Difference Between Viral Shedding and Viral Load
Viral shedding is the release and expulsion of viral particles from the body into the environment. Viral load is the amount of virus found in a certain volume of body fluid.
What is Viral shedding?
Definition:
Viral shedding is when viral particles are expelled into the environment from an infected person. It is common with respiratory viruses such as COVID-19, which can spread via respiratory secretions.
How it can be measured:
Viruses shed through a variety of ways, including the gastrointestinal system, urogenital tract, respiratory system, and through blood. It is through examining the fluids and secretions from such systems, that shedding can be recorded and determined. In the case of COVID-19 specifically, viral shedding is measured by performing an RT-PCR test on samples obtained from the respiratory tract.
How viral shedding occurs:
The way in which a virus is shed depends on the type of virus; for instance a stomach virus such as rotavirus sheds via feces or vomit, while a respiratory virus such as COVID-19 sheds mainly via sneezing, coughing, and talking.
Significance:
It is important to know the shedding time of a virus because it allows doctors to determine how long a person will be contagious for and, therefore, how long quarantine needs to be maintained.

What is Viral load?
Definition:
Viral load is defined as the quantity of virus that is present in a person’s bloodstream or other bodily fluid. People may confuse the term with viral shedding but the load is the amount present inside the body, measured quantitatively; it is not the same as the quantity of virus released into the environment.
How it can be measured:
With HIV-1, viral load is the number of virus particles that can be found in every ml of blood. COVID-19 viral load is measured by looking for the RNA of the virus in samples obtained from throat swabs and obtaining a measurement as number of copies of virus per ml. The viral RNA is detected by performing a RT-PCR test on patient samples.
How viral load occurs:
Viruses enter the body in different ways and usually travel via the bloodstream or other body fluids. The virus then enters and infects host cells in which they make copies of themselves before being released back into the fluid surrounding the cells. It is the viral particles that are found both before and after infection that make up the viral load.
Significance:
Viral load of COVID-19 is usually not detectable after two weeks. In the case of HIV, the higher the viral load the lower the number of CD4 white blood cells, because these are the very cells that the virus attacks. Therefore, viral load indicates how ill somebody is. This is also true for coronavirus, for instance, scientists have found that patients with the highest viral loads of COVID-19 had the highest death rates. The viral load can also indirectly show that a person is contagious and also how ill the person is.
Difference between Viral shedding and Viral load?
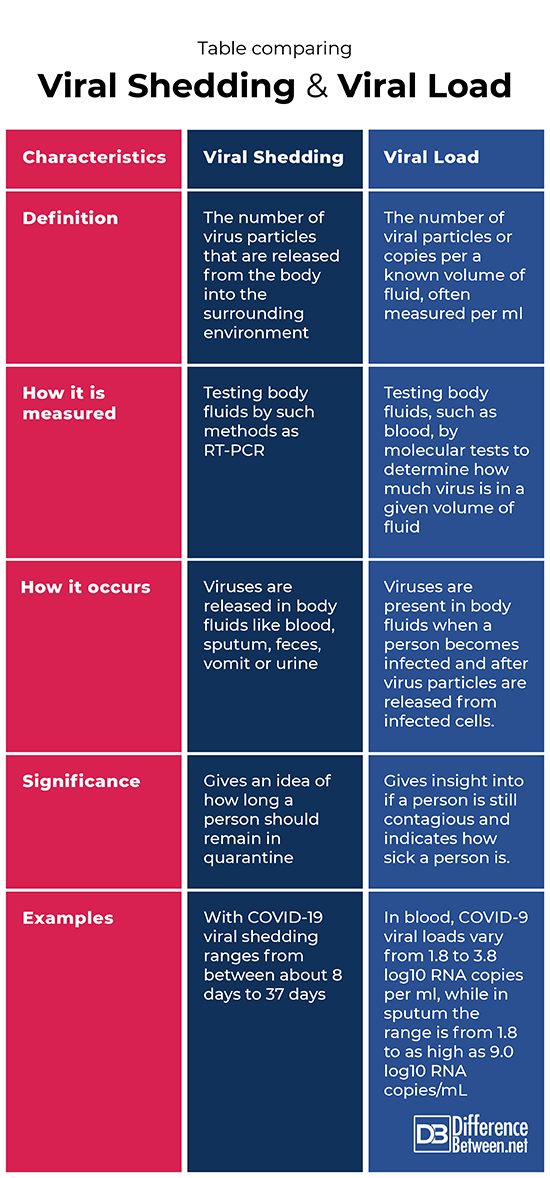
Definition
Viral shedding is the amount of virus particles that are released from the body into the surrounding environment. Viral load is the number of viral particles or copies per a known volume of fluid.
How it is measured
Viral shedding can be detected by testing body fluids by various methods including RT-PCR. Viral load is measured by testing for nucleic acid material using molecular methods and is recorded per ml of body fluid.
How it occurs
Viral shedding happens when viruses are released in body fluids like blood, sputum, feces, vomit or urine. Viral load happens when a person becomes infected and after virus particles are released from infected cells.
Significance
Knowing that a person is shedding virus helps to give an idea of how long a person should remain in quarantine. Viral load provides insight into if a person is still contagious and indicates how sick a person is.
Examples
In the case of COVID-19, viral shedding ranges from anywhere between about 8 days to 37 days. In the case of viral load of COVID-19, blood load varies from1.8 to 3.8 log10 RNA copies per ml, while sputum viral load has a range from 1.8 to as high as 9.0 log10 RNA copies/mL.
Table comparing Viral shedding and Viral load
Summary of Viral shedding and Viral load
- Viral shedding and viral load are both important to know when a person is ill with an infection such as COVID-19.
- Viral shedding is the release of virus into the environment outside of the body.
- Viral load is how many virus particles are found in the body fluids.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Pujadas, Elisabet, et al. "SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load Predicts COVID-19 Mortality." medRxiv (2020).
[1]Widders, Arabella, Alex Broom, and Jennifer Broom. "SARS-CoV-2: the viral shedding vs infectivity dilemma." Infection, Disease & Health (2020).
[2]Xu, Tianmin, et al. "Clinical features and dynamics of viral load in imported and non-imported patients with COVID-19." International Journal of Infectious Diseases (2020).
[3]Image credit: https://media.istockphoto.com/photos/viral-load-test-picture-id905964062?k=6&m=905964062&s=170667a&w=0&h=acJu2MYLw33ltHstl74fbk_C4pvp5vxy_vLST2KR85o=
[4]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Budding_of_generic_virus,_pictorial_represent.jpg
