Difference Between Adenosis and Adenoma
Adenosis and adenoma are both synonymous with the growth of non-cancerous masses. In the case of breast adenosis, it is most likely an increase in gland with breast tissue involvement. In adenoma, the cell lining around glands and organs is most often affected.
Both conditions have unique treatments approaches and medical procedures. The causal factors can remain unknown.
Although they are generally non-cancerous, certain factors can influence the change of cell type to a cancerous nature. Thus, it is of critical importance that these conditions are closely monitored and thoroughly tested.
This article will take a closer look at what differentiates the two terms, and clarify the definition, presentation, diagnosis and treatment of both.

Definition
Adenosis
Adenosis is defined as a condition of the breast tissue, where the lobules that produce milk become larger, swollen and could result in an increased number of glands.
These non-cancerous developments present as a mass or as tiny white deposits known as calcium deposits. They can result in the formation of fibrous tissue and may cause a higher risk of developing breast cancer.
Adenoma
An adenoma can be defined as a non-cancerous form of tumour, also known as benign tumours. Adenomas start growing in the tissue covering organs and glands, also known as epithelial tissue. These benign growths typically have a stalk-like structure when they grow, typically resembling a mushroom. Adenoma can be typed as Villous ,Tubular, Tubulovillous, and/or Sessile Serrated.
Adenomas can occur at any place throughout the body and can either be non-functioning or functioning (where they are responsible for the production of extra hormonal secretions). The most common occurrences in the body are:
- Adenomas across the adrenal glands
- Colon polyps along the colon lining
- Growths across the parathyroid gland
- Pleomorphic adenomas growing across salivary glands
Although adenomas are non-cancerous, it is important to keep in mind that they can become cancerous and should be monitored closely.
Characteristics and Clinical Presentation
Adenosis
The most frequent clinical presentation of breast adenosis is the feeling of a lump-type area deep within the breast tissue resembling the feeling of a cyst or a cancer.
Generally speaking, characteristics include:
- On and off swollen breast tissue with altering breast pain throughout the menstrual cycle
- Engorged breasts that change state with hormonal cycles
- A single painless lump in one or both breasts, appearing as a mass
Adenoma
Adenomas tend not to cause any signs or symptoms when they are small. This is greatly dependant on where they are located in the body. Large adenomas might present with symptoms such as pain in abdomen, tiredness and headaches, anaemia due to iron deficiency, weak muscles and a sensation of nausea.
Diagnosis
Adenosis
Diagnosing an adenosis through physical examination is not sufficient to diagnose the condition. Imaging tests such as mammograms and ultrasound scans can show the abnormality well. Once located, a biopsy is usually done where a core needle takes a sample of the tissue for testing.
Adenoma
Adenomas are generally diagnosed by starting with a physical examination. Thereafter, imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI scans and PET scans can be done. Once the abnormality is located, a sample biopsy is performed to analyze the tissue.
Treatment
Adenosis
The non-cancerous nature of adenosis means that treatment is not generally required. Symptoms of breast discomfort caused by the adenosis can be treated through clothing support and dietary changes.
A specialist physician will most likely recommend routine follow-up appointments routinely to screen for breast cancers.
Adenoma
If adenomas are not resulting in any health risks or complications, a physician may choose to wait and watch the progression of an adenoma. If, however, the adenoma tumours are the cause of health problems and hormone interference, a specialist physician will most likely opt to surgically remove the growth.
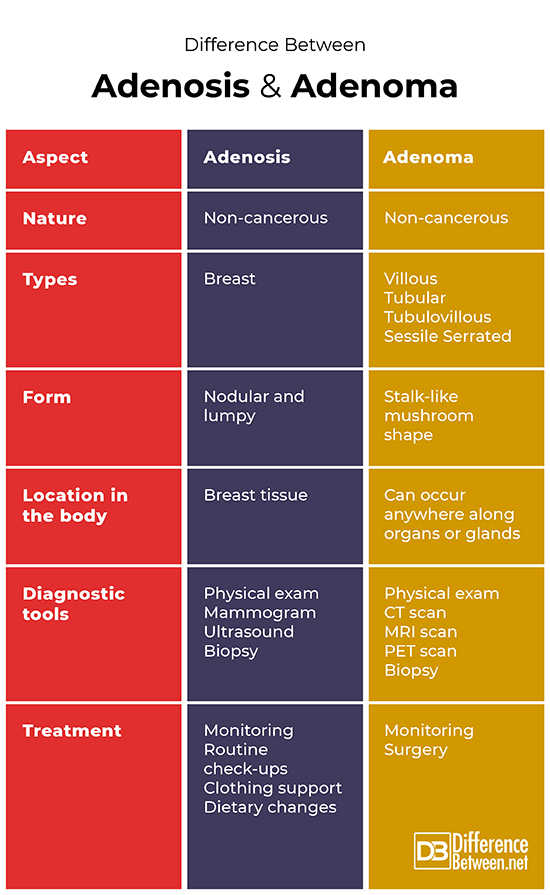
Table of comparison between adenosis and adenoma
Summary
Adenosis and adenoma are two terms which can be easily confused. Both terms relate to conditions where a mass may occur. Adenosis refers to the condition where breast tissue is affected by large and swollen lobules responsible for milk production. Adenoma on the other hand, refers to the growing of a tumour in the epithelial tissue, mostly over tissue found on organs and glands.
Both adenosis and adenoma are diagnosed upon physical exam and various imaging tests, as well as a biopsy procedure. Treatments, however, do significantly differ between the two. Adenosis is usually treated by monitoring the situation, routine check-ups, clothing support (such as a bra) and a change in diet. Adenomas are treated through monitoring and quite often include surgical removal.
Both conditions are non-cancerous but villous adenoma is the adenoma with a tendency to become of cancerous nature.
FAQ
What is an Adenosis tumor?
Adenosis is defined as a condition of the breast tissue, where the lobules that produce milk become larger, swollen and could result in an increased number of glands. These non-cancerous developments present as a mass or as tiny white deposits known as calcium deposits. They can result in the formation of fibrous tissue.
What are adenomas in the breast?
Adenomas found in the breast are tubular benign tumours that most often occur in young females. They are commonly referred to as pure adenomas.
What does Adenosis feel like?
The most frequent clinical presentation of breast adenosis is the feeling of a lump-type area deep within the breast tissue resembling the feeling of a cyst or a cancer.
What causes Adenosis?
Adenosis occurs in breast tissue and is caused when the lobules that produce breast milk become larger, swollen and could result in an increased number of glands.
- Difference Between a Cochlear Implant and Normal Hearing - October 4, 2022
- Difference Between Obstructive and Restrictive Spirometry - September 11, 2022
- The Difference Between White Box and Black Box Testing - September 11, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cleveland Clinic. “Adenomas”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21477-adenomas
[1]Jorns, Julie. “Breast: Fibrocystic changes: Adenosis”. PathologyOutlines.com, 2021. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastadenosisgeneral.html
[2]Ramji, Alnoor. “Villous Adenoma”. Medscape, 2016. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/170283-overview
[3]Soo, Mary., Dash, Nilima., Bentley, Rex., Lee, Lawrence. & Nathan, Girija. “Tubular Adenomas of the Breast Imaging Findings with Histologic Correlation”. American Journal of Roentgenology, vol. 174, no. 3, 2000, pp: 757-761
