Difference Between Thyroid Nodule and Cyst
What is Thyroid Nodule and Cyst?
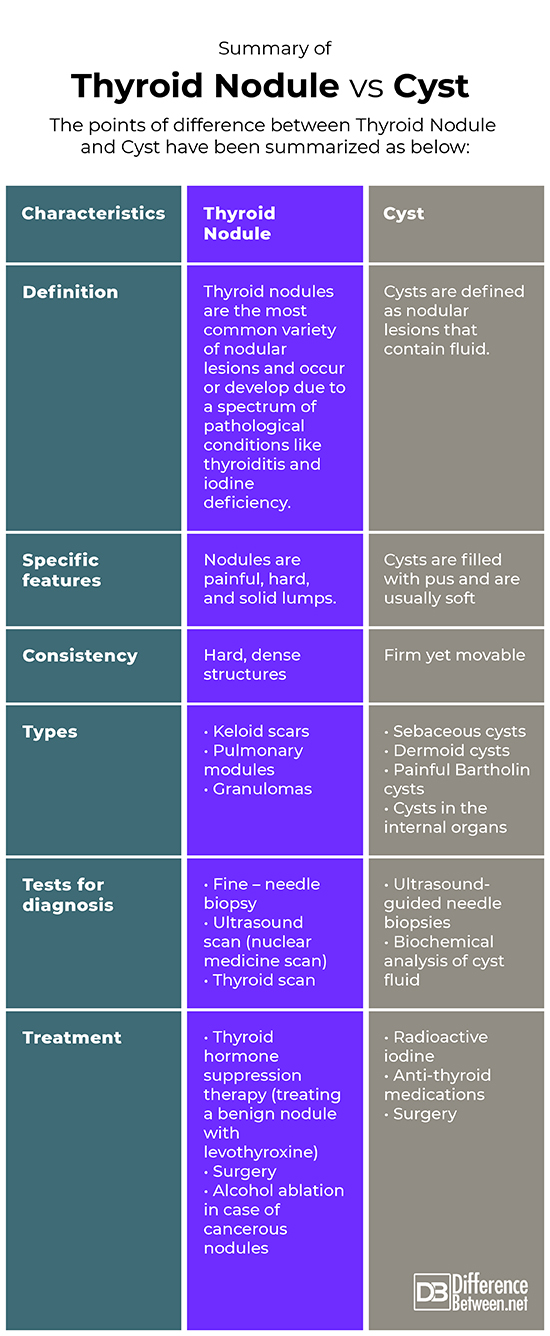
Both are bumps elevated from the skin. Both are palpable and are more than 0.5cm in diameter. However, thyroid nodules comprise of solid materials and cysts are nodular lesions that contain fluid.
What is Thyroid Nodule?
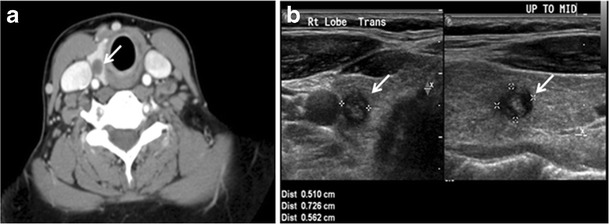
A thyroid nodule is a large, deep and painful bump that develops in your thyroid. It is firm, hard to touch, painful and very sensitive. These bumps are rarely cancerous. Thyroid nodules develop just below the skin.
Thyroid nodules may have no solid components present detectable within the fluid and thus they may be entirely cystic. Thyroid nodules that are complex in nature contain both solid and fluid components. Thyroid nodules are usually caused by thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, thyroid adenoma, thyroid cyst, and thyroid cancer
Some facts regarding thyroid nodules include:
- Thyroid nodule is detected in thirty percent of thirty-year-old women
- The problem of thyroid nodule is more common in women in comparison to men
- More than ninety-five percent of thyroid nodules are non-cancerous (non-malignant or benign) and result in no serious problems if left untreated
- Only five – ten percent of thyroid nodules are cancerous
- Only 1-2 percent men suffer from the problem of thyroid nodule.
- The incidence of thyroid nodules increases with age
- Purely cystic thyroid nodules (thyroid cysts) are almost always benign
- Some thyroid nodules are entirely cystic, that contain only fluid and there is total absence of any tissue
What is a Cyst?
