Difference Between AI and Cybernetics
Until a few years back, the very idea that humans might be able to construct something far more complex and smarter than themselves could only be regarded as a dream or a fantasy. For many years, we looked to a future where robots are outsmarting humans and cyborgs are commonplace. There are so many movies which are just the perfect examples of this vision, movies such as The Matrix, RoboCop, The Terminator, I, Robot, Chappie, Real Steel, and so much more. However, this changed when scientists and mathematicians began to think in innovative ways to make machines more smart and intelligent. Science has successfully combined human intelligence with machines in a relatively healthy merger.
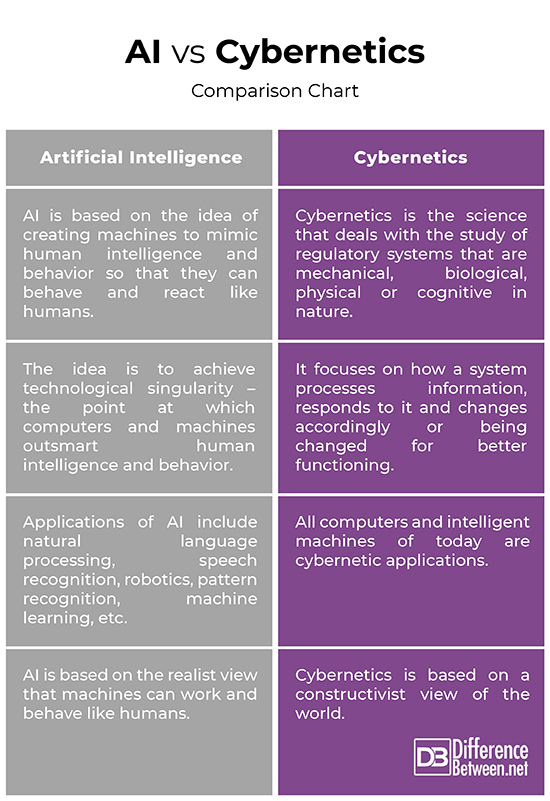
AI and Cybernetics are the perfect examples of this human-machine merger. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cybernetics are both based on the same principle, which is binary logic. Both the terms are often used interchangeably and thus confused one with the other. Both are slightly different; AI is based on the realist view that machines can work and behave like humans whereas Cybernetics is based on a constructivist view of the world. Studies suggest that the differences between AI and Cybernetics are not merely semantic but rather conceptual.
All about Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence, commonly referred to simply as AI, is a conceptual aspect of machine intelligence – that is intelligence demonstrated by machines. AI is an area of computer science that is based on the idea of computer programs that model aspects of intelligent behavior. It is based on the idea of creating machines to mimic human intelligence and behavior so that they could react like humans. Since the first computers were developed, AI has been an active scientific discipline and many developments in modern computing trace their roots to AI. Although the early phase of AI was concerned with developing programs for proving theorems and playing games, the modern AI encompasses several tools and techniques for reasoning, leaning, planning, language and pattern recognition, and more.
What is Cybernetics?
Cybernetics is the science of human-machine interaction that employs the principles feedback, control and communication. Cybernetics is a recently developed science that deals with the study of regulatory systems that are mechanical, biological, physical or cognitive in nature. It studies the concepts of control and communication in living organisms, machines and organizations including self-organization. Cybernetics is an interdisciplinary science that focuses on how a system processes information, responds to it and changes or being changed for better functioning. It is a general theory of information processing, feedback control and decision making. The modern interpretation of the term ‘Cybernetics’ was pioneered by Norbert Wiener in 1948 as “the scientific study of control and communication in the animal and the machine.”
Difference between AI and Cybernetics
Concept
– AI is an area of computer science that is based on the concept of computer programs that model aspects of intelligent behavior. It is based on the idea of creating machines to mimic human intelligence and behavior so that they could react like humans. Generally, AI is the conceptual aspect of machine intelligence. Cybernetics, on the other hand, is a recently developed science that deals with the study of regulatory systems that are mechanical, biological, physical or cognitive in nature. It is a general theory of information processing, feedback control and decision making.
Purpose
– The research goal of AI is to achieve technological singularity – the point at which computers and machines completely mimic human intelligence and behavior. The idea is to allow technology to outsmart human intelligence. The science of AI itself aims to clarify human intelligence. AI technology resembles an art where the contents are acquired through accumulation of various experiences. Cybernetics, on the other hand, is an interdisciplinary approach for exploring regulatory systems that are mechanical, biological, physical or cognitive in nature. It focuses on how a system processes information, responds to it and changes accordingly or being changed for better functioning.
Applications
– AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by computer systems, processes such as reasoning, learning, pattern recognition, knowledge reasoning, machine learning, etc. Machine learning is one of the more conventional areas of computation intelligence that refers to the development of automated system capable of processing large amounts of data for data mining. Some of the other applications of AI include natural language processing, speech recognition, robotics, and more. Cybernetics, on the other hand, provides coherent and non-vital explanations for continually ordered natural and biological phenomena which have historically been studied by scientific thinkers relying on vital functions.
AI vs. Cybernetics: Comparison Chart
Summary of AI vs. Cybernetics
In a nutshell, Both AI and Cybernetics are based on binary logic and based on the principle of human-machine interaction. However, they are two different but interrelated fields. AI is based on the realist view that machines can work and behave like humans whereas Cybernetics is based on a constructivist view of the world. AI is based on the idea of creating machines to mimic human intelligence and behavior whereas Cybernetics is the science of human-machine interaction that employs the principles feedback, control and communication.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Tzafestas, Spyros G. Systems, Cybernetics, Control, and Automation. Denmark: River Publishers, 2017. Print
[1]Johnston, John. The Allure of Machinic Life: Cybernetics, Artificial Life, and the New AI. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press, 2008. Print
[2]Novikov, D.A. Cybernetics: From Past to Future. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2015. Print
[3]He, Xingui, et al. Computer, Informatics, Cybernetics and Applications: Proceedings of the CICA 2011. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2011. Print
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/de/illustrations/kopf-gesicht-kybernetik-roboter-1536592/
[5]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/de/illustrations/k%C3%BCnstliche-intelligenz-roboter-ai-4417279/