Difference Between Constipation and Cramping
Constipation is defined as bowel movements with a frequency of no more than three times a week, with the need for straining, and firm consistency of the fecal mass. Cramp is a sudden short term involuntary spasmodic contraction of a muscle/group of muscles, sometimes with severe pain.
Cramps in the abdomen may occur as a result of constipation. In this case, cramping is due to the difficult passage of hard fecal masses through the end sections of the gastrointestinal tract.

What is Constipation?
Constipation is a relatively common problem, defined as bowel movements with a frequency of no more than three times a week, with the need for straining and a feeling of firm consistency of the fecal mass. Depending on the etiology, it is divided into primary (functional) constipation and secondary constipation. Primary constipation is the most common in clinical practice and is provoked by dietary peculiarities, unhealthy habits, sedentary lifestyle, etc. Secondary constipation is usually associated with underlying metabolic disorders, obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, side effects of medication, etc.
Most often, constipation is a result of a diet with limited fibers and fluids, excessive consumption of coffee, tea, alcohol.
Some medications can impair intestinal motility by different mechanisms. Such medications are iron-containing preparations, drugs with aluminum and calcium salts reducing stomach acidity, calcium channel blockers, chronic abuse of laxatives, psychotropic drugs, antidepressants, opioids.
Systemic diseases leading to constipation are hypothyroidism, conditions leading to hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, certain neurological diseases such as diabetic autonomic neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, trauma or diseases of the brain and spinal cord. Diseases of the connective tissue involving the intestinal wall worsen motility – amyloidosis, scleroderma. Systemic infections, as well as infections or other acute complications in the abdominal cavity (bleeding, perforation of a hollow abdominal organ, pancreatitis, etc.), may also block peristalsis and cause subacute constipation.
Diet and fluid intake are crucial for most patients with constipation. Cellulose-rich foods help with intestinal peristalsis and the proper consistency of fecal mass. Water intake supports the function of all glands with exocrine secretion, including the glands in the intestinal wall. Coffee, some types of tea, and alcohol have a dehydrating effect and excessive consumption can worsen if not lead to constipation. A sedentary lifestyle suppresses metabolism in general and one of its many disadvantages is the change in peristalsis.
The general measures against constipation are a fiber-rich diet, intake of fluids, and physical activity. They do not refer to a moment of discomfort but are rather a healthy lifestyle. Several types of medications are used in the management of chronic constipation – bulking, emollients, lubricants, laxatives, prokinetics. Surgical treatment is indicated in rare cases – when the etiology is associated with bowel obstruction or other acute diseases requiring surgery.

What is Cramping?
A sudden involuntary short term spasmodic contraction of a muscle/group of muscles, sometimes with severe pain, is called a cramp. Cramps are relatively common and may occur both in skeletal and smooth muscles. Abdominal cramps are conditions characterized by muscle spasms in the abdomen accompanied by pain. The reasons may be common to all or specific to women, men, children, and the elderly.
Abdominal cramping may occur due to:
- Digestive system diseases – constipation, diarrhea, gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, chronic ulcerative colitis, intestinal obstruction, stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer, dehydration, Crohn’s disease;
- Diseases of the reproductive system – dysmenorrhea, endometriosis;
- Pregnancy, childbirth, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy;
- Infectious and parasitic diseases – campylobacter infection, dysentery;
- Diseases of the blood, blood-forming organs, and individual disorders involving the immune mechanism – sclerodermia;
- Diseases of the nervous system – peripheral neuropathy;
- Diseases of the endocrine system, eating disorders, and metabolic disorders – hypothyroidism, hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia, hypermagnesemia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, diabetic ketoacidosis;
- Side effects from medications;
- Injuries, poisonings, and some other consequences of the impact of external causes – lead poisoning, heatstroke, allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock;
- Uremia, tetany.
Symptoms accompanying abdominal cramping appear in different combinations, with different intensities. In the first place, these symptoms include severe pain of a constant or periodic nature. The pain can be dull or sharp, with varying intensity. Abdominal cramping may also be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, shortness of breath, reflected pain in the perineum, chest, less neck, and shoulder, sweating, etc.
The treatment depends on the diagnosis and causes of the cramps. In general, treatment includes the use of painkillers to relieve pain, antibacterial and antiemetic drugs, therapeutic diet. In some cases, conservative treatment is insufficient and surgery may be necessary.
