Difference Between Bordetella Pertussis and Parapertussis
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative coccobacillus that causes whooping cough and releases pertussis toxin. Bordetella parapertussis is a less common cause of whooping cough. It does not release pertussis toxin.
What is Bordetella Pertussis?
Definition:
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative, aerobic coccobacillus bacterium that is the main causative agent of whooping cough.
Structure:
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative, aerobic, encapsulated bacterium that is motile due to the presence of a flagellate. The bacterium expresses a multitude of toxins, these include pertussis toxin, adenylate cyclase toxin, and tracheal cytotoxin. The organism is urease and citrate negative.
Symptoms:
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a readily transmissible respiratory tract infection that is caused by the Bordetella pertussis bacterium and rarely by B. parapertussis. It is characterized by a severe persistent cough that is accompanied by a deep, high-pitched “whoop”. Initially, the symptoms are mild and include a runny nose, fever, coryza, red eyes, and sneezing. Deteriorating symptoms include persistent vomiting, cyanosis, uncontrollable coughing, and extreme fatigue.
Transmission:
Bordetella pertussis spreads via respiratory droplets. The incubation period is about a week.
The organism only affects humans.
Diagnosis:
B. pertussis is diagnosed through nasopharyngeal swabs and cultures, PCR, and ELISA.
Treatment:
Strong antibiotics, particularly macrolides like erythromycin, are used to prevent and treat whooping cough.
Prevention:
The Pertussis vaccine is widely available since the late 20th century. It is given alongside diphtheria and tetanus immunization.
What is Bordetella Parapertussis?
Definition:
Bordetella parapertussis is a gram-negative, smaller bacterium that causes mild cases of whooping cough. It does not release pertussis toxin.
Structure:
Bordetella parapertussis is a non-motile bacterium. It is oxidase and urease negative.
Symptoms:
Parapertussis produces milder symptoms of whooping cough.
Transmission:
Bordetella parapertussis is also transmitted via respiratory droplets. It affects humans and sheep, causing whooping cough and pneumonia respectively.
Diagnosis:
The organism is detected in culture or PCR.
Treatment:
B. parapertussis infection is treated via antibiotics like clarithromycin and azithromycin.
Prevention:
No vaccine is available against B. parapertussis. Pertussis vaccine offers minimal or no protection against parapertussis infection.
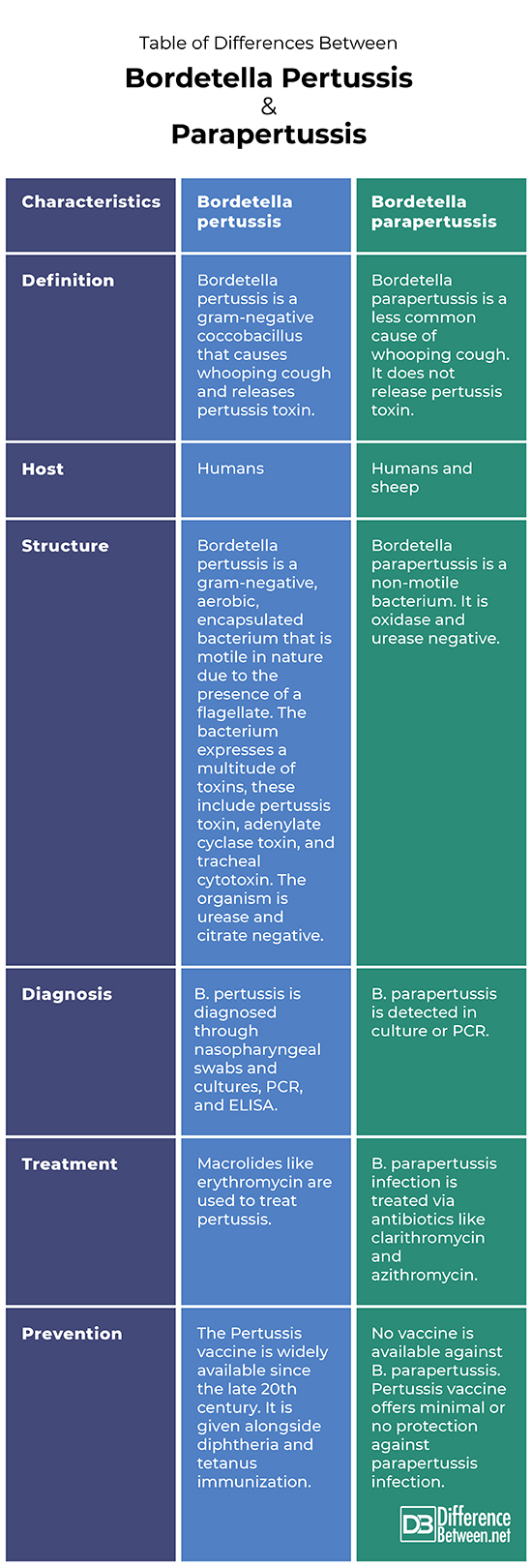
Difference between Bordetella pertussis and parapertussis
Definition:
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative coccobacillus that causes whooping cough and releases pertussis toxin. Bordetella parapertussis is a less common cause of whooping cough. It does not release pertussis toxin.
