Difference Between Metaphor and Personification
• Categorized under Language | Difference Between Metaphor and Personification
Metaphor and personification are figures of speech. They are easily confused because they are often used in the same sentence. The purpose of these figurers of speech is to bring more life and creativity into poetry and prose. A metaphor also persuades the reader that an object can be something else that in reality it could not be. Someone may say their job is a dream to create this feeling of a wonderful form of work.
Personification on the other hand gives human characteristics to an object and makes that object come alive in terms the reader can relate to. The writer can describe the sea as angry or the wind can be howling and pastries can tempt. These are all humanistic characteristics. When a metaphor and a personification appear in the same sentence the difference between them becomes blurred as the two roles of figurative speech seem to blend together.
‘The leaves are dancers, twirling with gay abandon.’ is a shining example of the metaphor ‘leaves are dancers’ and the personification with ‘gay abandon’ in the same sentence. Although the two forms of figurative speech are used together that does not make them the same.

Definition of a Metaphor
The metaphor tells the reader that an object, in a piece of poetry or prose, is something that it could not be in reality. This is a form of figurative writing and is used to create creative and imaginative writing. ‘I am drowning in a sea of grief.’ This example of a metaphor, the sea and grief, shows the reader how tragic the event was because of the overwhelming sensation of drowning in the sea of grief. The metaphor strengthens the point, or the purpose of the sentence, by setting two unlikely ideas into one statement. The metaphor is often an abstract idea or an emotion that could not be felt by an inanimate object.
Different types of metaphor used in figurative speech
There are six different types of metaphor listed in the following categories:
Absolute metaphors
These metaphors compare two things that absolutely could not be associated with each other. An example of this is the statement that a student is walking a tightrope with her grades. School work and tightrope walking are absolutely incompatible. One can not imagine them being part of the same activity.
Implied metaphors
Implied metaphors have vague unspecified terms and are very open ended. For example, ‘Spending too much time with my brother is like swimming in a sea of sharks.’ This statement does not specify where or when or how many sharks there are. It is open to interpretation.
Root metaphors:
These metaphors have become part of everyday life. They are rooted in well worn expressions. They have become clichés like ‘Life’s a Journey’ for example.
Mixed metaphors:
These metaphors are confusing and lack logic. They give a sense of mixed emotions and are difficult to understand. For example, ‘In the heat of the moment the wizard turned to ice and jumped to the beat of his own drum.’
Extended metaphor
A lengthy metaphor used in poetry and classical literature. Shakespeare loved to use extended metaphors. This passage comes from Romeo and Juliet and is a good example.
‘But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? Is it the east and Juliet the sun! Arise fair sun and kill the envious moon who is already sick and pale with grief.’
Dead metaphors
These metaphors have been over used and have become lifeless. The saying ‘You light up my life’ for example is no longer considered spontaneous and has lost its charm over the years due to its over usage.
How and why metaphor is used in literary circles?
A metaphor is used to create images that are strong and impress the reader. They allow a literal image to partner an intangible image to leave a lasting impression. They are exaggerations, but useful in creating a strong image or mood. Metaphor is particularly suited to poetry. It gives writing more creativity and color.
Metaphor has found its way into forms of pop culture and the stage and screen productions.
Pink Floyd used metaphor in their song ‘The Wall’ as the song’s lyrics talk of a wall – ‘teachers leave them kids alone. All in all its just another brick in the wall.’
The Wizard of Oz, a favourite children’s story, has characters making use of extended metaphor. The Lion seeks courage, the Scarecrow a brain and the Tin Man a heart.
An author may extend a metaphor into more than a sentence, the metaphor may continue through the story. A criminal for instance may be compared to a fox who steals the eggs laid by the chickens, from a farmer. The thief or fox extends his crime by attacking all the chickens and destroying their barn. This is the value of the extended metaphor it is there to be used throughout the story.
Looking at personification with persona in mind helps to see these two forms of figurative language differently.

The definition of personification.
Looking at personification with persona in mind helps to see the difference between metaphor and personification more easily.
Personification takes human characteristics and transfers them onto objects that are not human. It is the abstract quality of emotion and feeling that becomes part of the description of an inanimate object that gives the object its personification. Personification is often used to give types of weather a persona like wind that howls and the sun that smiles . Stars can wink and ants are able to march. All these human characteristics make the objects they describe seem more real to the reader.
How personification is used in literary circles.
Personification helps the reader to connect to the story or poem. The human traits and emotions, gestures and desires give something that does not have life, a living quality. In both prose and poetry this style of figurative language brings life to the writing. There is a great deal of personification in children’s literature and animation.
