Difference Between Sciatica and Radiculopathy
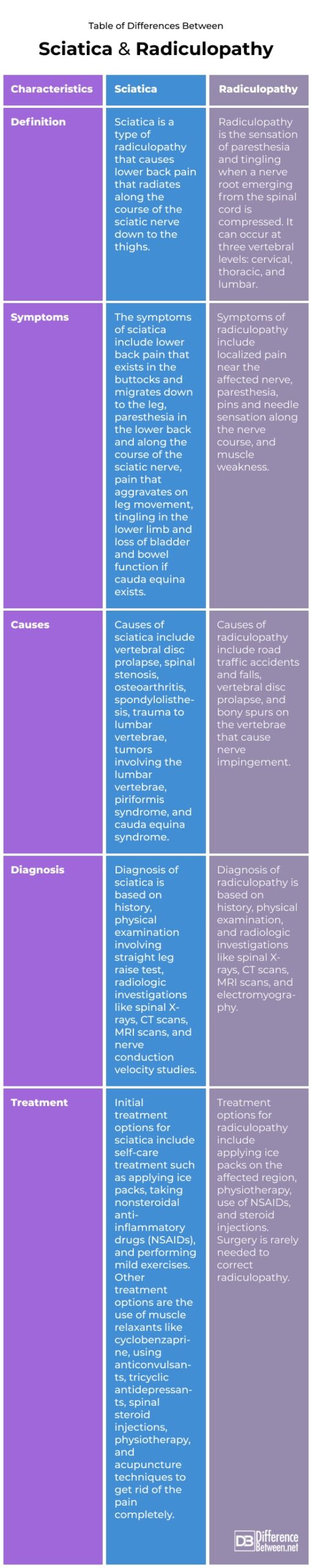
Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy that causes lower back pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve down to the thighs. Radiculopathy is the sensation of paresthesia and tingling when a nerve root emerging from the spinal cord is compressed. It can occur at three vertebral levels: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar.

What is sciatica?
Definition:
Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy that causes lower back pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve down to the thighs.
Causes:
Causes of sciatica include vertebral disc prolapse, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis, trauma to lumbar vertebrae, tumors involving the lumbar vertebrae, piriformis syndrome, and cauda equina syndrome.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of sciatica include lower back pain that exists in the buttocks and migrates down to the leg, paresthesia in the lower back and along the course of the sciatic nerve, pain that aggravates on leg movement, tingling in the lower limb and loss of bladder and bowel function if cauda equina exists.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of sciatica is based on history, physical examination involving straight leg raise test, radiologic investigations like spinal X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and nerve conduction velocity studies.
Treatment:
Initial treatment options for sciatica include self-care treatment such as applying ice packs, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and performing mild exercises. Other treatment options are the use of muscle relaxants like cyclobenzaprine, using anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, spinal steroid injections, physiotherapy, and acupuncture techniques to get rid of the pain completely.

What is radiculopathy?
Definition:
Radiculopathy is the sensation of paresthesia and tingling when a nerve root emerging from the spinal cord is compressed. It can occur at three vertebral levels: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar.
Causes:
Causes of radiculopathy include road traffic accidents and falls, vertebral disc prolapse, and bony spurs on the vertebrae that cause nerve impingement.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of radiculopathy include localized pain near the affected nerve, paresthesia, pins and needle sensation along the nerve course, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of radiculopathy is based on history, physical examination, and radiologic investigations like spinal X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and electromyography.
Treatment:
Treatment options for radiculopathy include applying ice packs on the affected region, physiotherapy, use of NSAIDs, and steroid injections. Surgery is rarely needed to correct radiculopathy.
Difference between Sciatica and Radiculopathy
Definition:
Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy that causes lower back pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve down to the thighs. Radiculopathy is the sensation of paresthesia and tingling when a nerve root emerging from the spinal cord is compressed. It can occur at three vertebral levels: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar.
Causes:
Causes of sciatica include vertebral disc prolapse, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, spondylolisthesis, trauma to lumbar vertebrae, tumors involving the lumbar vertebrae, piriformis syndrome, and cauda equina syndrome. Causes of radiculopathy include road traffic accidents and falls, vertebral disc prolapse, and bony spurs on the vertebrae that cause nerve impingement.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of sciatica include lower back pain that exists in the buttocks and migrates down to the leg, paresthesia in the lower back and along the course of the sciatic nerve, pain that aggravates on leg movement, tingling in the lower limb and loss of bladder and bowel function if cauda equina exists. Symptoms of radiculopathy include localized pain near the affected nerve, paresthesia, pins and needle sensation along the nerve course, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of sciatica is based on history, physical examination involving straight leg raise test, radiologic investigations like spinal X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and nerve conduction velocity studies. Diagnosis of radiculopathy is based on history, physical examination, and radiologic investigations like spinal X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and electromyography.
Treatment:
Initial treatment options for sciatica include self-care treatment such as applying ice packs, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and performing mild exercises. Other treatment options are the use of muscle relaxants like cyclobenzaprine, using anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, spinal steroid injections, physiotherapy, and acupuncture techniques to get rid of the pain completely. Treatment options for radiculopathy include applying ice packs on the affected region, physiotherapy, use of NSAIDs, and steroid injections. Surgery is rarely needed to correct radiculopathy.
Table of differences between Sciatica and Radiculopathy
FAQs
How to tell the difference between sciatica and neuropathic pain?
Sciatica pain increases with sitting and changes with movement. Neuropathic pain is consistent. It is shooting, burning, shock-like in nature, sensitive to touch, and has a pin and needle-sensation.
What kind of pain do you get with radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy pain is localized pain near the affected nerve.
What is lumbar radiculopathy or sciatica nerve pain?
Sciatica is a type of radiculopathy that causes lower back pain that radiates along the course of the sciatic nerve down to the thighs.
What triggers radiculopathy?
Aging, degenerative bone changes, and road traffic accidents can trigger radiculopathy.
What can be mistaken for sciatica?
Piriformis syndrome.
Can sciatica be so bad you can’t walk?
Yes.
What not to do with radiculopathy?
Excessive exercise should not be done in radiculopathy.
What are the red flags for lumbar radiculopathy?
“Red flags” of lumbar radiculopathy include pain for more than 6 weeks, in adolescents or older than 50 years, pain below the knee, history of trauma, and urinary and/or fecal incontinence.
What is the best treatment for radiculopathy?
The best treatment for radiculopathy includes physiotherapy, the use of NSAIDs, and steroid injections.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Carette, Simon, and Michael G. Fehlings. "Cervical radiculopathy." New England Journal of Medicine 353.4 (2005): 392-399.
[1]Tarulli, Andrew W., and Elizabeth M. Raynor. "Lumbosacral radiculopathy." Neurologic clinics 25.2 (2007): 387-405.
[2]Valat, Jean-Pierre, et al. "Sciatica." Best practice & research Clinical rheumatology 24.2 (2010): 241-252.
