Difference Between Hordeolum and Chalazion
The primary difference between a stye and a chalazion lies in their root cause. While a chalazion is often caused by a blocked oil gland without an infection, a stye usually occurs due to a bacterial infection in an oil gland. Although both conditions can lead to swollen and uncomfortable eyelids, the treatment approach varies depending on the underlying cause. If you suspect you have either of these conditions, it is advisable to seek medical attention as untreated cases may occasionally have repercussions.
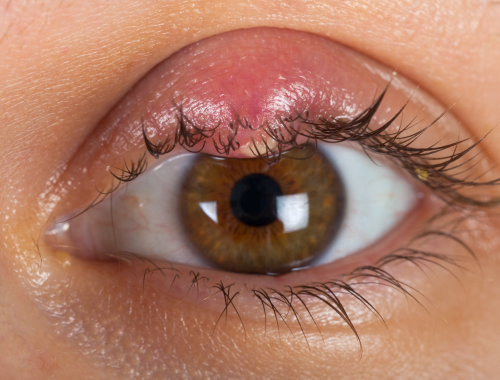
Hordeolum
Hordeolum or stye a painful, red mass surrounding the edge of the eyelid that looks like a boil or pimple. A stye may form if the microscopic glands lining the eyelid become clogged.
Pus fills sties often. From time to time, a stye may appear on the inside of the eyelid.
In a few days, a stye will typically begin to disappear on its own. Applying a warm washcloth to the eyelid could potentially ease pain and discomfort.
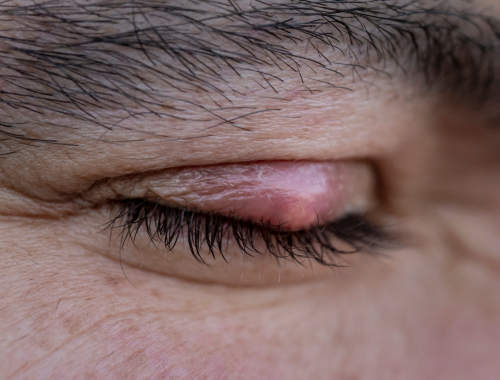
Chalazion
It is a painful, slowly expanding lump in the eyelid’s tear gland. Adults with blepharitis or rosacea who are between the ages of thirty and fifty are more likely to develop chalazion.
At first, a chalazion may feel like a tiny, harmless bead inside the eyelid. It might become larger, red, and rubbery over the course of a few days, but it won’t hurt.
It might not be necessary to treat all challenges. Larger ones might benefit from hot compresses. A physician may be required to remove a persistent chalazion.
Similarity
Both conditions affect the eyelid.
Difference between hordeolum and chalazion
Definition
Hordeolum
Hordeolums, also referred to as “styes,” are infections of the oil glands that border the eyelid. A bacterial staph infection is typically the source of a hordeolum, which causes discomfort, swelling, and redness. A hordeolum appears as a pimple or lump at the edge of the eyelid that is packed with pus.
Chalazion
A red lump on your eyelid is called a chalazion. It is occasionally referred to as a meibomian cyst or an eyelid cyst. It develops gradually as a result of a clogged meibomian oil gland. The chalazion may sting at first, but it normally goes away within a short while.
Causes
Hordeolum
Hordeolums, also called styes, are typically caused by bacterial infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The inflamed sebaceous glands in the eyelid produce oil, causing a bacterial infection.
Chalazion
- Rosacea acne.
- Chronic Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids, usually due to an overabundance of germs)
- Seborrhea
- The tubercle
- Viral ailment
- Chalazions seldom could be a sign of skin cancer or an infection.
Treatment
Hordeolum
- Warm compresses applied many times per day can help with drainage and symptom relief in the afflicted area.
- If bacteria are to blame for the infection, a doctor may advise using antibiotic drops or ointment.
- A healthcare professional might need to perform a stye drainage surgery if conservative treatments are ineffective in treating the problem.
Chalazion
- Applying warm compresses can mimic the symptoms of a stye by assisting in the softening of the blocked oil and promoting fluid evacuation.
- A medical professional may inject steroids into the chalazion to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- An ophthalmologist may undertake a minor surgical procedure to remove the chalazion if other therapies are unsuccessful.
