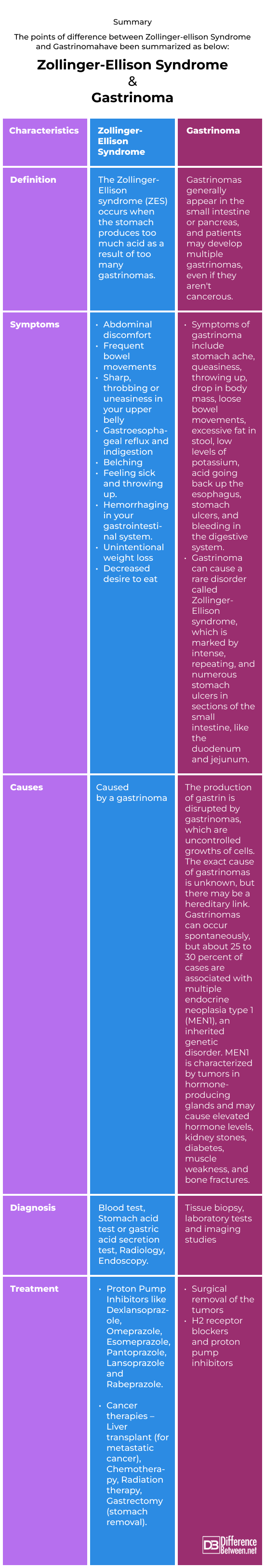
Difference Between Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome and Gastrinoma

An excess of gastric acid causes Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare digestive disorder. As a result of this, you can develop peptic ulcers in your stomach and intestines. In addition to abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and diarrhea, severe complications can result if left untreated.
In Gastrinoma, gastrin is secreted by the duodenum or pancreas, causing the Zollinger–Ellison syndrome (ZES). Approximately ten percent of gastrinomas develop as primary neoplasms in the lymph nodes of the pancreaticoduodenal region (gastrinoma triangle), with near-equal frequency. The vast majority of gastrinomas develop in the pancreas or duodenum.

Difference between Zollinger-ellison Syndrome and Gastrinoma
Symptoms
Zollinger-ellison Syndrome
- Acid reflux
- Shedding pounds
- Loose stools
- Sore or scorching sensation in the abdomen or midsection (typically situated between the center of the torso and navel)
- Throwing up or queasiness
Gastrinoma
- Symptoms of Discomfort
- Sickness or retching
- Reduced desire for food
- Feeling of fullness
- Belching
- Elevated levels of fat in your feces
Causes
Zollinger-ellison Syndrome
Tumours are collections of cells that keep growing due to overproduction. Occasionally, a genetic mutation modifies the DNA coding that regulates the rate of cell division in certain tissues. In other instances, the reason why some cells overproduce or why they do so more vigorously in some individuals than in others is unknown. We are aware that an excessive amount of any kind of cell may be harmful to the body. An excess of gastrin is produced by neuroendocrine cells, which leads to an excess of stomach acid in the body.
Gastrinoma
Although gastrinomas are caused in part by the unchecked division and proliferation of gastrin-producing cells, investigations are still being conducted to determine the precise origin of these tumours.
However, according to The National Pancreas Foundation, 25–30% of gastrinomas are known to be caused by multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) syndrome, a hereditary genetic disorder. Individuals with MEN1 have increased hormone production from tumours in the duodenum and/or endocrine glands.
Treatment
Zollinger-ellison Syndrome
- proton pump inhibitors
Gastrinoma
- Radiotherapy
- Interferon
- Chemotherapy
- Somatostatin analogues
Summary
The points of difference between Zollinger-ellison Syndrome and Gastrinoma have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
Does Zollinger-Ellison syndrome cause gastrinoma?
When you have Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES), you likely have one or more gastrinomas, which are tumors that release the hormone gastrin, which causes gastritis.
What is another name for a gastrinoma?
Another name for gastrinoma is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES). The gastrinoma is characterized by the secretion of gastrin with the resulting excessive production of stomach acid, resulting in severe diarrhea and peptic ulcer disease, a condition known as the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES).
Which test is most reliable for diagnosing Zollinger-Ellison syndrome?
For diagnosing Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (ZES), laboratory studies include measuring the pH of the stomach and levels of fasting gastrin, chromogranin A, and secretin stimulation. Fasting serum gastrin is the best test for ZES screening.
What are gastrinomas in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome?
As a consequence of gastrinoma, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome occurs when gastrin hyper secretes gastric acid, causing trophic effects. PPIs have been the main therapy to control the symptoms of esophageal, stomach, and duodenal ulcers, diarrhea, and heartburn. Multiple ulcers in the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum can cause severe abdominal pain.
What is the drug of choice for gastrinoma?
The most effective medical treatment for gastrinoma is the use of high doses of proton pump inhibitors. H2 receiver blockers are not as potent and have a shorter duration of action as proton pump inhibitors. Surgery is the only curative option.
What is the prognosis for gastrinomas?
A number of factors, including the size of the tumour, whether it is benign or malignant, and the extent to which it has metastasized (spread to other organs), affect a person’s prognosis when they have a gastrinoma. In general:
Noncancerous gastrinomas: Surgical excision is the most effective treatment for the majority of noncancerous gastrinomas. In most cases, the prognosis is favourable, and following effective treatment, patients can return to reasonably normal lives.
Gastrinomas that are cancerous: Because these tumours can spread to other areas of the body and are more likely to be aggressive, their prognosis is less favourable. Usually, a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and other medicines is used to treat malignant gastrinomas. When it comes to cancer instances, the prognosis might differ greatly; although some patients are able to maintain long-term control over their illness, others may encounter more difficulties along the way.
Maintaining regular monitoring and follow-up is also crucial to assess the efficacy of the treatment and handle any possible side effects. As surgical and medical treatments have advanced throughout time, the prognosis for gastrinomas has improved. Even yet, results might vary greatly from person to person, so it’s crucial to talk about specific situations with medical experts who can offer more detailed advice and information.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Fraker, D. L., Norton, J. A., Alexander, H. R., Venzon, D. J., & Jensen, R. T. (1994). Surgery in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome alters the natural history of gastrinoma. Annals of surgery, 220(3), 320.
[1]Jensen, R. T. (2015). Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. Yamada's Textbook of Gastroenterology, 1078-1102.
[2]Rossi, R. E., Elvevi, A., Citterio, D., Coppa, J., Invernizzi, P., Mazzaferro, V., & Massironi, S. (2021). Gastrinoma and Zollinger Ellison syndrome: A roadmap for the management between new and old therapies. World journal of gastroenterology, 27(35), 5890.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAFqoPW7o7U-man-suffering-from-heartburn-at-home-stomach-with-hot-chili-pepper-symbolizing-acid-indigestion-illustration/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAErd301U3Q-tired-woman-lies-on-couch-with-abdominal-pain/
