Difference Between Fomite and Vehicle
What are Fomite and Vehicle?
A fomite is an inanimate (lifeless) object that serves as a vehicle (carrier of infection) to transfer infection or an infectious disease from an infected individual to a healthy individual. For example, a water fountain might become infectious or contaminated by the saliva or the mucus of an infected individual and pass that infection or disease on to another individual who consumes water from the water fountain for drinking. Other examples of potential fomites include doorknobs, handrails, and shared computer keyboards.
Vehicle occurs when microbes or infectious pathogens are transmitted by a contaminated source. Example -food, water, medications, & invasive medical equipment’s.
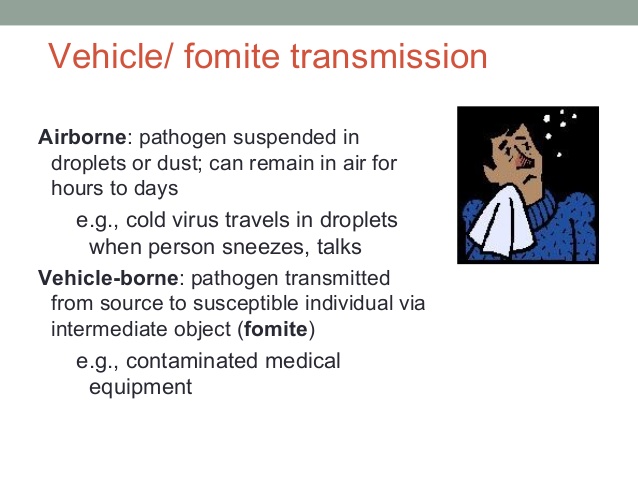
Fomite
A contaminated and infected inanimate (lifeless) object transmits or spreads infection or a disease agent from one susceptible living being to another. The transmission of the disease for the pathogen (infectious agent) to find its way into the host is through oral source or direct contact (a secondary route of transmission). Examples include clippers, utensils, contaminated shovels, cutting boards, clothing, bowls/buckets, kitchen sponges, brushes, tack, toothbrushes and cups
Infection or diseases caused involve inanimate objects termed as fomites that become contaminated or infected by infectious agents or pathogens from an infected person or reservoir. For example, a person infected with flu or common cold may sneeze, and the infected or contaminated sneeze droplets land on inanimate items or fomites like – a tablecloth or carpet or a towel, or the individual could spread infection or transmit disease to another person by transferring infected mucus or saliva to an inanimate (lifeless) items or fomites like – handkerchief, door handle or railings. Transmission or infection occurs in an indirect method when a new susceptible (capable or admitting of) host later touches the inanimate item or fomite and transmits or spreads the contaminated material to a susceptible portal of entry. Fomites can also include objects used in clinical or healthcare settings that are not sterilized or disinfected in a proper way, such as scissors, tubing, syringes, needles, catheters, sutures, staples, and surgical equipment. Infectious agents or pathogens spread or indirectly via such inanimate are the major cause of healthcare or medical industry – associated infections.