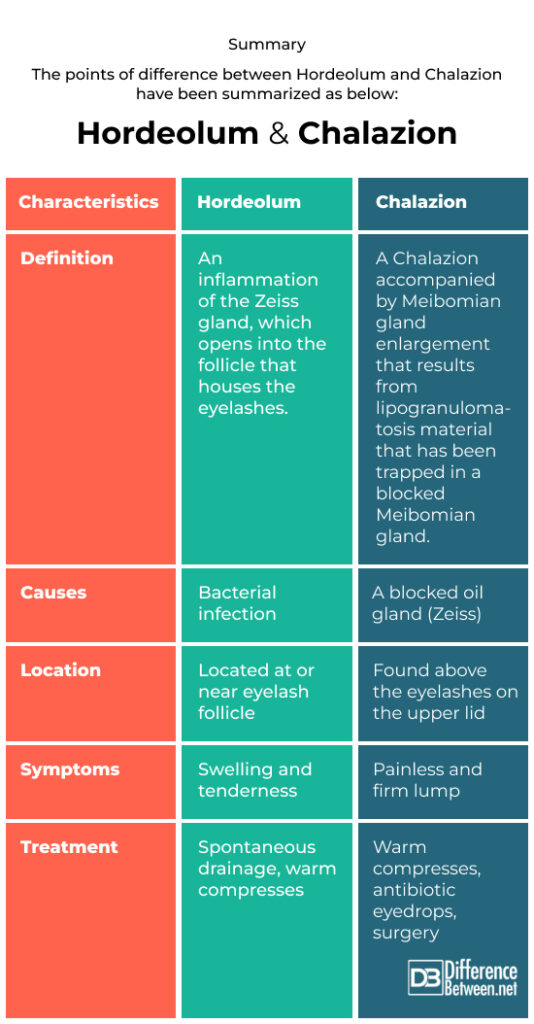
Summary
The points of difference between Hordeolum and Chalazion have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
What is the difference between chalazion and blepharitis?
Blepharitis is an inflammatory disorder of the eyelid margins that can cause a variety of symptoms and is often associated with issues like meibomian gland malfunction (a condition where the meibomian glands are inflamed or bacterial infections. Chalazion, on the other hand, is a localised, painless lump on the eyelid caused by a blocked meibomian gland.
How can you tell the difference between a chalazion and a hordeolum?
A chalazion is a non-contagious bump that forms when a meibomian gland becomes obstructed. It is larger than a stye and typically found on the upper eyelid. It causes mild discomfort and may impact vision if it enlarges.
A hordeolum, or stye, is a distressing bump that forms at the base of an eyelash or within an oil gland. It is triggered by a bacterial infection and can be found on both the upper and lower eyelids. It emerges swiftly and is often accompanied by swelling and sensitivity. It may cause itchiness, a sandy sensation, and increased tear production.
One distinguishing characteristic between a chalazion and a hordeolum is the presence of pus. Styes often have a small yellowish or whitish head, while chalazia do not produce pus and are characterized by a solid, painless lump.
How can you tell the difference between a stye and blepharitis?
When greasy flakes and germs are present near the base of your eyelashes, it is known as blepharitis. Your eyelids burn, are puffy, or have a red appearance. A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a tiny, painful, red lump that develops beneath the eyelid or at the base of your lashes. Bacterial infections cause the majority of styes.
Can blepharitis cause hordeolum?
It is true that blepharitis does not directly cause a hordeolum (stye), but it can cause conditions that can increase the likelihood of one developing as a result. Proper eyelid hygiene and the management of blepharitis can help reduce the likelihood of a stye developing.
What are the 4 stages of blepharitis?
Mild Blepharitis – occasional itching or irritation of the eyes.
Moderate Blepharitis – visible crusting or scales.
Severe Blepharitis – the skin around the eyes gets swollen, corneal complications,
Chronic or Recurrent Blepharitis – intermittent flare-ups of symptoms,
What are the three types of blepharitis?
Three types of blepharitis include anterior, posterior, and mixed blepharitis.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Alsoudi, A. F., Ton, L., Ashraf, D. C., Idowu, O. O., Kong, A. W., Wang, L., ... & Vagefi, M. R. (2022). Efficacy of care and antibiotic use for chalazia and hordeola. Eye & Contact Lens, 48(4), 162-168.
[1]Lindsley, K., Nichols, J. J., & Dickersin, K. (2010). Interventions for acute internal hordeolum. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (9).
[2]Rupani, S. R. (2023). Hordeolum and chalazion. JAAPA, 36(6), 43-44.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADOw7qKQ4o-hordeolum-on-upper-eyelid-viral-infection/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEbAFBOyEw-close-up-stye-hordeolum-chalazion-macro-detail-of-an-eye-infection-/
