Difference between Arthritis and Carpal Tunnel
What is Arthritis?
Definition of Arthritis:
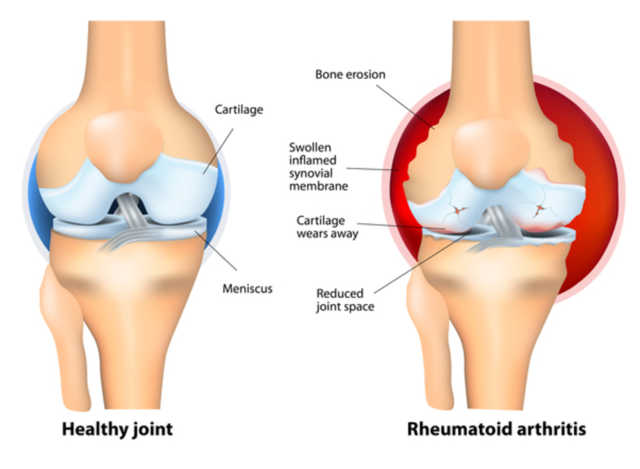
Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints of the body. The joints are the areas of the body where two or more bones come together. A joint is complex and consists of muscles, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and bone.
Symptoms of Arthritis:
The symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and a feeling that the joints are stiff. The condition worsens with age. Joints may swell and may become difficult to move. There also may be a redness of the joint along with swelling present over the affected joint
Diagnosis for Arthritis:
Diagnosis can be made based on physical exam, X-rays, and blood tests. There are several different types of arthritis. X-rays can help determine the type of arthritis and blood tests can show the presence of rheumatoid factors. These are antibodies that are produced in rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes of Arthritis:
There are many different causes of arthritis. For instance, acute infectious arthritis is caused by an infectious agent such as bacteria. Rheumatoid arthritis is when the lining of the joints break down while osteoarthritis is when the cartilage of the joints break down. Osteoarthritis is most often from aging or infection while rheumatoid arthritis is often an autoimmune condition.
Risk factors for Arthritis:
Infectious arthritis is more likely in people who are over 50 years of age who have had surgery on their joints. Genetics may play a role in risk and as you age you may be more likely to have joint problems. Obesity is a risk factor because it places excess pressure on the joints. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus also increase your risk of arthritis.
Treatment for Arthritis:
Patients can take anti-inflammatory medicines and steroids. Treatment may vary depending on what type of arthritis you have. People who have osteoarthritis sometimes benefit from having an injection of hyaluronic acid. Prescribing medicine to reduce the immune response can help people who have autoimmune problems that are causing rheumatoid arthritis. Surgery may be needed to repair badly damaged joints.
What is Carpal Tunnel?
Definition of Carpal Tunnel:
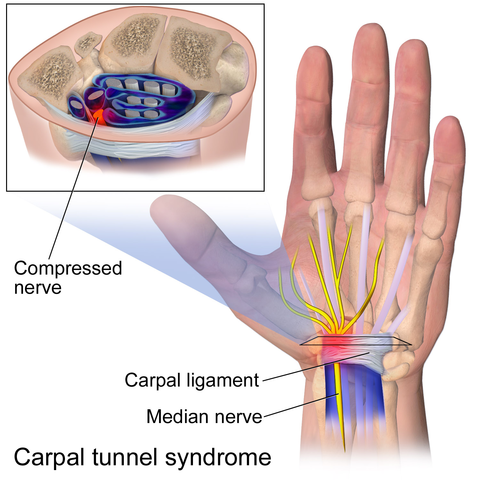
Carpal tunnel is a condition in which pressure is placed on the median nerve traveling into the hand, causing pain and a tingling or numb sensation in the hand. The carpal tunnel is a tunnel region formed by the bones, tendons, and ligaments of the hand through which the median nerve passes.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel:
Symptoms include pain, a sense of numbness and tingling in the hand. A person may start to drop items more often than usual as the hand feels weaker than normal.
Diagnosis for Carpal Tunnel:
A doctor performs a physical exam. In addition, an electromyogram (EMG) can be used to diagnose the condition. This test measures the muscular electrical activity in the hand. A nerve conduction study can be done in which the activity of the nerves can be assessed. In addition to these tests, ultrasound and MRI can provide more information on the median nerve and soft tissues in order to guide treatment efforts.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel:
Genetics and heredity may play a role, and any injury to the wrist can cause the condition. Repetitive hand motion may also play a role but there is no definitive evidence that it does cause the condition.
