Difference Between Multiplexer and Decoder
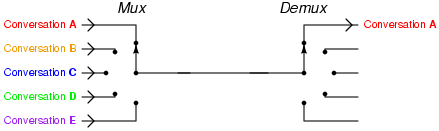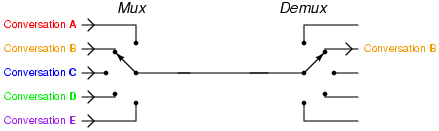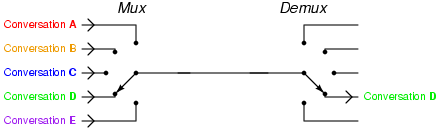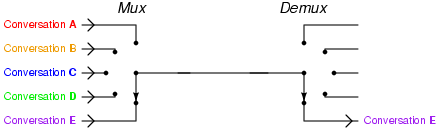
Telephony multiplexer system
The advancement of signal systems has expanded tremendously in various communication systems today. The basic signal transmissions can be attributed to key contributions of multiplexer and decoder devices. Both multiplexer and decoder work together to produce signal and data output for various communication and operations through several channels. Though multiplexers and decoders perform almost the same function, they differ with one another for several reasons.
By concept, multiplexers (MUS) are devices referred to “switch” which transmit a number of inputs to another destination through a single line while decoders (DeMUS) are devices which interprets multiple inputs and multiple outputs. Multiplexers are associated with “wires” and a series of “circuits which can be combined to another batch of circuits to produce a higher degree of output. On a different context, multiplexers produce unlimited raw information as in the case of document files. Every alphabet written on a document uses “ANCII codes, represented by logic values, then the decoder converts them to an output. Represented by letters or file sizes.
Decoder
Another example of the multiplexer is switch circuits found on basic electrical system. Lighting fixtures can be represented as inputs which runs over a single line and these circuit lines are connected to another switch located on a Panelboard. The main function of multiplexer basically is to connect information from one point to another point through wires while on the other hand, decoders converts the outputs for several operations such as data collection and calculations.
Multiplexer and decoder devices also differ on carrying coded data, information based from the input signals and conversion properties made from the receiving end. Multiplexers are equated with 2-to-1, 4-to-1, 8-to-1 or combination of inputs, then decoder which is equated with 2:4, 3:8 and 4:16 outputs, will interpret based from the operations or processes applied.Multiplexers also generate speed of data transmission over a period of time and decoders distribute them on various network systems.
Multiplexing process or combination of circuits is used on our railway systems, radio, television transmissions, air and naval navigation whether by wires or cable and signal equipment. However, multiplexers and decoders can work simultaneously to allow sharing of data transmissions by a number of signals in the cases of telecommunication and computer systems.
The discussion on this article can be summarized as follows:
1. Multiplexers transmit data while decoders interprets coded data.
2. Multiplexer is a device which consists of multiple input channels thru single line while decoders consist of multiple inputs passing thru multiple output.
3. Multiplexer converts inputs from unary codes (initial) to binary codes while decoder converts binary codes to inputs.
- Difference Between an Atomic Bomb and a Hydrogen Bomb - May 23, 2015
- Difference Between Multiplexer and Decoder - May 21, 2015
- Difference Between Chicken pox and Small pox - June 3, 2014
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]http://www.cs.umd.edu/class/sum2003/cmsc311/Notes/Comb/encoder.html
[1]https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/.../07-MuxLogic.pdf
[2]http://www.uspto.gov/web/patents/classification/uspc370/defs370.htm
[3]http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e0/Telephony_multiplexer_system.gif

There are some grammar and terminology problems that create confusion in this article.
Is it a “MUX” or “MUS”? “DEMUX” or “DEMUS”?
What are “ANCII” codes, a mixture of ANSI and ASCII?
The diagram of the decoder could use a little explaining.