Difference Between Depreciation and Amortization
When a company acquires an asset that is expected to generate benefits over time, it usually comes at a cost. The cost of that asset cannot be simply recognized during the year it was acquired. Because majority of the assets do not last forever, the cost is spread over that asset’s useful life in order to match the timing of the cost with its expected revenue generation. Expenses are matched to the period when revenue is generated as a direct result of using that asset. Depreciation and Amortization are two ways to ascertain asset value over a period of their useful life. We’re going to all break it down for you and help you understand the differences between depreciation and amortization.

John has purchased the red Mercedes last year. Due to some reasons he wants to sell it off but to his surprise, he was getting much less amount that what he had purchased. Like many of us, he was also confused because he does not know that the value of the car purchased today won’t remain same after few year of its use. The commonly used term to deduct the particular amount before re selling the car is Depreciation and amortization. On first look they may look same but they are not same. I am going to explain the basic differences between depreciation and amortization below. You can take a quick overview to make out the right difference of both!
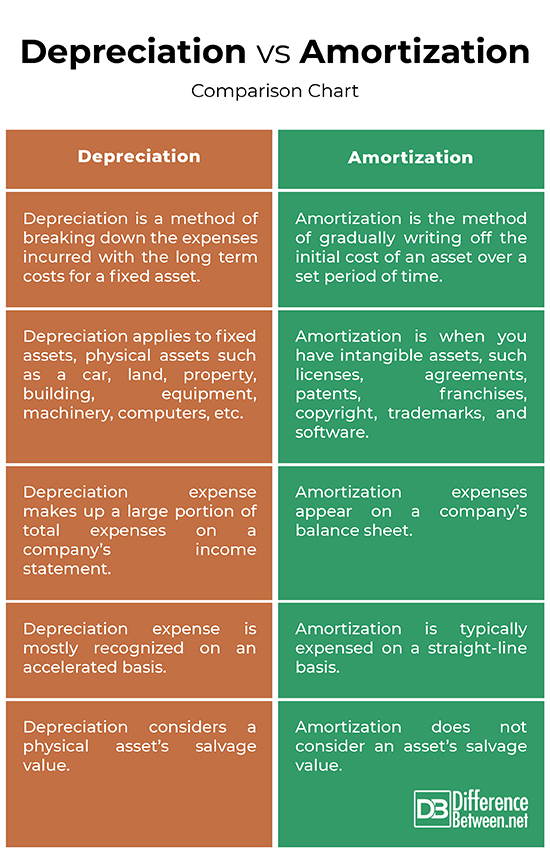
Depreciation is concerned with Tangible assets. The assets which we can see and touch can depreciate; like machinery and building among others. Their costs are spread over the number of years. Depreciation takes into account the wear and tear of the tangible assets. The moment you own or use the assets, it starts depreciating. There are at least 10 methods in accounting to take into account the depreciation. The income tax laws and company laws decide which method to use and how to use it.Suppose a company buys a machine for $12 million and expects it to have a useful life of 12 years, its cost will be depreciated over 12 years. In each accounting year, the company will write off $1 million (according to straight-line depreciation method), money depreciated would help company to make more money by that time.
Amortization is concerned with intangible assets. The assets which we can’t see or touch but we can feel like patents and copy rights come under intangible assets. It is the part of capitalized expenditure and preliminary expenditure which is usually distributed over the number of years. It is also fixed by company’s law and it can rapidly change. Basically, in amortization the intangible assets are written off over the number of years.
For example ABC Company spent $48 million US dollars on a Car engine technology and the patent on the engine lasts 12 years, this will mean that $4 million will be accounted each year as an amortization expense.
Both depreciation and amortization are non cash expense of the company and they decrease the earning while increasing the cash flow.
So What is Depreciation?
Depreciation describes the way in which accountants deal with the cost of a company’s long term assets. The monetary value of an asset gets decreased over time due to its use or wear and tear. Depreciation is the permanent or gradual reduction of the book value of such assets. Depreciation is a tax-deductible expense that makes up a large portion of total expenses on a company’s income statement. For example, when you buy a car or any type of fixed asset, you capitalize it and you don’t expense it, and it goes on your balance sheet. Over time, when you start to use the car, you start to slowly expense it and that’s what you call a depreciation expense. Depreciation applies to fixed assets on your balance sheet.