Risk factors involved in Carpal Tunnel:
Having certain conditions can increase your risk of developing carpal tunnel. For instance, conditions that increase your risk include if you have diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or if you are pregnant or obese. If you have an occupation in which you have a repetitive use of the hand, then this may possibly increase your chances of having carpal tunnel.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel:
A patient can wear a splint or brace at night while they are sleeping. The goal is to keep the wrist straight to stop the pressure on the nerve. Corticosteroids can be injected directly into the carpal tunnel region to relieve pain and patients can take anti-inflammatory medications. In extreme cases, surgery may be needed to reduce the pressure on the nerve.
Difference between Arthritis and Carpal Tunnel
-
Definition
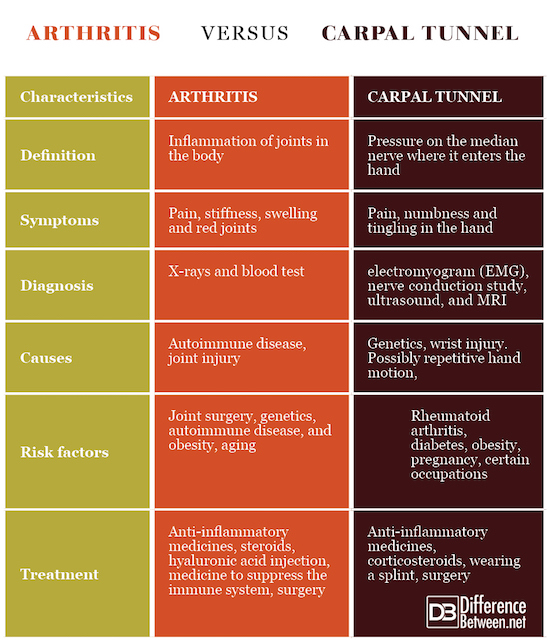
Arthritis is a condition in which the joints are inflamed while carpal tunnel is a condition in which pressure is placed on the median nerve as it enters the hand.
-
Symptoms
Arthritis symptoms include painful, red, swollen and stiff joints. Carpal tunnel symptoms include pain, numbness and tingling in the hand.
-
Diagnosis
Arthritis is diagnosed with X-rays and blood tests. Carpal tunnel is diagnosed with nerve conduction studies, an electromyogram, ultrasound and MRI.
-
Causes
Arthritis can be caused by genetics, a joint injury, or autoimmune disease. Carpal tunnel may be caused by genetics or by a wrist injury. It may also possibly be caused by repetitive motion of the hand.
-
Risk factors
Risk factors for arthritis include joint surgery, genetics, autoimmune disease, aging, and obesity. Risk factors for carpal tunnel include having rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, obesity, pregnancy, and possibly having certain occupations in which there is repetitive use of the hand.
-
Treatment
Treatment for arthritis can include taking anti-inflammatory medicines and steroids, getting an injection of hyaluronic acid or taking medicine to suppress the immune system. Sometimes surgery is needed. Treatment for carpal tunnel can include anti-inflammatory medicine and corticosteroids. Sometimes a splint can be worn, and in severe cases surgery may be needed for carpal tunnel.
Table comparing Arthritis and Carpal Tunnel
Summary of Arthritis Vs. Carpal Tunnel
- Arthritis is a condition in which there is inflammation of the joints while carpal tunnel is a condition in which the median nerve is affected.
- In arthritis joints become red and swollen, while in carpal tunnel the hand becomes painful with a tingling and numb feeling.
- Both conditions can be treated with anti-inflammatories and may in severe cases require surgery.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Rheumatoid-Arthritis.png/640px-Rheumatoid-Arthritis.png
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/38/Carpal_Tunnel_Syndrome.png/480px-Carpal_Tunnel_Syndrome.png
[2]Kontzias, Apostolos. “Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2017, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/joint-disorders/rheumatoid-arthritis-ra
[3]Solomon, Daniel H., et al. "Nonoccupational risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome." Journal of general internal medicine 14.5 (1999): 310-314.
[4]Steinberg, David R. “Carpal tunnel syndrome”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2016, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/musculoskeletal-and-connective-tissue-disorders/hand-disorders/carpal-tunnel-syndrome