Joseph A. Handbook of Display Technology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012. Print
[1]Whitaker, Jerry C. Electronic Displays: Technology, Design and Applications. NYC: McGraw-Hill, 1994. Print
[2]Tsujimura, Takatoshi. OLED Display Fundamentals and Applications. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2017. Print
[3]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jeepersmedia/26829936061
[4]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/kamikura/1728418823


I enjoyed the explanation
Sagar, you should substitute “reputable” for “reputed” in your bio lol