Difference Between Availability Heuristic and Representative Heuristic
Availability heuristic and representative heuristic are both mental shortcuts that are important but may also lead to inaccurate judgements. In availability heuristics, a person bases their decision on how well they can recall how frequently something occurs. In representative heuristics, a person makes decisions based on mental models, or stereotypes, that already exist. The following discussions further delve into their differences.

What is Availability Heuristic?
The availability heuristic describes our propensity to base future judgments on knowledge that comes to mind fast and easily (The Decision Lab, 2022). It is a mental shortcut that enables people to make quick judgments that are occasionally incorrect (Cherry, 2019). This is the reason why there were many times when we assumed that what recently occurred may likely happen again.
One example is how many people perceive plane accidents. We sometimes hear of terrible collisions or explosions that claim many lives. For instance, a passenger was murdered by an engine explosion on a US airliner called Southwest Airlines in 2019. Following the event, the airline experienced a dramatic drop in ticket sales, suffering a loss of between $50 million and $100 million in revenue. We can see here that the likelihood of a comparable incidence was greatly overestimated by consumers (Boyce, 2022).
When making decisions and acting on information from the outside world, heuristics are crucial and can be useful tools. However, it is vital to keep in mind that such mental shortcuts might occasionally result in inaccurate judgements. Just because something looms large in our memory does not necessarily suggest that it is more prevalent. Hence, it can be useful to rely on a variety of tools and decision-making technics such as considering statistical results and pertinent studies, asking for experts’ opinions, and checking long-term patterns.

What is Representative Heuristic?
The representative heuristic occurs when our estimates regarding the likelihood of an event is influenced by a prototype that is already in our minds. This prototype represents what we believe to be the most pertinent or typical illustration of a specific event or thing. The issue with this is that we frequently overestimate similarities (Cherry, 2021).
For instance, a recruiting manager assumed that an applicant wearing eyeglasses came for the accounting post. It was supposed that the job applicant was mathematically inclined due to the eyeglasses. Another example is when someone who frequents the gym and runs every morning is perceived to be a bodyguard rather than a bank teller or a salesperson (Kamiya, 2022).
We frequently rely on representativeness due to limited cognitive resources. An adult is estimated to make more than 35, 000 decisions every day and the brain is designed to do it as efficiently as possible. Because of this, we frequently rely on rapid conclusions about the outside environment. However, the representativeness heuristic can lead to stereotypes and poor choices (Cherry, 2021).
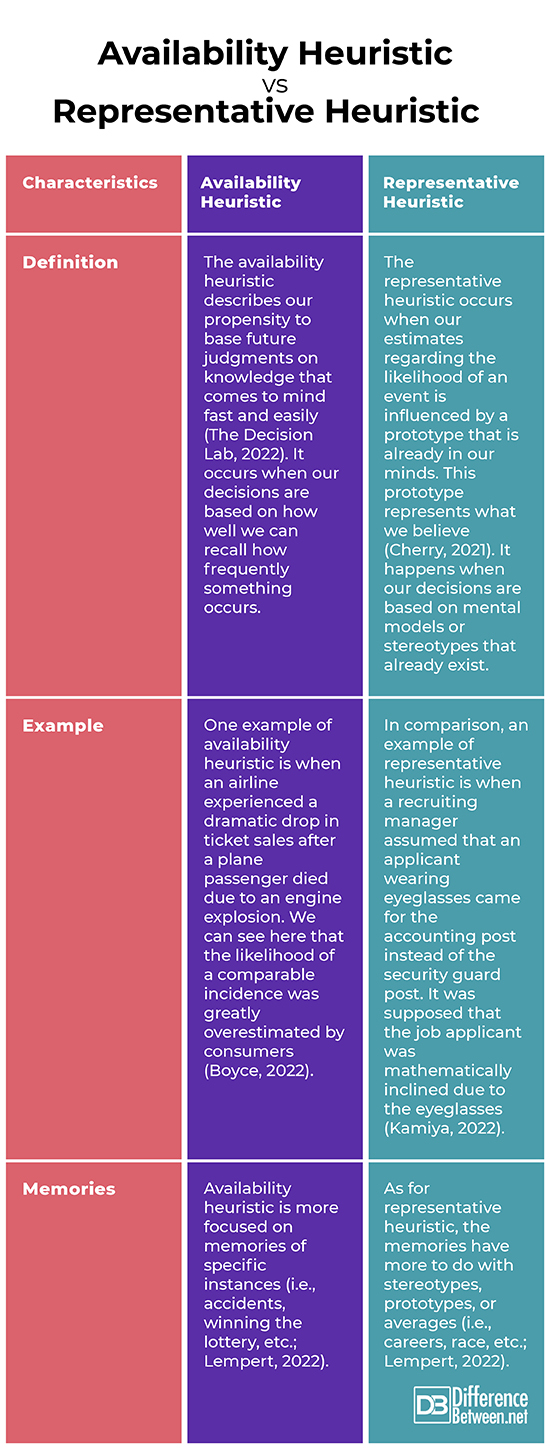
Difference between Availability and Representative Heuristic
Definition
The availability heuristic describes our propensity to base future judgments on knowledge that comes to mind fast and easily (The Decision Lab, 2022). It occurs when our decisions are based on how well we can recall how frequently something occurs. On the other hand, the representative heuristic occurs when our estimates regarding the likelihood of an event is influenced by a prototype that is already in our minds. This prototype represents what we believe to be the most pertinent or typical illustration of a specific event or thing (Cherry, 2021). It happens when our decisions are based on mental models or stereotypes that already exist.