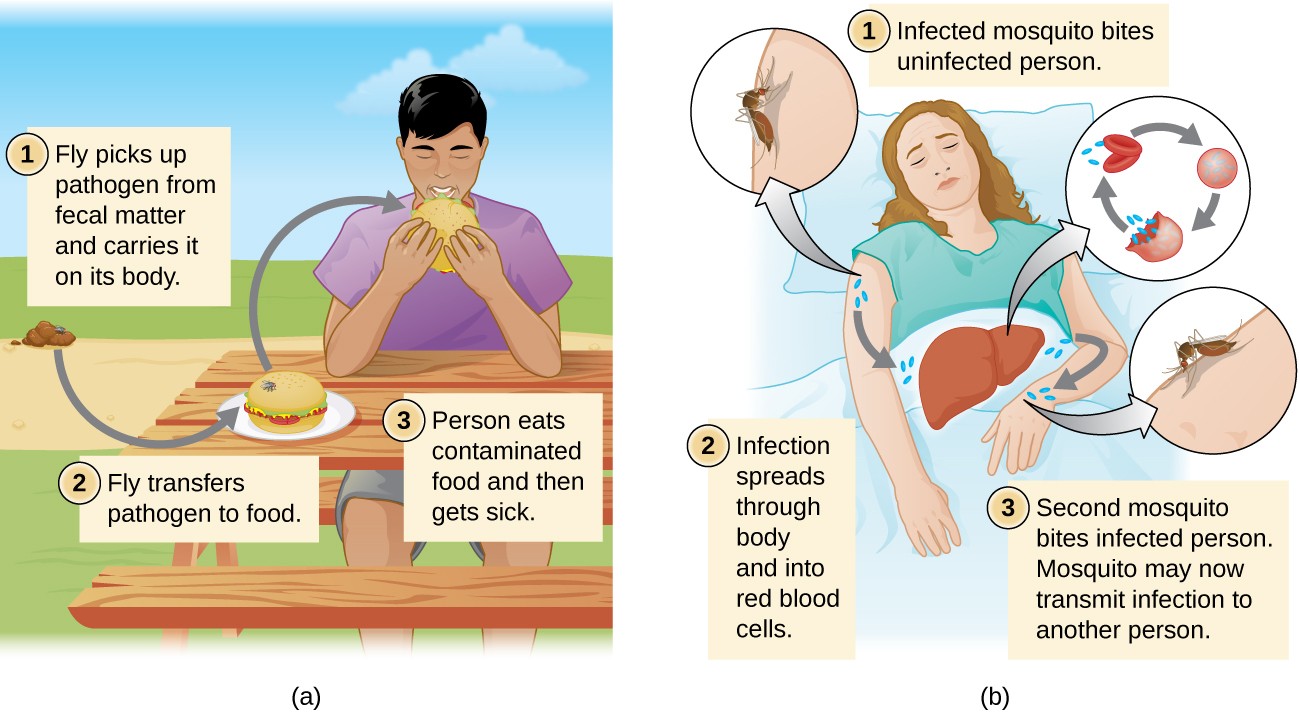
Vehicle
Vehicles that result in direct transmission of contaminated agents (infectious pathogens) include fomites or fomes (inanimate items like utensils, bedding, surgical equipment’s, handkerchiefs), food, water, and blood. A vehicle could be a passive pathogen carrier — as food or water may carry (Hep A) hepatitis A virus.
The term vehicle transmission means the spread of infectious agents or transmission of pathogens by means of vehicles such as – air, water and food. Water contamination through poor sanitation techniques that result in waterborne spread or transmission of infection or disease. Waterborne disease / infection remains a severe issue in many demographics throughout the globe. The WHO – (World Health Organization) estimates that contaminated drinking water is responsible for more than five hundred thousand deaths each year. In a similar way, contamination of food that tales place because of unhygienic, poor storage and handling results in food-borne transmission of infection or disease.
