Difference Between Adnexal Cyst and Ovarian Cyst
An adnexal cyst is when some type of cyst forms on the adnexa. An ovarian cyst is when a cyst forms on the ovary.
What is Adnexal cyst?
Definition:
An adnexal cyst is when a cyst-like structure forms on the adnexa of the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Adnexa is a general term for tissues that connect to or are on the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
Causes and risk factors:
A hemorrhagic ovarian cyst or fluctuations in hormone levels can sometimes lead to a woman developing an adnexal cyst. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was once thought to be a risk factor. However, HRT does not appear to increase the risk of adnexal cyst based on a study done in 1991. Risk factors for adnexal cysts can include having a history of previous cysts and problems with hormones.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is usually by means of an ultrasound done of the abdomen. An MRI is occasionally needed if the ultrasound does not give a good enough picture of the problem.
Symptoms and complications:
There are not always symptoms if an adnexal cyst is present. Symptoms of adnexal cysts are similar to those of ovarian cysts when present. A woman may feel pain or bloating. They may also have a feeling of fullness in the belly. A complication is that there is a slight risk a cyst can become cancerous, but it is rare.
Treatment:
An adnexal cyst on the fallopian tube is a problem because it is unlikely to go away on its own. In these cases, surgery is needed. Cysts on the ovary may not be a problem depending on size and where they are. Some ovarian cysts do go away after a few months.
What is Ovarian cyst?
Definition:
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that is found in or on the surface of the ovary.
Causes and risk factors:
Hormonal changes and imbalances can cause cysts to form on the ovaries. Risk factors for ovarian cysts, besides hormone issues, also include having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or a pelvic infection. If you have had a problematic ovarian cyst before then you at increased risk for it happening again.
Diagnosis:
A cyst can be diagnosed with an X-ray, CT-scan, and ultrasound. An ultrasound gives a better picture of a cyst than the former two imaging methods.
Symptoms and complications:
A small functional cyst may have no symptoms and usually such cysts do simply go away after a period of time. However, larger ovarian cysts can pose a problem and they often cause unpleasant symptoms like pain in the lower abdomen and pain in the back. The abdomen may also be very bloated and the person feels full quickly after eating food. Large cysts can have complications like ovarian torsion or they may burst and bleed causing problems such as internal infections and irritation.
Treatment:
Small ovarian cysts often go away after a while, often after a few menstrual cycles. However, much larger cysts may need more treatment such as surgical removal. Surgery may be done laparoscopically or, for very large cysts, open surgery may be needed.
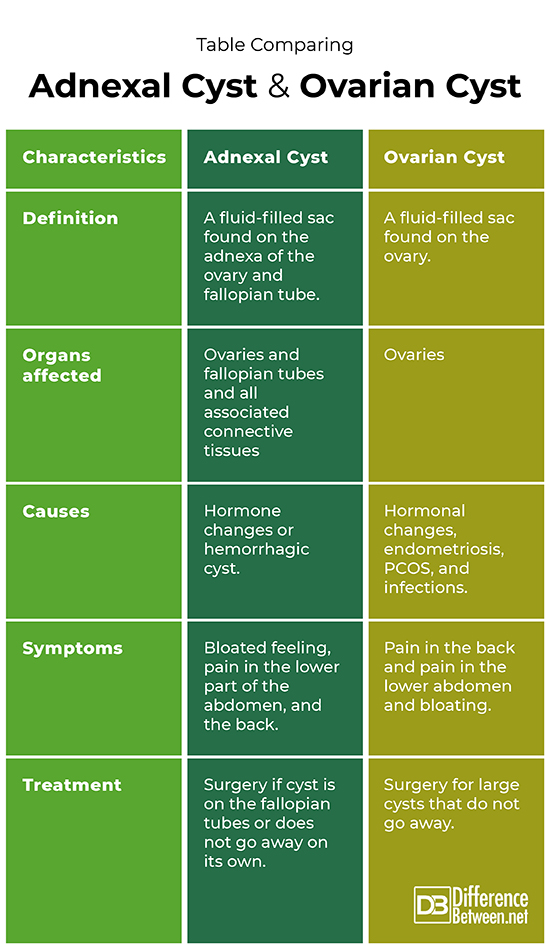
Difference between Adnexal cyst and Ovarian cyst
Definition
An adnexal cyst is a fluid-filled sac found on either the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, or tissue connected to these organs. An ovarian cyst is a cyst found on or in the ovary.
Organs affected
Adnexal cysts can be found on the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and connected tissues. Ovarian cysts occur only on or in the ovaries.
Causes
A hemorrhagic cyst or changes in hormones could cause an adnexal cyst to form. An ovarian cyst can form because of endometriosis or PCOS, or other hormone problems.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an adnexal cyst include pain in the back or abdomen and bloating. Ovarian cysts have symptoms such as pain in the lower abdomen and back.
Treatment
The treatment options for an adnexal cyst depend on where it is located, with fallopian tube cysts needing to be always be removed by surgery. Ovarian cysts may only need to be removed surgically if they are large or problematic.
Table comparing Adnexal cyst and Ovarian cyst
Summary of Adnexal cyst and Ovarian cyst
- An adnexal cyst and ovarian cyst both affect the female reproductive organs.
- Adnexal cysts can affect the ovaries but also the fallopian tubes and connective tissue that attaches to both organs.
- An ovarian cyst is a type of adnexal cyst.
- In both the case of an adnexal cyst and ovarian cyst, surgery may be required to remove the cyst.
FAQ
Is an adnexal cyst an ovarian cyst?
An adnexal cyst can sometimes refer to a cyst on the ovary but it can also refer to a cyst on the fallopian tube.
Is Adnexa and ovary the same?
No, adnexa is a general term that includes both ovaries and fallopian tubes and their associated connective tissues.
What is an adnexal ovarian cyst?
An adnexal ovarian cyst is a cyst that forms on the tissue of the ovary.
Is an ovarian cyst an adnexal mass?
An ovarian cyst is also classified as an adnexal mass. However, the term adnexal mass is more general in that it can also include cysts and masses found on other reproductive structures such as the fallopian tubes.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hall, Deborah A., and Kathleen A. McCarthy. "The significance of the postmenopausal simple adnexal cyst." Journal of ultrasound in medicine 5.9 (1986): 503-505.
[1]Kilpatrick, Charlie C. “Benign Ovarian Masses”. Merck Manual, 2021, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/gynecology-and-obstetrics/miscellaneous-gynecologic-disorders/benign-ovarian-masses
[2]Levine, D., et al. "Simple adnexal cysts: the natural history in postmenopausal women." Radiology 184.3 (1992): 653-659.