Example
One example of availability heuristic is when an airline experienced a dramatic drop in ticket sales after a plane passenger died due to an engine explosion. We can see here that the likelihood of a comparable incidence was greatly overestimated by consumers (Boyce, 2022). In comparison, an example of representative heuristic is when a recruiting manager assumed that an applicant wearing eyeglasses came for the accounting post instead of the security guard post. It was supposed that the job applicant was mathematically inclined due to the eyeglasses (Kamiya, 2022).
Memories
Availability heuristic is more focused on memories of specific instances (i.e., accidents, winning the lottery, etc.). As for representative heuristic, the memories have more to do with stereotypes, prototypes, or averages (i.e., careers, race, etc.; Lempert, 2022).
Availability Heuristic vs Representative Heuristic
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is an example of representative heuristic?
An example of representative heuristic is when a recruiting manager assumed that an applicant wearing eyeglasses came for the accounting post instead of the security guard post. It was supposed that the job applicant was mathematically inclined due to the eyeglasses (Kamiya, 2022).
What are the two types of heuristics?
There are different kinds of heuristics; the two main types are representativeness and availability (Lempert, 2022).
What is the representative heuristic in psychology?
The representative heuristic occurs when our estimates regarding the likelihood of an event is influenced by a prototype that is already in our minds. This prototype represents what we believe to be the most pertinent or typical illustration of a specific event or thing (Cherry, 2021).
What is availability heuristic?
The availability heuristic describes our propensity to base future judgments on knowledge that comes to mind fast and easily (The Decision Lab, 2022).
What is the availability heuristic? Give an original example.
It is a mental shortcut that enables people to make quick judgments that are occasionally incorrect (Cherry, 2019). This is the reason why there were many times when we assumed that what recently occurred may likely happen again. For instance, when asked about the most common cause of death, it is probable that some people will say, respiratory disease (or COVID-19) due to the pandemic. However, the World Health Organization states that the most common cause of death is coronary artery disease (Death meters, 2022).
Why is representativeness heuristic?
The representative heuristic occurs when our estimates regarding the likelihood of an event is influenced by a prototype that is already in our minds. This prototype represents what we believe (Cherry, 2021).
Summary:
- In availability heuristics, a person bases their decision on how well they can recall how frequently something occurs. In representative heuristics, a person makes decisions based on mental models, or stereotypes, that already exist.
- One example of availability heuristic is when an airline experienced a dramatic drop in ticket sales after a plane passenger died due to an engine explosion. In comparison, an example of representative heuristic is when a recruiting manager assumed that an applicant wearing eyeglasses came for the accounting post instead of the security guard post.
- Availability heuristic is more focused on memories of specific instances while representative heuristic has more to do with memories on prototypes or averages.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Boyce, P. (2022). Availability heuristic definition. Boyce Wire. https://boycewire.com/availability-heuristic-definition-and-examples/
[1]Cherry, K. (2021). What is the representativeness heuristic? Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/representativeness-heuristic-2795805#:~:text=how%20it%20works.-,What%20Is%20the%20Representativeness%20Heuristic%3F,a%20particular%20event%20or%20object.
[2]Kamiya, A. (2022). Representative heuristics: Examples, advantages, and disadvantages. Study.com. https://study.com/learn/lesson/representativeness-heuristic-bias-examples.html#:~:text=Representativeness%20heuristics%20are%20biased%20judgments,the%20stereotype%20of%20a%20lawyer.
[3]Lempert, K. (2022). What are heuristics? Cambridge Coaching. https://blog.cambridgecoaching.com/the-psychology-tutor-what-are-heuristics
[4]The Decision Lab. (2022). The availability heuristic. Bias. https://thedecisionlab.com/biases/availability-heuristic
[5]Valenzuela, A. (2021). What is the availability heuristic? https://study.com/learn/lesson/availability-heuristic-example.html
