Difference Between Heartburn and Angina
What is Heartburn and Angina?
Both medical conditions are types of chest pain. Heartburn is however different from Angina. The former is a burning sensation in the chest and the latter is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Signs and symptoms of heart attack and heartburn which are similar include nausea, upset stomach and chest pain.
What is Heartburn?
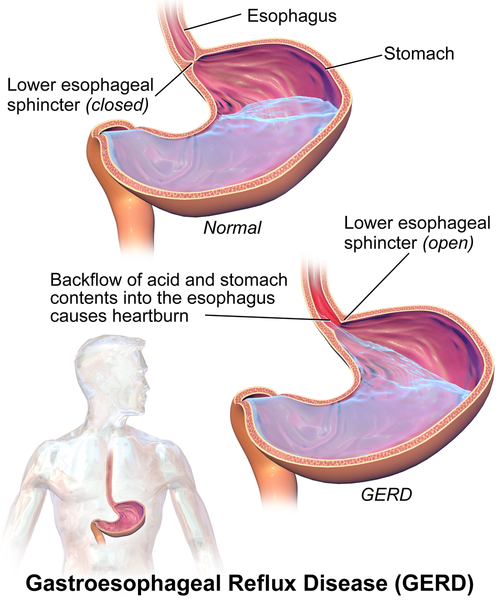
Heartburn is a symptom, and not a medical condition or disease. Heartburn is a chest pain which is actually a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition is triggered by acid refluxing back into the oesophagus. Potential risk factors include those which elevate the formation of acid in the stomach, as well as structure related issues that result in acid reflux into the oesophagus.
What is Angina?
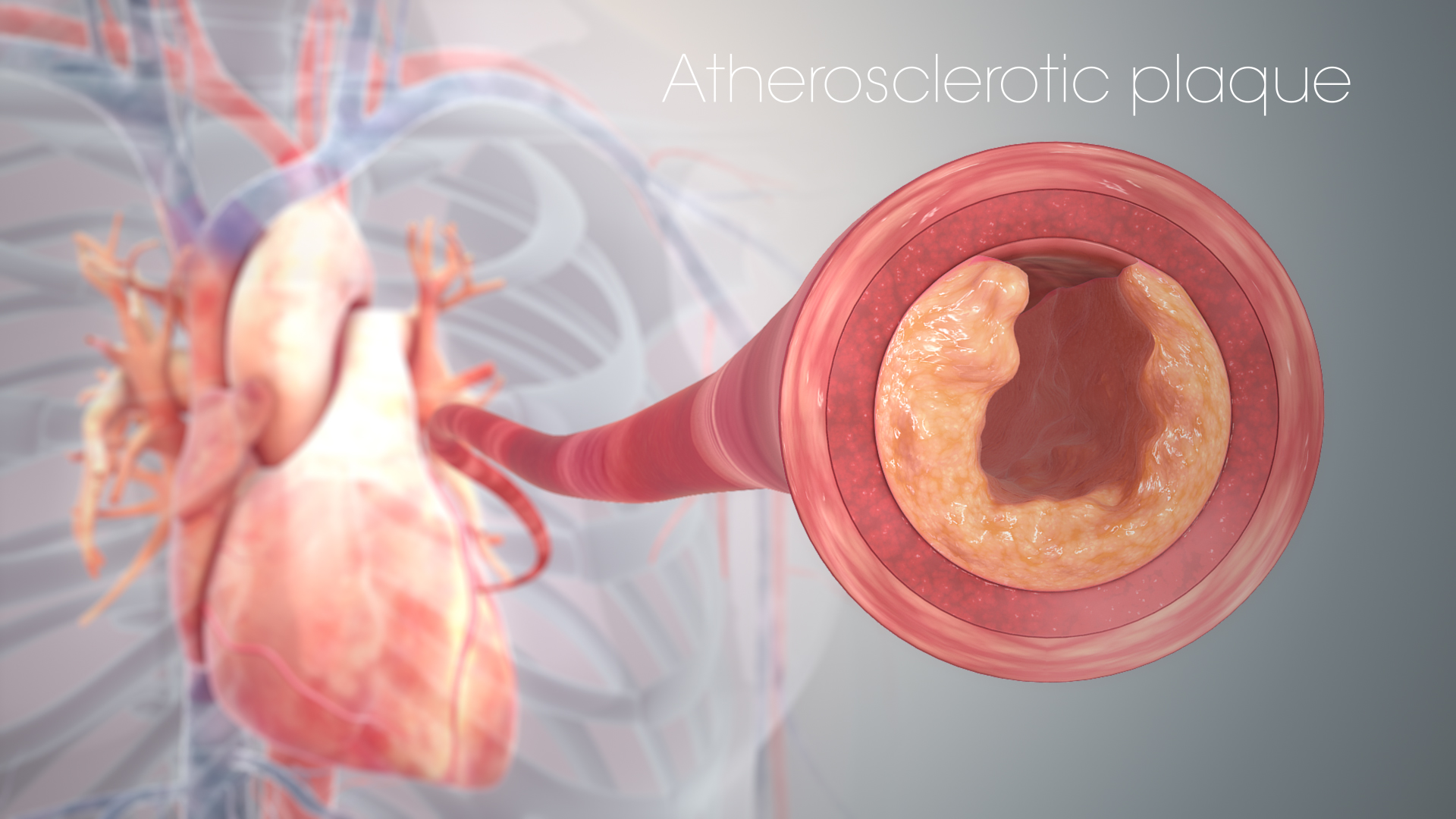
Angina is a chest pain caused due to coronary heart disease. The symptoms include squeezing, heaviness, acute chest pain and tightness. It is a sudden condition. When the heart muscle is not getting proper and adequate oxygen supply, it results in a condition called ischemia. This condition causes lower level of blood flow reaching the heart muscle thereby causing angina.
Difference between Heartburn and Angina
-
Definition
Heartburn
Heartburn is a medical condition caused by the acid reflux. It is actually a symptom of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), In this condition, the stomach contents are pushed back up into the oesophagus, causing a burning sensation and pain in the upper belly or lower chest.
Angina
Angina is a kind of chest pain triggered by the narrowing of the arteries by heart disease. It happens when heart doesn’t get enough blood supply. When heart arteries become narrow, angina occurs accompanied by acute chest pain.
Depending on the severity, angina can be treated by eating healthy, lifestyle changes, proper and right medication, surgery and even angioplasty.
-
Symptoms
Heartburn
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Burning sensation or feeling – behind the breastbone or in the middle of the chest
- Sore throat and coughing
Angina
- Pain and discomfort in the chest
