Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage
Both brain hematoma and brain hemorrhage involve injury, bleeding, brain function loss, confusion, dizziness, and headache. Specifically, a brain hematoma occurs when there is a buildup of blood that is not inside the blood vessels in the brain while a brain hemorrhage is bleeding in the brain. The following discussions look into their differences.
What is Brain Hematoma?
“Hematoma” came from the Greek word “haima” which means “blood” and the Greek suffix “-oma” which is used in pathology to indicate a mass. It is generally defined as a bad bruise or a collection of blood outside of blood vessels. Hence, brain hematoma occurs when there is a buildup of blood outside the brain blood vessels.
Epidural Hematoma
An epidural hematoma is a traumatic blood accumulation between the skull and the brain’s protective covering. This is typically caused by traumatic head injury which generally includes a skull fracture and artery laceration. This is a potentially fatal disorder that may need prompt treatment and, if untreated, is associated with severe morbidity and mortality. Many visits to the emergency room due to epidural hematoma are associated with extreme sports. A targeted blow to the head, such as one delivered with a hammer or baseball bat, frequently serves as the initiating event (Price, 2021). The symptoms include loss of consciousness, decline of brain function, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, enlarged pupil in one eye, dizziness, confusion, slurred speech, and weakness on one side of the body. More severe symptoms include seizures, breathing difficulties, brain function loss, coma, and death.
Intracerebral Hematoma
Also known as intraparenchymal hematoma, intracerebral hematoma occurs when blood gathers in the brain’s tissues. The most common causes are high blood pressure and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (proteins build up on the brain’s arterial walls). Other causes include trauma, aneurysm, weakly connected arteries and veins from birth, and tumors (Kutty, 2016; Mayo Clinic, 2022).
Subdural Hematoma
An accumulation of blood outside the brain is known as a subdural (below the epidural membrane) hematoma. Blood gathers between the layers of tissue that encircle the brain. Specifically, the bleeding occurs between the dura (topmost layer) and the arachnoid (the next layer). It is typically brought on by severe head injuries. A subdural hematoma can cause life-threatening bleeding and increased pressure on the brain. Some abruptly come to a stop, while others require surgical drainage. The symptoms include headache, confusion, dizziness, vomiting, lethargy, weakness, and seizures. A person with serious bleeding may immediately pass out, go into a coma, or even die. As for a person with a slow-growing subdural hematoma, there may be no apparent symptoms for more than a couple of weeks (Hoffman, 2022).
What is Brain Hemorrhage?
The word “hemorrhage” came from the Latin word “haemorrhagia” which translates to “a violent bleeding”. Brain hemorrhage is also known as brain bleed, cerebral hemorrhage, intracranial hemorrhage, or intracerebral hemorrhage which is responsible for 13% of strokes. It occurs when the blood from trauma irritates the tissues of the brain which leads to swelling (cerebral edema). Blood that has accumulated forms a mass known as a hematoma. These conditions put more strain on the surrounding brain tissue, which decreases critical blood flow and destroys brain cells. The risk factors and causes include head trauma, high blood pressure, aneurysm, blood vessel abnormalities, amyloid angiopathy, blood or bleeding disorders, liver disease, and brain tumors (Wright, 2022).
The symptoms may include weakness, tingling, paralysis of the extremities or face on one side, headache, difficulty swallowing, vision problems, loss of balance or coordination, confusion, slurred speech, seizures, lethargy, stupor, and unconsciousness. Brain hemorrhage requires immediate medical attention (Felman, 2019).
Difference between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage
Definition
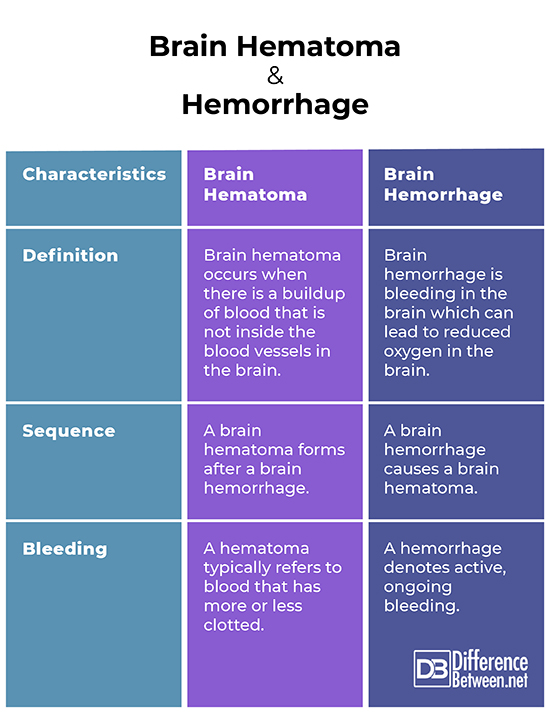
Brain hematoma occurs when there is a buildup of blood that is not inside the blood vessels in the brain. As for brain hemorrhage, it is bleeding in the brain which can lead to reduced oxygen in the brain.