Host:
Bordetella pertussis affects humans only whereas Bordetella parapertussis affects humans and sheep.
Structure:
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative, aerobic, encapsulated bacterium that is motile in nature due to the presence of a flagellate. The bacterium expresses a multitude of toxins, these include pertussis toxin, adenylate cyclase toxin, and tracheal cytotoxin. The organism is urease and citrate negative. Bordetella parapertussis is a non-motile bacterium. It is oxidase and urease negative.
Diagnosis:
B. pertussis is diagnosed through nasopharyngeal swabs and cultures, PCR, and ELISA. B. parapertussis is detected in culture or PCR.
Treatment:
Macrolides like erythromycin are used to treat pertussis. B. parapertussis infection is treated via antibiotics like clarithromycin and azithromycin.
Prevention:
The Pertussis vaccine is widely available since the late 20th century. It is given alongside diphtheria and tetanus immunization. No vaccine is available against B. parapertussis.
Table of differences between Bordetella pertussis and parapertussis
FAQs
What is the difference between Bordetella pertussis and parapertussis?
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative coccobacillus that causes whooping cough and releases pertussis toxin. Bordetella parapertussis is a less common cause of whooping cough. It does not release pertussis toxin.
Does Bordetella parapertussis need to be treated?
Yes, Bordetella parapertussis needs prompt antibiotic treatment to stop the disease transmission and reduce its severity.
What is another name for Bordetella pertussis?
Whooping cough.
What disease is Bordetella parapertussis?
Bordetella parapertussis also causes whooping cough but the symptoms are milder.
What are the symptoms of parapertussis?
Symptoms of parapertussis include cough, runny nose, a low-grade fever and malaise. The cough progresses to whoops and bursts. The child may become cyanosed and have shortness of breath.
Is Bordetella Parapertussis contagious?
Yes.
What antibiotics treat Bordetella parapertussis?
B. parapertussis infection is treated via antibiotics like clarithromycin and azithromycin.
Does wearing a mask protect against pertussis?
Yes. Wearing a mask help prevent getting pertussis from the infected patient.
Do masks protect against pertussis?
Yes.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Nieves, Delma J., and Ulrich Heininger. "Bordetella pertussis." Emerging Infections 10 (2016): 311-339.
[1]Melvin, Jeffrey A., et al. "Bordetella pertussis pathogenesis: current and future challenges." Nature Reviews Microbiology 12.4 (2014): 274-288.
[2]Parkhill, Julian, et al. "Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica." Nature genetics 35.1 (2003): 32-40.