Difference Between Constipation and Cramping
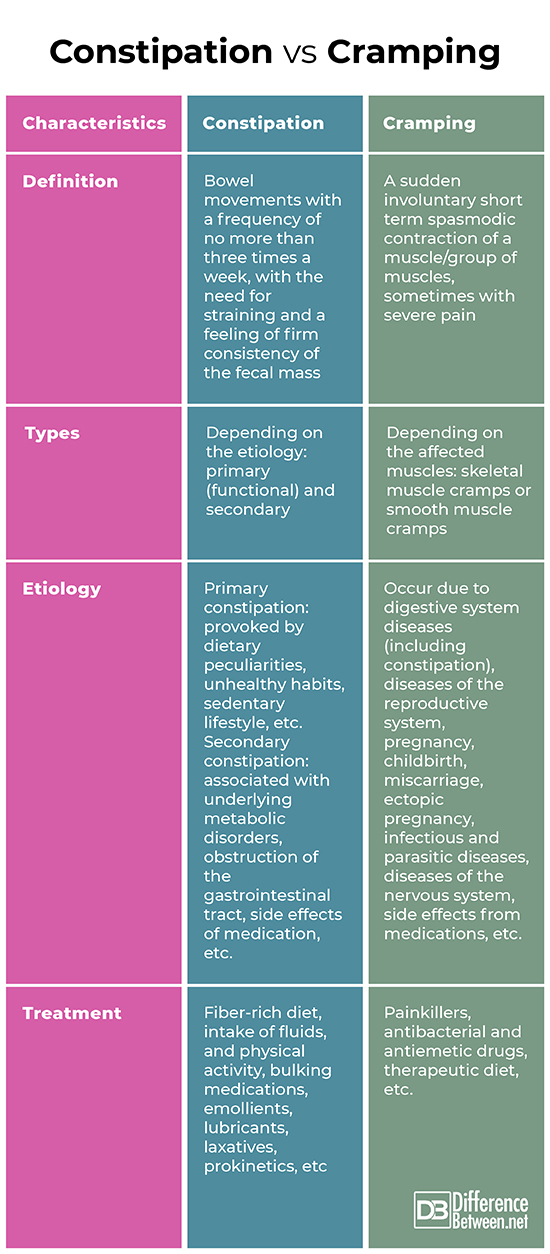
Definition
Constipation: Constipation is bowel movements with a frequency of no more than three times a week, with the need for straining and a feeling of firm consistency of the fecal mass.
Cramping: A sudden involuntary short term spasmodic contraction of a muscle/group of muscles, sometimes with severe pain, is called cramp.
Types
Constipation: Depending on the etiology, constipation is divided into primary (functional) and secondary.
Cramping: Depending on the affected muscles, cramps can be skeletal muscle cramps orsmooth muscle cramps.
Etiology
Constipation: Primary constipation is provoked by dietary peculiarities, unhealthy habits, sedentary lifestyle, etc. Secondary constipation is usually associated with underlying metabolic disorders, obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, side effects of medication, etc.
Cramping: Abdominal cramping may occur due to digestive system diseases (including constipation), diseases of the reproductive system, pregnancy, childbirth, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, infectious and parasitic diseases, diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs, diseases of the nervous system, side effects from medications, etc.
Treatment
Constipation: Depending on the etiology treatment may include a fiber-rich diet, intake of fluids, and physical activity, bulking medications, emollients, lubricants, laxatives, prokinetics. Surgical treatment is indicated in rare cases.
Cramping: Depending on the etiology treatment may include painkillers, antibacterial and antiemetic drugs, therapeutic diet. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
Constipation Vs Cramping
Summary:
- Constipation is bowel movements with a frequency of no more than three times a week, with the need for straining and a feeling of firm consistency of the fecal mass.
- A sudden involuntary short term spasmodic contraction of a muscle/group of muscles, sometimes with severe pain, is called a cramp.
- Cramps in the abdomen may occur as a result of constipation. In this case, cramping is due to the difficult passage of hard fecal masses through the end sections of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Depending on the etiology, constipation is divided into primary (functional) and secondary. Depending on the affected muscles, cramps can be skeletal muscle cramps orsmooth muscle cramps.
- Primary constipation is provoked by dietary peculiarities, unhealthy habits, sedentary lifestyle, etc. Secondary constipation is usually associated with underlying metabolic disorders, obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract, side effects of medication, etc. Abdominal cramping may occur due to digestive system diseases (including constipation), diseases of the reproductive system, pregnancy, childbirth, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, infectious and parasitic diseases, side effects from medications, etc.
- Depending on the etiology, constipation treatment may include a fiber-rich diet, intake of fluids, and physical activity, bulking medications, emollients, lubricants, laxatives, prokinetics. Cramping treatment may include painkillers, antibacterial and antiemetic drugs, therapeutic diet.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Khurana, V. Demystifying Digestive Tract Symptoms: Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea and Constipation in the Language of Gut. 2015. Kindle Edition.
[1]Pirjova, B., N. Nachev. Physiology. A textbook for students in medicine and dentistry. Sofia: Arso. 2000. Print.
[2]Warrell, D., T. Cox, J. Firth. Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2010. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Period_pain_menstrual_cramps_uterus.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://pix4free.org/assets/library/2021-03-25/originals/constipation.jpg
