Difference Between COPD and Pneumonia
What is COPD?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease, causing poor airflow and long-term breathing problems. It is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality from respiratory illnesses worldwide. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are the two most common conditions that contribute to COPD. Some researchers add asthma to the COPD group.
Chronic bronchitis is a prolonged inflammation of the respiratory tract resulting in a cough and mucus formation in the respiratory tract. Emphysema is a breakdown or structural deformity in the alveoli and the small airways, which occurs with pronounced dyspnea and impaired ventilation function.
The most common causes of COPD are:
- Smoking;
- Occupational dangers – dust and chemicals;
- Hereditary deficiency of alpha – 1 – antitrypsin.
COPD occurs more often in men over 40 years of age.
The complications of COPD are:
- Frequent respiratory infections;
- Increased pressure in the lungs;
- Development of right-sided heart failure;
- Chronic oxygen deficiency;
- Respiratory failure, and fatal outcome.
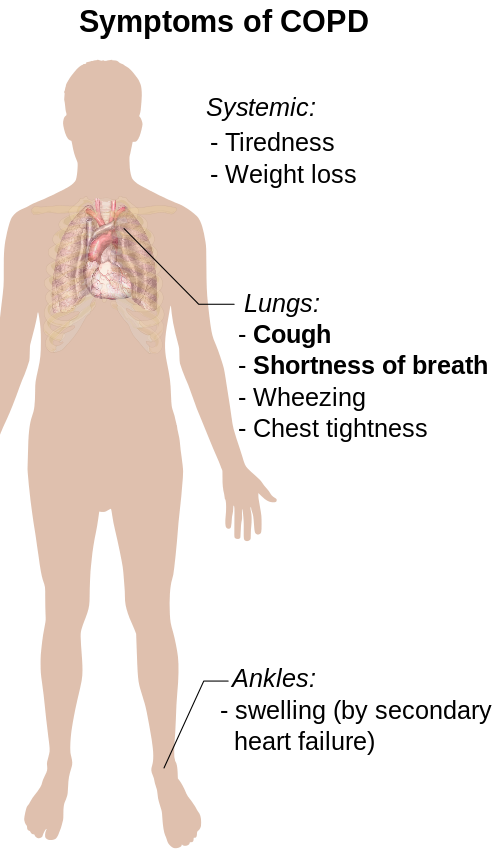
The most common symptoms of COPD are:
- Shortness of breath;
- Productive cough with mucus – purulent or mucus expectoration;
- Chest pain;
- Reduced physical capacity;
- Hiss in the chests.
In emphysema, the dyspnea is more pronounced, while in chronic bronchitis – the cough with mucus – purulent or mucus expectoration.
Additional symptoms of COPD are:
- Decreased oxygen content in the blood;
- Mental changes;
- Changing the rhythm of sleep;
- Changes in the nails and the joints of the hands;
- Symptoms from the cardiovascular system, digestive system, etc.
Diagnosis is done through laboratory, functional, and imaging studies.
The treatment of COPD can include cough medicines, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and anti-asthma drugs. The only definitive solution in case of emphysema is lung transplantation.
What is Pneumonia?
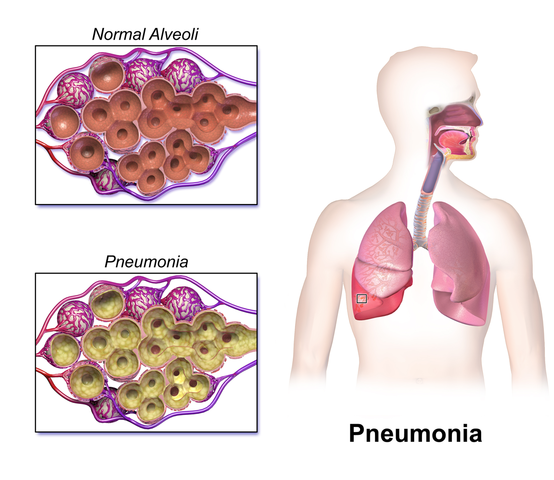
Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection in one or both lungs. It causes inflammation in the alveoli. They fill with pus or fluid, which makes breathing difficult.
Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The main types of pneumonia are classified according to the cause of the infection:
- Bacterial pneumonia – the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viral pneumonia – caused by respiratory viruses.
- Mycoplasma pneumonia – mycoplasma usually causes mild cases of pneumonia, most commonly in older children and young adults.
- Fungal pneumonia – fungi can cause pneumonia, mainly in people with chronic illness or a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of pneumonia can be mild to life-threatening. The most common symptoms of pneumonia may include:
- Cough with sputum (mucus);
- Shortness of breath;
- Sweating, chills, and fever;
- Pain in the chests.
Other symptoms may vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection, as well as the age and general health of the individual.
Viral pneumonia can begin with flu-like symptoms. High temperature can occur after 12-36 hours. Bacterial pneumonia can cause fever, along with abundant sweating, bluish lips and nails, and confusion.
Both viral and bacterial pneumonia are contagious, the infection is spread by airborne droplet.
The fungal pneumonia does not spread from person to person.
Everyone can get pneumonia, but the risk is higher in:
- Babies from birth to 2 years of age;
- People over 65 years of age;
- People with a weakened immune system;
- People who smoke, abuse alcohol or drugs;
- People with certain chronic diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, diabetes or heart failure.
Diagnosis is done through laboratory, functional and imaging studies.
The possible complications of pneumonia are:
- Bacteremia – bacteria in the bloodstream;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Fluid accumulation around the lungs;
- Lung abscess.
The treatment depends on the type of pneumonia, how severe it is, and the general health of the patient. Antibiotics, antiviral, and antifungal drugs are used to treat pneumonia depending on the specific cause of the disease. Medicines can be prescribed to relieve pain and fever, if necessary, as well as cough medicines.
Difference Between COPD and Pneumonia
-
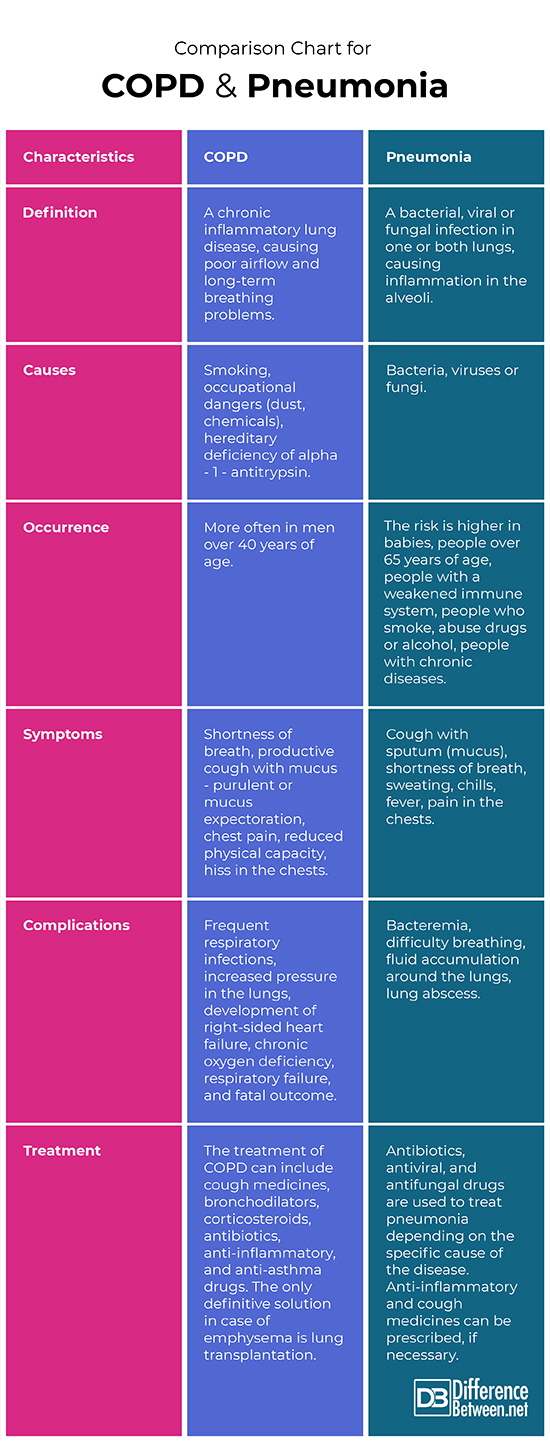
Definition
COPD: COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease, causing poor airflow and long-term breathing problems.