What is Amortization?
Amortization is used to describe a similar principle but in relation to intangible assets, such as licenses, software, agreements, patents, franchises, copyright, trademarks, and so on. Amortization is a method of spreading the cost of an intangible asset over a set period of time. Amortization basically is the same concept as depreciation, but instead of physical assets, it factors in intangible assets. For example, when you borrow money, you pay a simple interest rate either on a monthly basis or a yearly basis. With an amortized loan, you spread that principle and interest payment throughout the term. Your mortgage is the perfect example of this. The objective is same with amortization – that is to match the expense of acquiring an asset with the revenue it generates over time.
Difference between Depreciation and Amortization
-
Meaning
Sometimes people confuse there two terms as they both relate to assets. Depreciation is a method of breaking down the expenses incurred for the long term costs with a fixed asset. These assets record a gradual decrease in their value over their useful life over multiple years. Amortization, on the other hand, is the method of incrementally charging the cost of an asset to expense over a set period of time. Amortization is basically fixed payments done over a period of time.
-
Assets
One of the major differences between the two is that amortization is used in relation to intangible assets. Amortization basically is the same concept as depreciation, but instead of physical assets, it factors in intangible assets, such licenses, agreements, patents, franchises, copyright, trademarks, and software. Depreciation applies to fixed assets on your balance sheet, physical assets such as a car, land, property, building, equipment, machinery, computers, etc. Amortization is used to describe a similar principle but in relation to non-physical assets.
Depreciation vs. Amortization: Comparison Chart
Depreciation vs Amortization
Summary
Mathematically speaking, depreciation and amortization are basically the same things and even philosophically, they are not very different. The idea behind these two is to instead of expensing these expenses, spread out the expense over their useful life. The difference between the two is that depreciation is when you have physical assets such as a car, property, building, machinery, or any tangible asset. Amortization, however, is when you have non-physical assets, something less tangible like licenses, copyright, agreements, and software. If you have intangible assets, you would simply amortize it instead of depreciate it.
What are two types of amortization?
Amortization mainly refers to two types of situations: when paying off debt payments in regular intervals and for long-term loans like mortgage, and distribution of non-physical assets over a set period of time.
How do you calculate depreciation and amortization?
Depreciation is calculated by subtracting the asset’s resale value from its original cost. Amortization is the paying off debt payments over time till loan principle reduces to zero.
What are three different methods of amortization?
The three common amortization methods are straight line, declining balance, and annuity.
Why do you amortize?
Most assets lose their value over time. Amortization helps you understand and forecast the costs of assets over time. It allows you to quantify gradual losses in your account statements.
What are the similarities and differences between depreciation and amortization?
Both depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses, meaning no cash are spent during the time they are expensed. The difference between the two is that depreciation is used for physical assets whereas amortization is used for intangible assets.
What is the difference between accrual and amortization?
Accrual refers to the recording of revenues or expenses that a company has earned or incurred for which the company has not yet received payment or it expects to receive cash in a future period. Amortization, however, is to pay off gradually or in installments.
- Difference between Hypothesis and Theory - August 20, 2009
- Difference Between Jews and Christians - August 17, 2009
- Difference Between Jealousy and Envy - August 12, 2009
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
4 Comments
Trackbacks
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Feldman, Matan and Arkady Libman. Crash Course in Accounting and Financial Statement Analysis. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. Print
[1]Loughran, Marie. Auditing for Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Print
[2]Ross, Sean. “Amortization vs. Depreciation: What's the Difference?” Investopedia, 26 Jan. 2022, https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/06/amortizationvsdepreciation.asp.

I’m happy and very interestinng with the article, let others read and know each and everything across the boarders especial on this mentioned article
Thanks
Interesting! In accounting the distinction between the two is of a matter semantics. Both achieve the same thing i.e. to make a charge against profit for the consumption of the asset (or perceived or implied deduction in its value) and to reflect write down the value on the balance sheet. Don’t confuse this with an actual market value of the asset – either tangible or intangible.
great ,,love to visit everyday 4m now onwards