Difference Between Dyslexia and Dysgraphia
Dyslexia is the learning disorder in which people have a very hard time with reading. Dysgraphia is a learning disorder in which people have a hard time writing properly.
What is Dyslexia?
Definition:
Dyslexia is a learning disorder of language in which individuals have problems learning the rules of the language which can result in problems with reading.
Symptoms:
Patients may have problems in remembering what words mean and they may have delayed development and difficulty in speech ability. They may incorrectly reverse or substitute letters in a word. They also often struggle with understanding and solving word problems in mathematics.
Diagnosis:
The condition is often diagnosed in early childhood once the child starts school and usually the reading and language is evaluated through a series of tests. Children who have difficulty processing sounds are said to have a deficit in phonological processing, which means the child has dyslexia. It is important that the hearing and vision of the child is also tested and other possible causes for the reading difficulties are eliminated.
Causes:
The cause is thought to be related to problems that arose in the brain during development. Parts of the brain that concern language such as Wernicke and Broca areas are thought to be dysfunctional resulting in dyslexia. Problems in other regions of the brain are also believed to be involved in causing the condition. It also appears to be partly genetic since dyslexia does run in families.
Risk factors:
The condition is inherited often, so children born into families where dyslexia is present are more likely to have the condition. Dyslexia is also more frequently diagnosed and present in boys than in girls.
Treatment:
The treatment includes instruction on how words sound, and how sounds join together to form words. The use of additional methods such as audio books may also be helpful for students.
What is Dysgraphia?
Definition:
Dysgraphia is a learning disorder in which individuals have a hard time writing correctly and they often write the wrong word or space letters and words incorrectly. Handwriting is also often ineligible.
Symptoms:
Symptoms include difficulty writing the letters and converting sounds into the correct words when writing. The child will also often hold the pen or pencil in a strange manner that looks awkward. They may have a hard time spacing letters and words out evenly and may mix up printed and cursive writing. The individual may also be very slow when copying letters and words.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is made when a child is evaluated by a psychologist who will give the child various tests to determine how well and easily they can write. Motor skills should also be tested to determine if that is not part of the problem. The problem may also be diagnosed in adults who have suffered a traumatic brain injury.
Causes:
Dysgraphia can be caused by a problem with language. However, the problem may not be caused by a language issue but rather problems with motor skills in some cases. Scientists do not know for certain what the cause of dysgraphia is in children although it seems to co-occur often with other disabilities such as dyslexia, ADHD and autism. Dysgraphia can occur in adults who have suffered a brain trauma which suggests that it could be due to a problem in the development of the child’s brain.
Risk factors:
There is little information available on what would increase the risk of a child developing dysgraphia. It is worth noting though that most children just learning to write will show the condition, but most will develop normal handwriting by grade 3. It does also often co-occur with other learning problems, so having ADHD or dyslexia may increase the risk of dysgraphia but more research is needed on risk factors.
Treatment:
Occupational therapy may be helpful in dysgraphia and children can be taught to hold the pen in a more comfortable position. In a few cases, medication to treat ADHD has helped improve dysgraphia in children who have both conditions. Children may need to be accommodated in school if the condition is very severe and an impediment to learning.
Difference between Dyslexia and Dysgraphia?
-
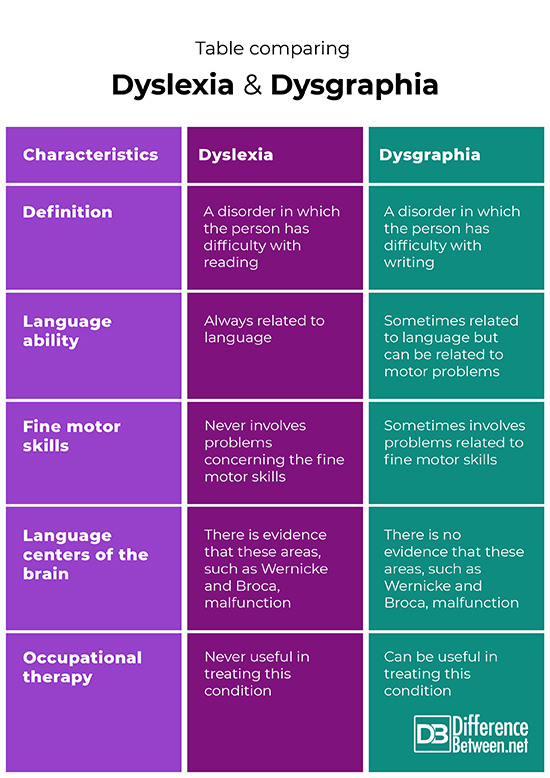
Definition
Dyslexia is the condition in which individuals have difficulty with reading. Dysgraphia is the condition in which individuals have difficulty with writing.
-
Language ability
The disorder dyslexia always involves a problem with language. The disorder dysgraphia can involve a problem with language, but this is not always the case.
-
Fine motor skills
Problems with fine motor skills are not an issue with dyslexia. Problems with fine motor skills can sometimes be a problem with dysgraphia.
-
Language centers of the brain
With dyslexia, there is evidence that the language centers of the brain malfunction. With dysgraphia, there is no evidence that the language centers of the brain malfunction.
-
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy is not useful in treating dyslexia. Occupational therapy can sometimes be useful in treating dysgraphia.
Table comparing Dyslexia and Dysgraphia
Summary of Dyslexia Vs. Dysgraphia
- Dyslexia and dysgraphia are both disorders that can occur that affect students and learning.
- Dyslexia is a problem with reading, while dysgraphia is a problem with writing.
- Dyslexia involves problems in how the language areas of the brain function.
- Scientists are not sure what causes the disorder dysgraphia, but it appears to be related to the brain malfunctioning.
- Both dyslexia and dysgraphia often co-occur with other disabilities such as ADHD.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Molfese, V., et al. "Developmental dyslexia and dysgraphia." Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics. Elsevier Ltd, 2006.
[1]Sulkes, Stephen Brian. “Dyslexia”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/learning-and-developmental-disorders/dyslexia
[2]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/23/Dual_route_model_and_deep_dyslexia_diagram.svg/500px-Dual_route_model_and_deep_dyslexia_diagram.svg.png
[3]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Dysgraphia.jpg