Difference Between Omega-3 and Vitamin D
Omega-3 is a fatty substance known as a polyunsaturated fat. Vitamin D is calciferol, a type of organic micronutrient needed by the body.

What is Omega-3?
Definition:
Omega-3 is a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in certain animals and plant materials.
Chemical structure and properties:
The molecular formula for omega-3 is C60H92O6. The name omega-3 comes from the location of a double bond between carbons near the tail part of the molecule. Omega-3 is a fatty acid, which means it repels water.
Types of Omega-3:
There is more than one type of omega-3 fatty acids. The three commonly known types of omega-3 include docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA).
Health benefits:
Some types of omega-3 fatty acids such as DHA and EPA have been shown to help people who suffer from depression. The omega-3 fats also have strong anti-inflammatory properties which helps prevent many types of illness. These fatty acids are also healthy for the brain and heart.
Sources:
There are many different foods that contain good amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. The most familiar food source to most people is fish like herring, sardines, salmon, and mackerel but the fatty acids are also found in walnuts, flax seeds and hemp seeds.
Deficiency symptoms:
A deficiency of omega-3 may manifest as mood problems, including depression. A lack of omega-3 may leave you feeling tired, having dry skin, and dry eyes, and feeling joint pain.

What is Vitamin D?
Definition:
Vitamin D is a type of fat-soluble vitamin that is also known as calciferol, that is needed in small amounts by the body.
Chemical structure and properties:
The molecular formula for vitamin D is C33H52O7. Vitamin D is fat-soluble. This means that it is stored in the liver along with other fat-soluble vitamins when you have enough of it in the body.
Types of Vitamin D:
Vitamin D comes in two forms, namely D2 and D3. Vitamin D2 is known as ergocalciferol while vitamin D3 is called cholecalciferol. Both types of vitamin D are important for good health.
Health benefits:
Vitamin D plays an important role in the human body. Your bones need phosphorus and calcium to stay strong and healthy and in order to properly absorb and take up these minerals, you also need to have enough vitamin D. Vitamin D also is believed to help the immune system and prevent infection from viruses like Covid-19 and influenza.
Sources:
Exposure to sunlight helps the body to make vitamin D. There are also foods that contain some of the vitamin, for instance, oily fishes like salmon, as well as eggs and liver. Fortified foods which have had vitamin D added are also a source of the vitamin. This includes fortified milk and fortified cereals.
Deficiency symptoms:
A deficiency of vitamin D can result in symptoms like bone and joint discomfort and pain. Muscle pain, exhaustion, and depression can also occur if you do not have enough vitamin D.
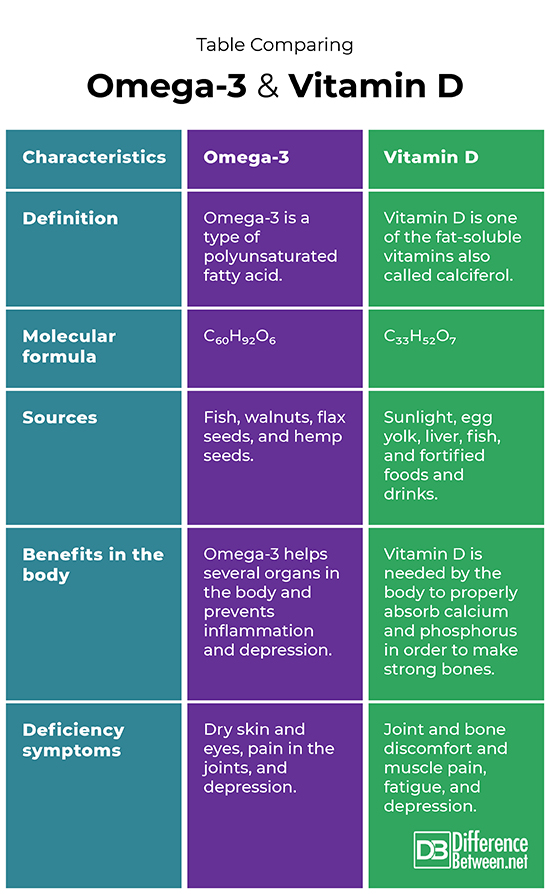
Difference between Omega-3 and Vitamin D
Definition
Omega-3 is a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid. Vitamin D is one of the fat-soluble vitamins also called calciferol.
Molecular formula
The molecular formula of Omega-3 is C60H92O6. The molecular formula of vitamin D is C33H52O7.
Sources
Omega-3 can be found in foods like walnuts, fish, hemp seeds, and flax seeds. Vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight, fish, egg yolk, liver, and fortified food products.
Benefits in the body
Omega-3 is beneficial in many ways including in helping to prevent inflammation and depression. Vitamin D is beneficial in helping phosphorus and calcium to be properly absorbed for strong bones.
Deficiency symptoms
Dry skin and eyes, painful joints, and depression are symptoms of a deficiency of omega-3. Joint and bone discomfort and muscle pain, fatigue, and depression are possible signs that there is a deficiency of vitamin D.
Table comparing Omega-3 and Vitamin D
Summary of Omega-3 and Vitamin D
- Both omega-3 and vitamin D are needed by the body for good health.
- Omega-3 and vitamin D are both nutrients present in oily fish.
- Vitamin D can partly be formed by exposure to sunlight.
- Omega-3 may help with inflammation in the body.
FAQ
Is omega-3 fish oil the same as vitamin D?
Omega-3 is not the same as vitamin D. However, it is possible that certain types of fish oil supplements may contain both omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D.
Does omega-3 contain vitamin D?
Omega-3 in supplement form may contain some vitamin D depending on what it is made from. For example, some types of fish oil contain relatively more vitamin D in addition to the omega-3.
Can I take vitamin D and omega-3 together?
You can combine omega-3 with vitamin D when supplementing because no adverse interaction has been found. Some have even suggested that it is very beneficial for the body to take both substances together.
When should I take omega-3 and vitamin D?
Although both substances can be taken at any time of day or night, it is suggested that they not be taken at night if you suffer from acid reflux. It may also be helpful to take the omega-3 and vitamin D with a meal to improve absorption.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cholewski, Mateusz, Monika Tomczykowa, and Michał Tomczyk. "A comprehensive review of chemistry, sources and bioavailability of omega-3 fatty acids." Nutrients 10.11 (2018): 1662.
[1]Grant, William B., et al. "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths." Nutrients 12.4 (2020): 988.
[2]Mozaffari-Khosravi, Hassan, et al. "Eicosapentaenoic acid versus docosahexaenoic acid in mild-to-moderate depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial." European Neuropsychopharmacology 23.7 (2013): 636-644.
