Difference Between Anterolisthesis and Spondylolisthesis
Anterolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior slippage of the vertebra in the backbone while spondylolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior or posterior slippage of the vertebrae in the backbone.
What is Anterolisthesis?
Definition:
Anterolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior slippage of the vertebra in the backbone.
Causes:
Anterolisthesis occurs due to blunt trauma, fractures secondary to road traffic accidents or falls, or after intensive physical exercise. Aging is also linked with anterolisthesis. Vertebral tumors and arthritis can also cause anterolisthesis. or fractures.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of anterolisthesis are proportional to the degree of slippage and its location. Anterolisthesis causes severe, worsening pain over the affected area, which is mostly the lower limbs and lower back. Anterolisthesis causes partial immobility. Other symptoms include muscle rigidity, paresthesia, poor posture, loss of temperature sensations, and in severe cases paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel function.
Diagnosis:
Anterolisthesis is diagnosed via physical examination and radiologic findings on X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
Treatment:
Treatment options for mild to moderate anterolisthesis include bed rest to relieve pain and further slippage, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids and steroids, and physiotherapy. Surgery may be required in severe cases.
What is spondylolisthesis?
Definition:
Spondylolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior or posterior slippage of the vertebrae in the backbone.
Causes:
Spondylolisthesis can be secondary to congenital spinal deformities, high-velocity trauma causing vertebral dislocation, vertebral pathologies like tumors and bone diseases, iatrogenic, overextension of the backbone in athletes, and due to degenerative bone changes in the elderly.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of spondylolisthesis include backache, muscle rigidity, paresthesia, localized pain, and inability to walk or stand for a long time.
Diagnosis:
Spondylolisthesis is diagnosed via physical examination and radiologic findings on X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
Treatment:
Treatment options for spondylolisthesis consist of rest, analgesia in the form of oral medications such as NSAIDs and opioids, physiotherapy, bracing, and mild exercise. Surgical options include decompression and vertebral realignment.
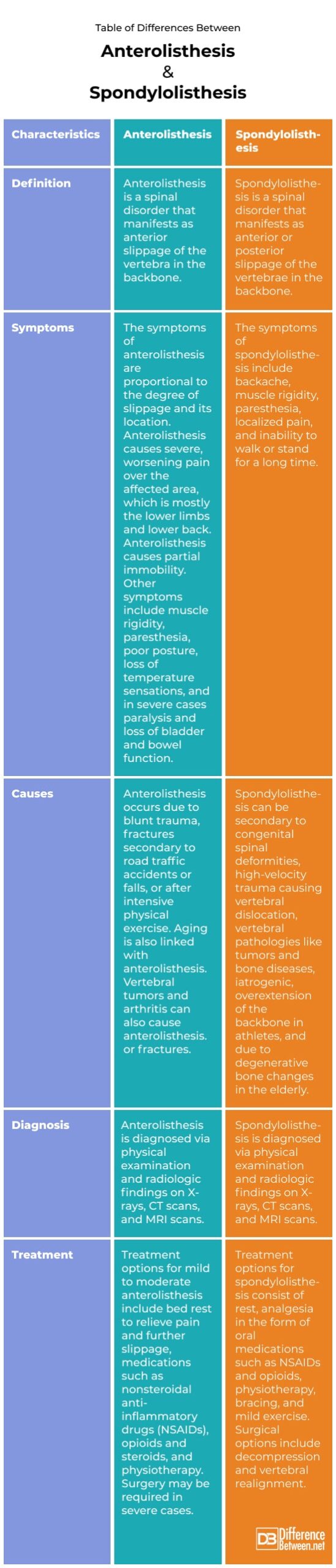
Difference between Anterolisthesis and Spondylolisthesis
Definition:
Anterolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior slippage of the vertebra in the backbone. Spondylolisthesis is a spinal disorder that manifests as anterior or posterior slippage of the vertebrae in the backbone.
Causes:
Anterolisthesis occurs due to blunt trauma, fractures secondary to road traffic accidents or falls, or after intensive physical exercise. Aging is also linked with anterolisthesis. Vertebral tumors and arthritis can also cause anterolisthesis. or fractures. Spondylolisthesis can be secondary to congenital spinal deformities, high-velocity trauma causing vertebral dislocation, vertebral pathologies like tumors and bone diseases, iatrogenic, overextension of the backbone in athletes, and due to degenerative bone changes in the elderly.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of anterolisthesis are proportional to the degree of slippage and its location. Anterolisthesis causes severe, worsening pain over the affected area, which is mostly the lower limbs and lower back. Anterolisthesis causes partial immobility. Other symptoms include muscle rigidity, paresthesia, poor posture, loss of temperature sensations, and in severe cases paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel function. The symptoms of spondylolisthesis include backache, muscle rigidity, paresthesia, localized pain, and inability to walk or stand for a long time.
Diagnosis:
Anterolisthesis is diagnosed via physical examination and radiologic findings on X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans. Spondylolisthesis is diagnosed via physical examination and radiologic findings on X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans.
Treatment:
Treatment options for mild to moderate anterolisthesis include bed rest to relieve pain and further slippage, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids and steroids, and physiotherapy. Surgery may be required in severe cases. Treatment options for spondylolisthesis consist of rest, analgesia in the form of oral medications such as NSAIDs and opioids, physiotherapy, bracing, and mild exercise. Surgical options include decompression and vertebral realignment.
Table of difference between Anterolisthesis and Spondylolisthesis
FAQ
Is Anterolisthesis and spondylolisthesis the same thing?
Anterolisthesis is a type of spondylolisthesis as spondylolisthesis is the anterior or posterior slippage of the vertebrae in the backbone.
How serious is anterolisthesis?
Mild or moderate anterolisthesis is not very dangerous, however in severe cases it can cause paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel function.
What is the other name for Anterolisthesis?
Spondylolisthesis.
Is Anterolisthesis degenerative?
Yes, arthritis can lead to degenerative anterolisthesis.
What grade is mild Anterolisthesis?
Grade 1.
Is spondylolisthesis always L5 S1?
No, but it is the most common location.
How do you stop spondylolisthesis from progressing?
Treatment options for spondylolisthesis consist of rest, analgesia in the form of oral medications such as NSAIDs and opioids, physiotherapy, bracing, and mild exercise. Surgical options include decompression and vertebral realignment.
How do you fix L5-S1 spondylolisthesis?
Treatment options for spondylolisthesis consist of rest, analgesia in the form of oral medications such as NSAIDs and opioids, physiotherapy, bracing, and mild exercise.
How do you sit with L5-S1 spondylolisthesis?
The lower back should be supported with pillows while sitting and the feet should be on the ground.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Iguchi, Tetsuhiro, et al. "Lumbar multilevel degenerative spondylolisthesis: radiological evaluation and factors related to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis." Clinical Spine Surgery 15.2 (2002): 93-99.
[1]Rowe, L., and I. Steiman. "Anterolisthesis in the cervical spine--spondylolysis." Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics 10.1 (1987): 11-20.
[2]Capener, Norman. "Spondylolisthesis." (1932).