- Pain can also travel to jaw, throat, shoulders, neck, arms, back and even teeth.
- Inability to exercise
- Fatigue, sweating and light headedness
- Squeezing and tightening feeling
- Cramping
- Shortness of breath
-
Causes
Heartburn
- Irritants like caffeine, aspirin, alcohol, carbonated beverages, acidic juices like orange and grapefruit, chocolate and drugs like Nuprin and Advil.
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Consumption of high-fat foods that affect the performance of the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES), making it to relax from the stomach and allowing acid to reflux inside the oesophagus.
- Pregnancy can result in elevated pressure on the abdominal cavity and affect LES function and activate it to reflux.
- Critical medical conditions of the oesophagus like scleroderma and sarcoidosis.
- Individuals having a hiatal hernia, in which the stomach bulges up into the chest by means of an opening in the diaphragm
Angina
- The most important cause is reduced blood flow to the heart muscles. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the reason for this reduced blood flow
- An obstruction in the primary artery of the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Enlarged heart (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy)
- Inflammation of the vesicle enveloping the heart (pericarditis)
- Contracting of the passage in the main part of the heart (aortic stenosis)
- Rupture in the membrane of the biggest artery in the body (aorta) (aortic dissection)
-
Diagnosis
Heartburn
- Oesophageal Manometry
- X-Ray
- Endoscopy
- Ambulatory acid probe tests
- Oesophageal motility testing
Angina
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Stress test without imaging
- Chest X-ray
- Chest CT
- Blood tests
- Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging/angiography
- Catheter angiography
- Echocardiogram
-
Treatment and Medication
Heartburn
- Avoid spicy, greasy and fatty foods, citrus fruits, peppermint, alcohol, coffee, chocolate and tomatoes
- Avoid large meals. Eat frequent and smaller meals
- Avoid high-impact exercises
- Do not wear tight clothes that put pressure on the stomach triggering heartburn.
