Difference Between Omega-6 and Omega-3
Both Omega-3 and Omega-6 are a class of healthy polyunsaturated fatty acids and important components of cell membranes. The beneficial effects of omega-3 intake are widely publicized, but omega-6 fats are far less featured because of the lack of adequate research. So what are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and how are they any different?

What is Omega-3?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a class of polyunsaturated fats that you get from different foods (or supplements) to help build and maintain a healthy body. They are healthy unsaturated fats and they are an integral part of cell membranes and affect the function of cell receptors in these membranes. Omega-3 fatty acids are divided into three main types: ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Most of the health benefits you get from omega-3 fatty acids can be attributed to EPA and DHA, which are mainly found on fatty fish, such as salmon, sardine, and anchovies.
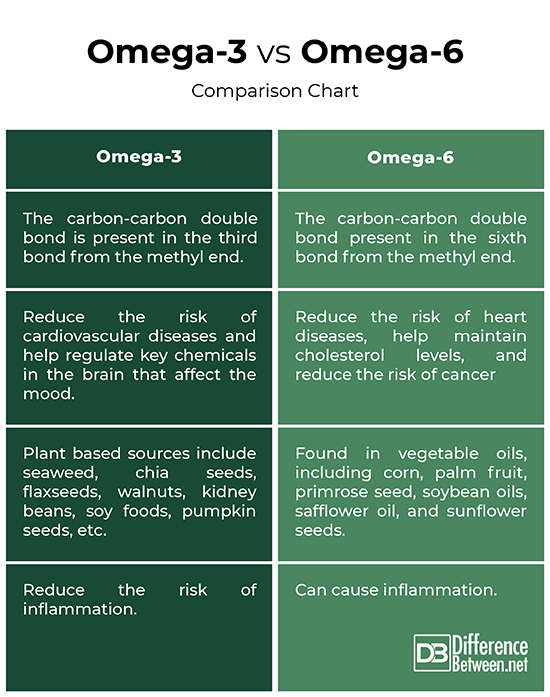
Many studies revealed that omega-3 fatty acids can greatly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and help regulate key chemicals in the brain that affect your mood. These fats are required for growth and development of the brain and are important for vision throughout the life cycle. Omega-3 fats also keep your blood flowing smoothly, allowing your heart to pump blood effortlessly. You can also get omega-3 fats from plant-based sources, such as seaweed, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, kidney beans, soy foods, pumpkin seeds, and more.

What is Omega-6?
Omega-6 fatty acids are also a type of healthy polyunsaturated fats that are important components of cell membranes. They are found everywhere in the body and like omega-3 fats, they are found in certain foods and supplements. Omega-6 fats also play an integral role in brain function, and normal growth and development. These fats reduce the risk of heart diseases, help maintain cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of cancer. One of the major sources of omega-6 fatty acids are vegetable oils, including corn, palm fruit, primrose seed, soybean oils, safflower oil, and sunflower seeds.
Omega-6 fats are mainly divided into four types: LA (linoleic acid), GLA (gamma linoleic acid), ARA (arachidonic acid), and CLA (conjugated linoleic acid). The only problem with omega-6 fats are that the human body really works best when they are in balance. The human body already has a lot of omega-6 because we eat a lot of grains and many foods have vegetable oils hidden in them. High intake of omega-6 fats can cause inflammation in the body and can contribute to many diseases.
Difference between Omega-6 and Omega-3
Structure
– The primary difference between the two fatty acids is their structure. Omega-3 fatty acids have the carbon-carbon double bond present in the third bond from the methyl end (CH3), which is the omega three-position. Omega-6 fatty acids, on the other hand, have the double bond present in the omega six-position, which is the sixth bond from the methyl end.
Function
– Omega-3 fatty acids can greatly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and help regulate key chemicals in the brain that affect your mood. These fats are required for growth and development of the brain and are important for vision throughout the life cycle. Omega-6 fats play an integral role in brain function, and normal growth and development. These fats reduce the risk of heart diseases, help maintain cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of cancer.
Cell Membranes
– One of the main distinguishing points where they do have quite distinct functions is in the kinds of cell membranes they support. For example, the omega-6 fats go into the cell membranes in one part of the brain, basically a group of cell types in the brain. The omega-3 fats go to a different one.
Sources
– Omega-3 fatty acids are mainly found on fatty fish, such as salmon, sardine, and anchovies. Plant based sources of omega-3 fats include seaweed, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, kidney beans, soy foods, pumpkin seeds, etc. Omega-6 fats are dominantly found in vegetable oils, including corn, palm fruit, primrose seed, soybean oils, safflower oil, and sunflower seeds. Fish, eggs, cereals, whole-grain bread, nuts, etc. are also good sources of omega-6 fatty acids.
Omega-3 vs. Omega-6: Comparison Chart
Summary
Both omega-3 and omega-6 are a family of healthy polyunsaturated fats that are essential for proper functioning of the body. Although their structural functions are very similar, their regulatory role as precursors of the eicosanoids is very different. Eicosanoids are important hormone-like substances that are important for many vital metabolic processes at the cardiovascular, nervous system and immune system level. Omega-3 fats are dominantly found in fatty fish such as salmons, sardines, anchovies, and herring. Vegetable oils are a major source of omega-6 fatty acids.
Which is better omega-3 or omega-6?
Both are essential fats, but people should eat more omega-3 because our body already has too much omega-6 fats. In fact, people consume more omega-6 fats than omega-3 fats on an average, about 10 times more. A better balance of the two fatty acids is good for health and reduces the risk of many chronic illnesses.
Why omega-6 is bad for you?
The human body already has enough of omega-6 fatty acids and too much of them can cause inflammation, raise blood pressure, cause blood clots that may lead to heart attack.
Why do we need more omega-6 than omega-3?
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for a health heart and normal growth and development. Vegetable oils, nuts and seeds are the major sources of omega-6 fats. Omega-6 fats are found everywhere in the body, but too much of omega-6 can have adverse effects on the cells in the heart and blood cells.
Do Americans need more omega-3 or omega-6?
Most Americans have more omega-6 intake, on average about 10 times more than omega-3 fats. Scientific studies suggest omega-6 fats are pro-inflammatory, meaning they can cause inflammation in the body whereas omega-3 fats are anti-inflammatory.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Tribole, Evelyn. The Ultimate Omega-3 Diet. New York, United States: McGraw Hill, 2007. Print
[1]Meester, Fabien De, et al. Omega-6/3 Fatty Acids: Functions, Sustainability Strategies and Perspectives. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2012. Print
[2]Watson, Ronald R. and Victor R. Preedy. Omega Fatty Acids in Brain and Neurological Health. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 2019. Print
