Difference Between Ringworm and Athlete’s Foot
Fungal skin infections are quite common, but there have been numerous significant developments in the diagnosis and management of fungal infections. Among the many species of fungi, fewer than 500 have been associated with human disease, and more than a hundred are capable of affecting otherwise normal individuals. Fungal infections can be divided into many types, but the most common of fungal infections is ringworm and athlete’s foot.
What is a Ringworm?
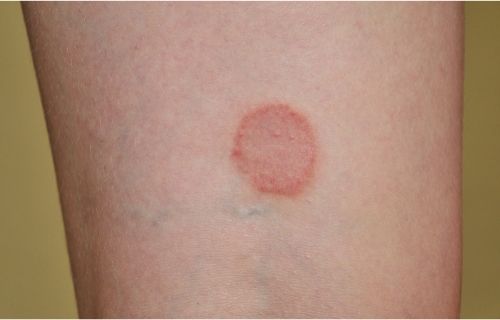
Ringworm is a type of skin and nail infection caused by fungus. It is a common skin disease caused by skin-to-skin contact or by touching an infected animal or object. It is common in children but adults are equally vulnerable to this type of infection. Ringworm is a red, itchy circular ring-shaped rash that is also called “dermatophytosis” or “tinea.” It is very common and the risk increases in hot, humid weather. It typically looks like a circular rash with a raised, scaly border that snakes its way around the edge like a worm, hence the name ringworm.
Dermatophytosis or ringworm is caused by a closely related group of fungi known as dermatophytes which have the ability to utilize keratin as a nutrient source. Additional symptoms of ringworm include round to oval scaly patches on the skin that can be very itchy. The patches tend to be red or pin on light colored skin, while it looks brown or gray on skin of color. The patches can grow slowly and increase in size, spreading to other areas of the body.
What is Athlete’s Foot?
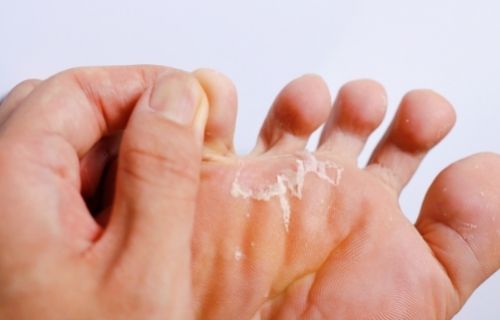
Athlete’s foot is the most common type of fungal skin infection. It is an itchy, burning and sometimes gooey fungal infection that commonly occurs among athletes, but athletes are not the only ones affected. It is a contagious skin infection that most often appears as a rash between the toes, hence the name. It can also cause scaly, flaky skin on the bottom of the foot or blisters anywhere on the foot. It is also known as tinea pedis – tenia means a fungal skin infection and pedis means foot.
According to traditional Chinese medicine, the condition was thought to be an illness of digestion. In the West, however, the doctors believed athlete’s foot was caused by insect bites. It is a common type of ringworm, but each causes different symptoms. It is the most common dermatophyte infection in adults and the most common dermatophyte infection in children is ringworm. Blisters usually first appear on the arch of the foot, but they can show up anywhere I the foot. Scratching the blisters easily bursts them.
Difference between Ringworm and Athlete’s Foot
Condition
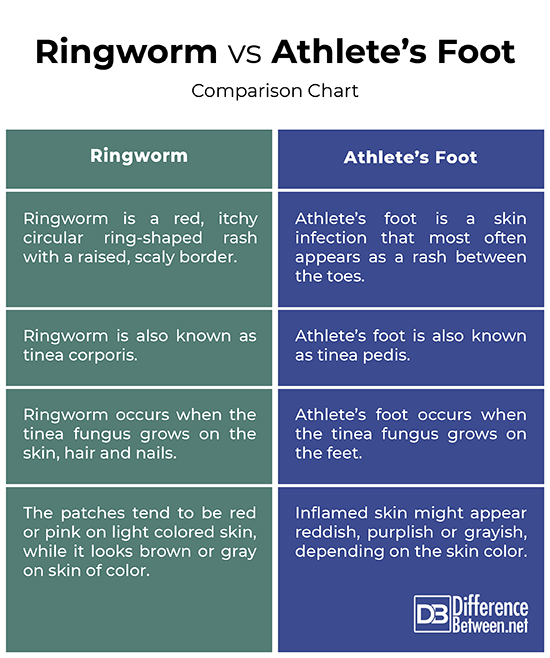
– Ringworm is a type of skin and nail infection caused by fungus and is also known as tinea pedis wherein tinea means a fungal skin infection and pedis means foot. Athlete’s foot is the most common form of ringworm that commonly occurs among athletes, but athletes are not the only ones affected. They are both tinea infections; when it grows on the feet, it is called athlete’s foot. But, if it grows anywhere on the body, it is called ringworm.
Cause
– Both are fungal skin infections known collectively as tinea. Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common ringworm infection of the feet which is caused by the same type of fungi (dermatophytes) that causes ringworm. Both are caused by a closely related group of fungi known as dermatophytes which have the ability to utilize keratin as a nutrient source. Ringworm occurs when the tinea fungus lives on the skin, hair and nails, while athlete’s foot occurs when the tinea fungus grows on the feet.
Symptoms
– The common symptoms of both the skin infections are basically the same, which include itchy skin, rashes, red cracked skin, etc. However, the ringworm patches tend to be red or pink on light colored skin, while it looks brown or gray on skin of color. The patches are typically ring-shaped, itchy rashes. Athlete’s foot can cause scaly, flaky skin on the bottom of the foot or blisters anywhere on the foot; cracked skin between the toes; burning or stinging sensation; and itchiness.
Ringworm vs. Athlete’s Foot: Comparison Chart
Summary
Tinea pedis, commonly known as athlete’s foot is a fungal skin infection of the foot that may involve the toe webs and most often appears as a rash between the toes, and depending on the skin color, they may appear reddish, purplish, or grayish. Hot, moist climates are particularly conducive to this skin condition. Ringworm is a common fungal infection caused skin-to-skin contact or by touching an infected animal or object, and is also known as tinea corporis. Both are tinea infections and are contagious.
Is Athlete’s foot a type of ringworm?
Yes, athlete’s foot is the most common ringworm infection; particularly a fungal skin infection of the foot often appears as a rash between the toes.
Is athlete’s foot as contagious as ringworm?
Both are caused by the same organism and both are contagious. However, ringworm is highly contagious and spreads easily from one person to another through direct or indirect contact.
Will athlete’s foot spray kill ringworm?
Most ringworm infections including athlete’s foot can be treated using over-the-counter antifungal creams, gels or sprays. However, a foot spray for athlete’s foot might not be affective against ringworm infections on other part of the body.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Suhonen, Raimo E., et al. Fungal Infections of the Skin and Nails. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2020. Print
[1]Richardson, Malcolm and David W. Warnock. Fungal Infection: Diagnosis and Management. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Print
[2]Kamberg, Mary-Lane. The Gross Science of Athlete’s Foot. New York, United States: The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc., 2019. Print