Personification brings humour to children’s literature and especially to nursery rhymes. The classic rhyme of ‘Hey Diddle Diddle, the cat and the fiddle,’ shows the funny side of the rhyme through the idea of a cat and a fiddle and a cow jumping over the moon. It is a silly nursery rhyme, but very appealing to the young age group it is written for.
Breakfast cereal gets brought to life in a poem called ‘The Little Corn Flakes’ by Kelly Roper. The little corn flakes have such fun swimming in a milky pool. Sadly, their fun doesn’t last as a spoon dips in to take them for a ride. This frivolous poem illustrates how personification can be part of a poem making breakfast cereal a fun food to eat for kids.
Walt Disney is a master at personification. Animals assume human qualities and even inanimate objects, like cups and saucers and candle sticks in Beauty and the beast, have human characteristics. They talk and have feelings although they are just made of pottery.
One great example of personification is evident in Henry Wadsworth Longfellow’s poem Paul Revere’s Ride.
He writes:
‘And the meeting house windows, blank and bare,
Gaze at him with spectral glare.
As if they already stood aghast,
At the bloody work they would look upon.
Emily Dickinson writes about a landscape that listens and shadows that hold their breath and these forms of personification bring vivid imagery to the land and the shadows.
There is no end to the creativity and vivid imagery conjured up through personification.
Chart to compare the two aspects of figurative language:
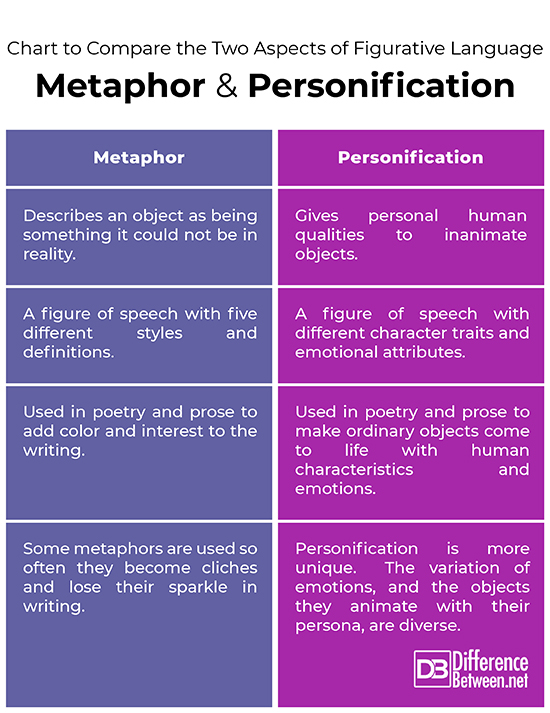
Summary of the Difference between Metaphor and Personification.
Using figurative language brings life to the written word. It allows authors and poets to create work that is more animated and easier to relate to. Poetic pictures are created and visual imagery made more relatable. There can be a blurring of the lines between these two forms of figurative language, especially, when they can be used in the same sentence for added description and impact. The difference comes with the metaphor comparing or relating one object to another that it is not like. While personification adds the emotional personal touch to objects that would not be able to express those kinds of emotions or be able to show human qualities.
- Difference Between Lagoon and Bay - October 20, 2021
- Difference Between Futurism and Preterism - August 12, 2021
- Difference Between Dichotomy and Paradox - August 7, 2021
Sharing is caring!
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Cite
APA 7
Wither, C. (2021, November 11). Difference Between Metaphor and Personification. Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects. http://www.differencebetween.net/language/difference-between-metaphor-and-personification/.
MLA 8
Wither, Christina. "Difference Between Metaphor and Personification." Difference Between Similar Terms and Objects, 11 November, 2021, http://www.differencebetween.net/language/difference-between-metaphor-and-personification/.
Leave a Response
Written by : Christina Wither. and updated on 2021, November 11
References :
[0]Brewer Robert Lee. 17th February 2020. www.writersdigest.com/write-better-fiction/metaphor personification Pub. Active Interest Media.
[1]Brewer Robert Lee. 17th February 2020. www.writersdigest.com/write-better-fiction/metaphor personification Pub. Active Interest Media.
[2]Oliver R. April 11th 2018. www.socratic.org/questions/what-is-the-difference-between-a-metaphor-and-personification? Pub. Socratic.org.
[3]Leengen Marcus. 26th November 2019. www.figurativelanguage.net/personification.hrml/ Pub. Figurative language blog.
[4]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Compositional_models_of_idiom_comprehension.png
[5]Image credit: https://pixy.org/src/428/4280331.jpeg
See more about : metaphor, Personification