Sequence
A brain hematoma forms after a brain hemorrhage. When the blood from a brain injury leads to cerebral edema, the accumulated blood forms a mass (hematoma).
Bleeding
A hemorrhage denotes active, ongoing bleeding, while a hematoma typically refers to blood that has more or less clotted. In relation to their etymology, “hematoma” came from the Greek word “haima” which means “blood” and the Greek suffix “-oma” which is used in pathology to indicate a mass. In comparison, “hemorrhage” came from the Latin word “haemorrhagia” which translates to “a violent bleeding”.
Brain Hematoma vs Hemorrhage
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Does a hemorrhage cause a hematoma?
Brain hemorrhage occurs when the blood from trauma irritates the tissues of the brain which leads to swelling (cerebral edema). The blood that has accumulated forms a mass known as a hematoma.
What’s the difference between brain bleed and hemorrhage?
Brain hemorrhage is also known as brain bleed
How serious is a hematoma on the brain?
An intracranial (within the skull) hematoma may require immediate medical attention as it can be life-threatening. In the event of a head injury, seek emergency medical care right away.
What are 3 types of hemorrhage?
The three types of hemorrhage differ from one another in terms of location, flow, and intensity. In particular, capillary bleeding trickles from the body whereas venous bleeding flows gradually. Arterial bleeding occurs in spurts (West, 2021).
What are 3 categories of hematoma?
The categories are subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma and intracerebral (intraparenchymal) hematoma (Mayo Clinic, 2022).
Which hematoma is serious?
It is important to seek medical assistance if a hematoma is very painful or if it keeps becoming bigger after a few days. People who have head injuries, ear injuries, or who exhibit infection-related symptoms should consult a doctor immediately.
What happens if a hematoma is not treated?
Some hematomas do not need to be treated. Over time, the body will reabsorb the blood from the hematoma. However, complications can result from an untreated hematoma. For instance, if a person does not undergo specialized tests, a brain hematoma may be difficult to detect. He may feel symptoms like a persistent headache, vertigo, or impaired speech (Johnson, 2019).
Who is at risk for hematoma?
The people who are at risk for hematoma are those who engage in contact sports, have aneurysms, are taking anticoagulation medications, have bleeding disorders, and heavily drink alcohol (Sampson, 2022).
Summary
- When hemorrhage, or blood from a brain injury leads to cerebral edema, the accumulated blood forms a mass or a hematoma.
- A hemorrhage denotes active, ongoing bleeding, while a hematoma typically refers to blood that has more or less clotted.
- Brain hematoma and hemorrhage require immediate medical attention as they can be life-threatening.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Felman, A. (2019). What to know about brain hemorrhage. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317080
[1]Johnson, J. (2019). Hematoma: Everything you need to know. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324831
[2]Kutty, S.A. (2016). Intracerebral hematoma. Hemorrhagic stroke. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/53545
[3]Hoffman, M. (2022). Subdural hematoma. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/brain/subdural-hematoma-symptoms-causes-treatments
[4]Mayo Clinic. (2022). Intracranial hematoma. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/intracranial-hematoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20356145#:~:text=without%20prompt%20treatment.-,Intracerebral%20(intraparenchymal)%20hematoma,the%20tissues%20of%20the%20brain.
[5]Price, D. (2021). Epidural hematoma management in the ED. Medscape. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/824029-overview
[6]Sampson, S. (2022). Everything to know about hematoma. Healthgrades. https://www.healthgrades.com/right-care/symptoms-and-conditions/hematoma#risk-factors
[7]West, M. (2021). What to know about different types of bleeding. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/types-of-bleeding#:~:text=These%20three%20types%20of%20bleeding,and%20veins%20can%20be%20severe.
[8]Wright, S. (2022). Brain hemorrhage: Causes, symptoms, treatments. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/brain/brain-hemorrhage-bleeding-causes-symptoms-treatments