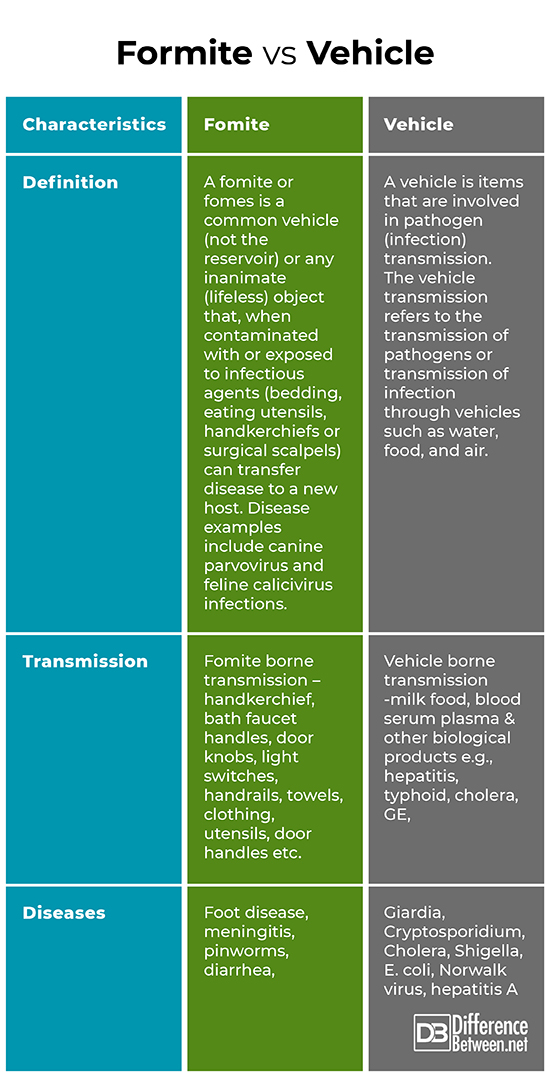
Difference between Fomite and Vehicle
Description
Fomite
A fomite or fomes is any inanimate (lifeless) object that, when infected or contaminated with or exposed to infectious agents or pathogens can transmit disease to a new host. For example – touch screens, coffeepot handles, countertops, common-use phones, keyboards,
Vehicle
Vehicle borne infections result from contact with vehicles, which are contaminated, non-moving objects. Examples include – contaminated or impure water, unhygienic or unsanitary food and Fomites
Examples
Fomite
This includes tissues, doorknobs, hand rails, utensils, toilet seats, bed linens, clothing, medical equipment’s and supplies, or surfaces that have become contaminated with pathogens can become a fomite.
Vehicle
This involved transmission by an inanimate reservoir. These infections result from contact with vehicles, which are contaminated, nonmoving objects. Examples: – Fomites – Unsanitary food – Impure water
Diseases
Fomite
Diseases that typically spread by means of fomites include the common cold, cold sores, conjunctivitis (pink eye-Inflammation or infection of the external membrane of the eyeball), hand-foot-mouth disease, influenza (the flu – a common viral infection), lice infestation, meningitis, pinworms (tiny worms which live in the bowel), diarrhea, and strep infections.
Vehicle
Water is vital to life, but it is also a potential “common vehicle” for disease.
The five major classes of disease-causing agents that can be found in water are:
- Viruses (example – Norwalk virus, hepatitis A)
- Parasites (example – Giardia (beaver fever), Cryptosporidium (also called crypto, and usually cause a respiratory and gastrointestinal illness)
- Chemical contaminants (example – pesticides, heavy metals, organic solvents)
- Neurotoxins from “algal blooms”
- Bacteria (example – Cholera (an acute, diarrheal illness), Shigella (shigellosis), E. coli (Escherichia coli, is a Gram – ive, facultative anaerobic, coliform bacterium and rod shaped)
Summary
The points of difference between Fomite and Vehicle have been summarized as below:
Formite Vs Vehicle
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kraay, A. N., Hayashi, M. A., Hernandez-Ceron, N., Spicknall, I. H., Eisenberg, M. C., Meza, R., & Eisenberg, J. N. (2018). Fomite-mediated transmission as a sufficient pathway: a comparative analysis across three viral pathogens. BMC infectious diseases, 18(1), 540.
[1]Olise, C. C., & Simon-Oke, I. A. (2018). Fomites: Possible vehicle of nosocomial infections. J pub health catalog. 2018; 1 (1): 16-16. J pub health catalog 2018 Volume 1 Issue, 1.
[2]Sattar, S. A., Lloyd-Evans, N., Springthorpe, V. S., & Nair, R. C. (1986). Institutional outbreaks of rotavirus diarrhoea: potential role of fomites and environmental surfaces as vehicles for virus transmission. Epidemiology & Infection, 96(2), 277-289.
[3]Image credit: https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wk3hostpathogeninteractions1-131208023405-phpapp02/95/host-pathogen-interactions-16-638.jpg?cb=1386470083
[4]Image credit: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1094/2016/11/03165504/OSC_Microbio_16_03_Vector.jpg