Pneumonia: Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection in one or both lungs, causing inflammation in the alveoli.
-
Causes
COPD: The most common causes of COPD are smoking, occupational dangers (dust, chemicals), and hereditary deficiency of alpha – 1 – antitrypsin.
Pneumonia: Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi.
-
Occurrence
COPD: COPD occurs more often in men over 40 years of age
Pneumonia: The risk of pneumonia is higher in babies, people over 65 years of age, people with a weakened immune system, smokers, people who abuse alcohol or drugs, people with chronic diseases.
-
Symptoms
COPD: The most common symptoms of COPD are shortness of breath, productive cough with mucus – purulent or mucus expectoration, chest pain, reduced physical capacity, hiss in the chests.
Pneumonia: The most common symptoms of pneumonia are a cough with sputum (mucus), shortness of breath, sweating, chills, fever, pain in the chests.
-
Complications
COPD: The possible complications of COPD are frequent respiratory infections, increased pressure in the lungs, development of right-sided heart failure, chronic oxygen deficiency, respiratory failure, and, fatal outcome.
Pneumonia: The possible complications of pneumonia are bacteremia, difficulty breathing, fluid accumulation around the lungs, lung abscess.
-
Treatment
COPD: The treatment of COPD can include cough medicines, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and anti-asthma drugs. The only definitive solution in case of emphysema is lung transplantation.
Pneumonia: Antibiotics, antiviral, and antifungal drugs are used to treat pneumonia depending on the specific cause of the disease. Anti-inflammatory and cough medicines can be prescribed, if necessary.
Comparison Chart for COPD and Pneumonia
Summary of COPD Vs. Pneumonia
- COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease, causing poor airflow and long-term breathing problems.
- Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection in one or both lungs, causing inflammation in the alveoli.
- The most common causes of COPD are smoking, occupational dangers (dust, chemicals), and hereditary deficiency of alpha – 1 – antitrypsin. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- COPD occurs more often in men over 40 years of age. The risk of pneumonia is higher in babies, people over 65 years of age, people with a weak immune system, people with chronic diseases, etc.
- The most common symptoms of COPD are shortness of breath, productive cough, chest pain, reduced physical capacity, hiss in the chests. The most common symptoms of pneumonia are a productive cough, shortness of breath, sweating, chills, fever, pain in the chests.
- The possible complications of COPD are frequent respiratory infections, increased pressure in the lungs, development of right-sided heart failure, chronic oxygen deficiency, respiratory failure, and fatal outcome. The possible complications of pneumonia are bacteremia, difficulty breathing, fluid accumulation around the lungs, lung abscess.
- The treatment of COPD can include cough medicines, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, and anti-asthma drugs. The treatment of pneumonia includes antibiotics, antiviral, or antifungal drugs, depending on the specific cause of the disease. Anti-inflammatory and cough medicines can be prescribed, if necessary.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/26/Symptoms_of_COPD.svg/500px-Symptoms_of_COPD.svg.png
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/14/Blausen_0994_Pneumonia.png/554px-Blausen_0994_Pneumonia.png
[2]Haas, F., S. Haas, R. Human. The Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Handbook. 1st Edition. New York, Toronto: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 2000. Print.
[3]Warrell, D., T. Cox, J. Firth. Oxford Textbook of Medicine, Vol. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2010. Print.
[4]Yankova, Z. New Guide to Pulmonary Diseases and Tuberculosis. Sofia: Medical University Press. 2012. Print.