A cyst is a semi-solid, liquid or air-filled lump that develops in any part of the body. Cysts that develop in the thyroid grow in size because of sudden bleeding within them. If the thyroid cysts keep becoming bigger and bigger, they cause issues like pain, difficulty in swallowing and compression of the vocal cords.
In about fifteen percent of cases, these cysts resolve without any treatment. Thyroid cysts may be quiet large or as small as 1cm or even less than 1cm and sometimes arise very suddenly. The treatment of thyroid cysts involves radioactive iodine, anti-thyroid medications and in some cases surgery. Pure thyroid cysts that are less than or 3 cm in size are observed for changes. Management approaches include aspiration and instillation of ethanol or other ablative approaches.
The thyroid cysts that are completely fluid filled are at a much lower risk of thyroid malignancy in comparison to the cysts that possess solid components.
Difference between Thyroid Nodule and Cyst
Definition
Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid nodules are rarely malign and relatively common. A thyroid nodule is an elevated lump that usually develops or grows in your thyroid gland. A nodule is either filled with fluid or it can be solid.
Cyst
Thyroid cysts are enlarged fluid-filled cavities that are usually less than 1 cm in size. Sometimes they are quite large and develop suddenly. Thyroid cysts are caused by degenerating thyroid adenomas. Cysts are usually benign (non-cancerous), but they occasionally contain malignant solid components. Fluids and solid components are mixed in thyroid cysts.
Symptoms
Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid nodules produce additional thyroxine (a hormone the thyroid gland secretes into the bloodstream). This additional extra thyroxine can cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism such as:
- Elevated perspiration
- An enlarged thyroid gland, known as a goitre
- Irregular and rapid heartbeat
- Swallowing difficulties
- Muscle weakness
- Breathing difficulties
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tremor
- Nervousness
Cyst
- A noticeable lump in the neck
- Pain
- Change in voice
- Difficulty in swallowing
Causes
Thyroid Nodule
- Overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue (strong genetic basis)
- Hashimoto’s disease – It is a condition in which your immune system attacks your thyroid, a small gland at the base of your neck below your Adam’s apple
- Thyroid cancer
- Chronic inflammation of your thyroid
- Iodine deficiency
- Structural abnormalities of the thyroid gland from birth
Cyst
Fluid-filled cavities (cysts) in the thyroid are caused by degenerating thyroid adenomas. The fluid is usually mixed with some solid components in thyroid cysts.
Specific characteristic
Thyroid Nodule
It is filled with solid materials
Cyst
It is filled with fluids
Pus filled
Thyroid Nodule
No pus
Cyst
No pus but filled with fluid
Types
Thyroid Nodule
- Keloid scars- Nodular lesions caused due to repair mechanisms meant to heal injuries to the body organs
- Pulmonary modules – nodular lesions in inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis
- Granulomas – nodular lesions occurring in conditions like Tuberculosis
Cyst
- Sebaceous cysts – formed over the skin and possess a bluish discoloration. Surgery is mostly recommended in these kinds of cysts in order to prevent them from getting an infection.
- Dermoid cysts – A sac-like non-cancerous lump in the skin
- Painful Bartholin cysts – these develop in the females in Bartholin glands
- Cysts in the internal organs such as thyroid gland, ovaries, and kidney
Summary of Thyroid Nodule Vs. Cyst
The points of difference between Thyroid Nodule and Cyst have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Myxoid-cyst-left-index.jpg
[1]Image rcedit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:CT_and_ultrasound_of_thyroid_colloid_nodule.jpg
[2]Popoveniuc, G., & Jonklaas, J. (2012). Thyroid nodules. Medical Clinics, 96(2), 329-349.
[3]Shimizu, J., Kawaura, Y., Tatsuzawa, Y., Maeda, K., & Suzuki, S. (2000). Cervical bronchogenic cyst that presented as a thyroid cyst. The European journal of surgery, 166(8), 659-661.
[4]Treece, G. L., Georgitis, W. J., & Hofeldt, F. D. (1983). Resolution of recurrent thyroid cysts with tetracycline instillation. Archives of internal medicine, 143(12), 2285-2287.
[5]Welker, M. J., & Orlov, D. (2003). Thyroid nodules. American family physician, 67(3), 559-566.