- Quit smoking as it increases acids in your stomach
- Use two to three pillows under your head or increase the head of the bed to allow gravity to make acid stay in your stomach and prevent acid reflux.
- Avoid aspirin and ibuprofen
- Certain medications for heartburn include Antacids, rabeprazole (Aciphex), cimetidine (Tagamet), ranitidine (Zantac), and famotidine (Pepcid), pantoprazole (Protonix), omeprazole (Prilosec, Rapinex), and esomeprazole (Nexium).
Angina
- Reduce and manage stress
- Keep yourself warm
- Eat a healthy diet (whole grains, fruits and vegetables) and adopt a safe exercise plan (Heart exercises)
- Do not consume alcohol and manage blood sugar levels
- Try to maintain weight. Avoid saturated fats that encourage weight gain
- Since angina is caused by exertion, it is helpful to pace yourself and take intermittent breaks
- Certain medications include Nitrates, Beta-blockers, Statins, clot-preventing drugs- such as clopidogrel (Plavix), prasugrel (Effient) and ticagrelor (Brilinta), Calcium Channel Blockers, Ranolazine (Ranexa), Blood pressure lowering medications like – angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Medical procedures to treat Angina include:
- Angioplasty and stenting
- Coronary artery bypass surgery
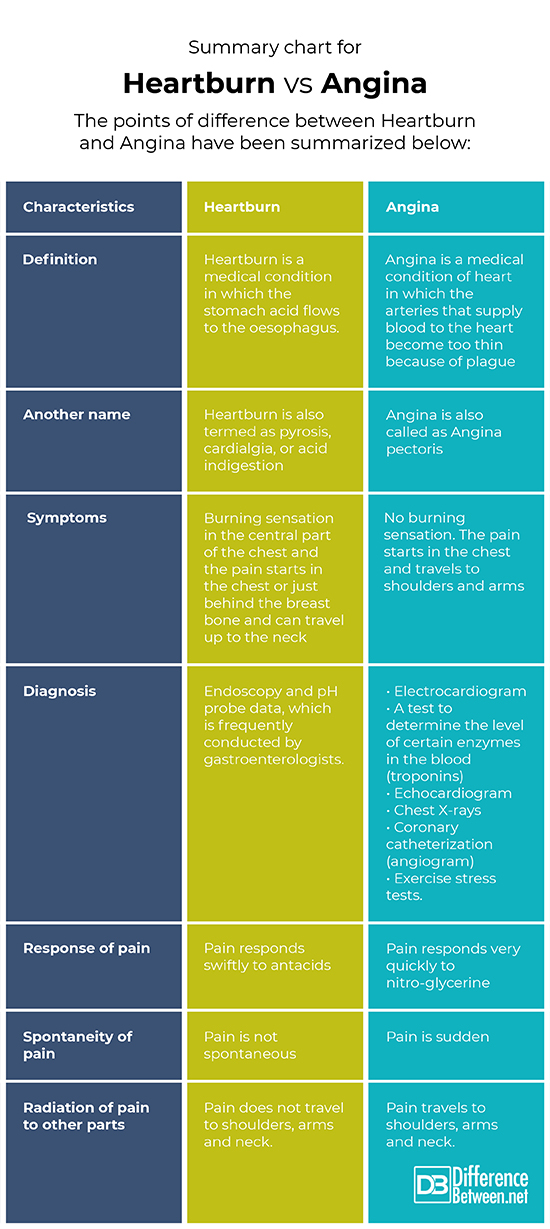
Summary chart for Heartburn Vs. Angina
The points of difference between Heartburn and Angina have been summarized below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microvascular_angina#/media/File:Clogged_Heart_Artery.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f5/GERD.png/500px-GERD.png
[2]Bösner, S., Haasenritter, J., Becker, A., Hani, M. A., Keller, H., Sönnichsen, A. C., ... & Donner-Banzhoff, N. (2009). Heartburn or angina? Differentiating gastrointestinal disease in primary care patients presenting with chest pain: a cross sectional diagnostic study. International archives of medicine, 2(1), 40.
[3]Kato, H., Ishii, T., Akimoto, T., Urita, Y., & Sugimoto, M. (2009). Prevalence of linked angina and gastroesophageal reflux disease in general practice. World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG, 15(14), 1764.