Difference Between Whooping Cough and Croup
Infections respiratory diseases are quite common, both in adults and in children. But there are some types of infectious respiratory diseases that affect mostly children.
Two examples of respiratory diseases that are particularly relevant to children are whooping cough and croup.
What is whooping cough?
Whooping cough, is a very infectious respiratory disease. Because it’s caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis and this disease is also known as Pertussis.
The name “whooping cough” comes from the “whooping” sound that someone makes after coughing for a long time (the sound of gasping for air).
This disease is rare and particularly dangerous for babies.
Whooping cough has symptoms that are divided between early and late-stage.
Early-stage symptoms
The first symptoms are similar to a cold, like fever and a very mild cough. The main symptoms that are characteristic of this stage are:
- Low-grade fever
- Runny nose
- Mild occasional cough
- Apnea (a pause on breathing). This one is more common in babies.
This stage usually from 1 to 2 weeks.
Late-stage symptoms
This is the stage where the traditional symptoms occur. They start after 1 to 2 weeks and include:
- Coughing fits – many rapid coughs that are followed by a high-pitched sound. The excessive coughs make the air leave the lungs. After there is no air left, you are forced to inhale, and this is what causes this high-pitched sound.
- Exhausting after the coughing fits
- Vomiting, which is usually caused by the excessive coughs
The coughing fits can last up to 10 weeks, and because of that It’s known as “100 day cough” in some places.
The whooping cough can be treated with antibiotics. Vaccination is available for Whooping cough.
What is Croup?
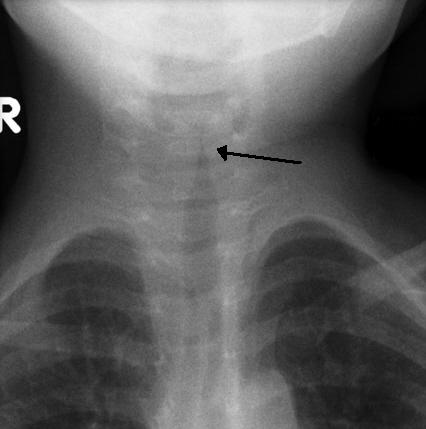
Croup is a respiratory infection that occurs in the upper respiratory tract (nose and throat). It blocks the respiration, causing a strong and characteristic cough. It’s a quite common disease and it affects mostly babies and young children.
The main symptoms of croup are:
- Strong barking coughs. Some people describe as the sound of a seal.
- Runny nose
- Fever
- Difficulty breathing
- Hoarse voice
The croup is a quite mild disease. It’ a short-term disease that usually goes away in a few days, so it can be managed at home. However, in more serious and persistent cases, the doctor can prescribe medicines such as steroids.
Similarities between whooping cough and croup
- Both croup and whooping cough are infectious respiratory diseases.
- Both start with very generic symptoms that are similar to a cold.
- The spreading of the disease is also similar: both can be transmitted via saliva and air (usually when someone infected coughs and/or sneezes).
- Also, both diseases are particularly relevant to babies and young children.
Differences between whooping cough and croup
That are a few particularities that differ both conditions. Some examples are:
Cause of whooping cough and croup
Both conditions are caused by microorganisms, but the type of microorganism is different.
The whooping cough is caused by bacteria while croup is caused by viruses.
Treatment of whooping cough and croup
Because the type of microorganism that causes the disease is different, the treatment is different as well. For the whooping cough it is necessary the use of antibiotics, that will kill the bacteria and stop the spreading.
On the other hand, antibiotics are useless for the treatment of croup. The croup usually gets better by itself, with additional care at home.
In worse cases steroids will be prescribed and not antibiotics.
Prevention of whooping cough and croup
Whooping cough: Vaccines are available to prevent whooping cough. Emergency medication can be prescribed to prevent the development of the disease when someone is exposed to the bacteria that causes the disease.
Croup: No preventive treatments for croup. The only preventive methods to avoid being infected by following basic hygiene habits such as:
- Washing hands with soap or alcohol sanitizer before eating
- Avoid touching your mouth, nose or eyes (specially when the hands are not properly clean)
- Keep distance from people coughing or sneezing
The length of whooping cough and Croup
Croup is a short-term disease. It normally goes away in 3 to 5 days, and it can even disappear within 48 hours.
On the other hand, whooping cough can last up to 10 weeks.
In the table below it’s possible to analyze some differences between these two diseases:
Whooping cough vs. Croup : Comparison table
Summary of whooping cough vs. Croup
- Although whooping cough and croup start with symptoms that are similar to a cold, the severity of both diseases and the way they should be handled is different.
- Both diseases have a cough as the main symptom. But the severity of the cough is worse with whooping cough. This is also one of the reasons why someone with whooping cough should go to a doctor as soon as possible. Whooping cough is a condition that needs medical care and should not be neglected.
- On the other hand, croup is a very common condition that can go away by itself. Simple treatments at home like drinking a lot of fluids and resting, is enough to take care of the disease.
- Whooping cough is rare and more dangerous the croup, fortunately it can be easily avoided by vaccination. Croup is not as severe, and no preventive treatment is available at this point.
- Difference Between Whooping Cough and Croup - March 10, 2018
- Difference between Hypomania and Mania - January 15, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Danthis, Michael. "Whooping Cough." Nursing Standard, vol 28, no. 36, 2014, pp. 53-53. RCN Publishing Ltd., doi:10.7748/ns2014.05.28.36.53.s51.
[1]Bentley, Jackie et al. "Whooping Cough: Identification, Assessment And Management." Nursing Standard, vol 28, no. 11, 2013, pp. 50-57. RCN Publishing Ltd., doi:10.7748/ns2013.11.28.11.50.e7911.
[2]Bjornson, Candice L, and David W Johnson. "Croup." The Lancet, vol 371, no. 9609, 2008, pp. 329-339. Elsevier BV, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60170-1.
[3]Image credit:By Frank Gaillard - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6792682

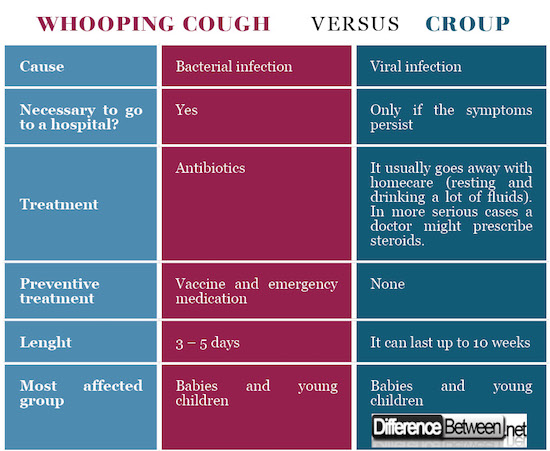
thanks for the good article but on the graphic table the durations (length) are the oppposite Croup should be 3-5 days where Whooping cough should be up to 10 weeks