Difference Between Bell’s Palsy and Stroke
Bell’s palsy is a problem related to a cranial nerve. A stroke is when there is an interruption of blood flow to the brain.

What is Bell’s palsy?
Definition:
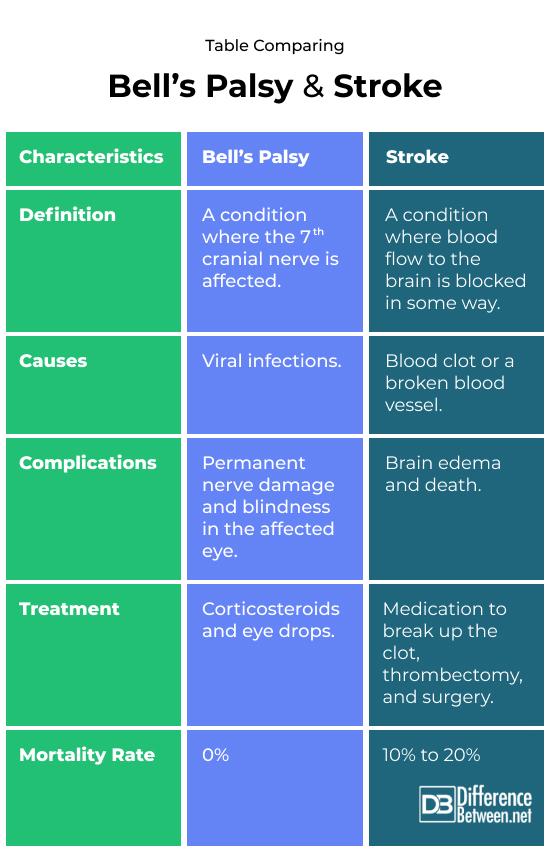
Bell’s palsy is when the muscles located on one side of the face become weak or paralyzed because of issues with the 7th cranial nerve.
Causes:
Bell’s palsy can be caused by viral infections, specifically Herpes zoster and Herpes simplex. However, Epstein-Barr virus, influenza, mumps, and cytomegalovirus can also cause Bell’s palsy.
Symptoms and complications:
One of the early signs of Bell’s palsy is the sensation of pain behind the ear. Only one part of the face, on the left or right side, is affected. Weakness and varying degrees of paralysis of the face sets in. The condition does not worsen after 72 hrs. The condition may make closing or opening the eye problematic and the eye may water The weakness leads to drooping of the face on the affected side. The person may also have a headache and lose hearing on the afflicted side. Complications include blindness of the affected eye and permanent nerve damage.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of Bell’s palsy is achieved by excluding other potential causes for the condition. X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and blood tests can help eliminate other conditions that could mimic Bell’s palsy.
Treatment:
Treatment involves using corticosteroids like prednisone. The dose given is usually 60 mg to 80 mg once a day for 7 days. If the condition is due to a virus, antiviral medication may be given. Patients also need to use eye drops, such as methylcellulose drops, to stop the cornea of the eye getting dry. Due to the paralysis, the eye may not close in which case wearing a patch over the eye is recommended.

What is a Stroke?
Definition:
A stroke is when something blocks blood flow to the brain. It is also called a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) and can be either hemorrhagic or ischemic.
Causes:
The cause of an ischemic stroke is often a blood clot while the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke is a burst blood vessel. Ischemic is more common.
Symptoms and complications:
Symptoms of a stroke include numbness of the face and weakness of limbs, often on one side of the body but this may vary depending on where the problem is in the brain. The person may also be confused and have problems with their vision. Headache and slurred speech may be present. Stroke can result in complications like swelling of the brain, disability, and even death.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis includes having a CT scan. A CT scan can show bleeding or areas where a clot has formed. However, tiny clots may not be seen in imaging. A diffusion-weighted MRI may be done to find ischemic stroke if this is not evident on a CT. Ruling out other conditions like low blood sugar, also helps in diagnosis.
Treatment:
The type of treatment varies depending on what type of stroke is occurring. With ischemic strokes this often means giving thrombolytics or recombinant tissue plasminogen activator to break apart a clot. Sometimes a thrombectomy is done where they use a catheter that is threaded through to where the clot is, and then the clot is removed. With a hemorrhagic stroke, surgery may be required to repair the broken blood vessel and take the spilled blood out of the brain.
Difference between Bell’s palsy and Stroke?
Definition
Bell’s palsy is a condition where the 7th cranial nerve is affected. A stroke is when blood flow to the brain is obstructed.
Causes
Causes of Bell’s palsy include viral infections. Causes of a stroke include a blood clot or ruptured blood vessel in the brain.
Complications
Permanent nerve damage and blindness in the affected eye are complications of Bell’s palsy. Brain edema and death are complications of a stroke.
Treatment
Treatment of Bell’s palsy includes using corticosteroids and eye drops. Treatment of a stroke varies and may include using medication to break up a clot, a thrombectomy, or surgery.
Mortality rate
Bell’s palsy has a 0% mortality rate. A stroke has a 10% to 20% mortality rate.
Table comparing Bell’s palsy and Stroke
Summary of Bell’s palsy Vs. Stroke
- Bell’s palsy and a stroke can look similar but a stroke is more dangerous.
- Bell’s palsy is related to a cranial nerve.
- A stroke is due to either a clot or bleed in the brain.
FAQ
How can you tell the difference between Bell’s palsy and a stroke?
In Bell’s palsy, only the face and eye are affected, but in a stroke, weakness extends to the limbs and the person has mental confusion often and a headache.
Is Bell’s palsy considered a stroke?
No, Bell’s palsy is not a stroke.
Should I go to ER for Bell’s palsy?
Since some symptoms of stroke mimic Bell’s palsy, it is safer to go to the ER so they can rule out a stroke. A stroke can lead to death so it is best to be cautious.
Can you tell the difference between Bell’s palsy and a stroke eyebrow?
If you cannot move your eyebrow, it is likely Bell’s palsy; if you can move your eyebrow, it is likely a stroke.
Is Bell’s palsy a form of MS?
Bell’s palsy is not a form of MS but the symptom of facial drooping may occur in MS.
What is the main cause of Bell’s palsy?
Viral infections are the main reason for developing Bell’s palsy.
Is Bell’s palsy caused by stress?
Bell’s palsy is not directly due to stress but stress can weaken the immune system and, thus, this can contribute to developing Bell’s palsy.
What is the best treatment for Bell’s palsy?
Using corticosteroids is thought to be the best way to treat Bell’s palsy.
What are the warning signs of Bell’s palsy?
Having trouble closing your eyes and facial drooping along with pain behind the ear are signs you may be developing Bell’s palsy.
Which side of the face droops in a stroke?
It depends what side of the brain a stroke occurs in as to what side of the face would droop. A stroke on the right side of the brain causes drooping on the left side of the face.
Is Bell’s palsy life threatening?
No, Bell’s palsy is not life threatening.
Is Bell’s palsy serious?
It is usually not serious but is best to check with your doctor.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Chong, Ji Y. “Overview of Stroke””. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2022, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/stroke/overview-of-stroke
[1]Rubin, Michael. “Facial Nerve Palsy (Bells Palsy; Bell’s Palsy)”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2022, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/neuro-ophthalmologic-and-cranial-nerve-disorders/facial-nerve-palsy
[2]Tiemstra, Jeffrey D., and Nandini Khatkhate. "Bell's palsy: diagnosis and management." American family physician 76.7 (2007): 997-1002.
