Difference Between AI in Cybersecurity and AI in Financial Services
Businesses and organizations these days are spending billions of dollars globally on cybersecurity alone. And artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in building smarter and safer security systems for all. As organizations venture into this new AI era, they need to understand how to best harness the power of AI. In this article, we’ll discuss how AI is revolutionizing the digital realm, particularly in cybersecurity and financial services. Let’s take a look at the differences between AI in cybersecurity and AI in financial services.

AI in Cybersecurity
AI is a revolutionary technology that brings a heightened level of efficiency and responsiveness to the cybersecurity realm. AI has emerged as a powerful ally, fortifying defenses and revolutionizing the way we combat cyber threats.
- Threat detection: AI excels in threat detection by analyzing vast datasets at speeds unattainable by humans. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns indicative of malicious activities, swiftly recognizing anomalies that might go unnoticed through traditional methods.
- Rapid incident responses: Automated systems equipped with AI can analyze and contain threats in real-time, minimizing the impact and mitigating potential damage.
- Behavioral analysis: By continuously monitoring and learning from user interactions, AI can detect unauthorized access or suspicious activities based on anomalous behavior, providing an added layer of security.
- Adaptive learning and evolution: Machine learning models continually refine their understanding of emerging threats, ensuring that the defense mechanisms stay ahead of the ever-changing tactics employed by cybercriminals.
For instance, Darktrace, a British cybersecurity company, employs AI to create a self-learning cybersecurity system that adapts to new threats without human intervention. It utilizes machine learning to understand ‘normal’ network behavior and can swiftly identify and respond to anomalies.

AI in Financial Services
Finance is a key sector in every industry. In recent years, the financial services industry has undergone a profound transformation, largely propelled by advancements in technology. Among these technological advancements, AI has emerged as a pivotal force, revolutionizing the way financial institutions operate, make decisions, and interact with their clients.
- Risk management: AI plays a crucial role in enhancing risk management within the financial sector. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate potential risks.
- Fraud detection and prevention: AI algorithms can analyze transaction patterns, user behavior, and other data points to identify irregularities that may signify fraudulent transactions.
- Customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants have transformed customer service in the financial sector. These intelligent systems can handle routine inquiries, provide account information, and offer personalized recommendations based on user preferences.
- Algorithmic trading: AI has revolutionized the landscape of algorithmic trading by enabling machines to analyze market trends, execute trades, and manage portfolios at speeds and capacities far beyond human capabilities.
- Credit scoring and underwriting: AI-driven credit scoring models utilize a diverse range of data points to assess creditworthiness more accurately. These models also consider alternative data sources. This enables financial institutions to make more informed lending decisions and expand access to credit.
For example, Zest Finance uses machine learning to improve credit underwriting, enabling lenders to assess the creditworthiness of individuals who may have a limited credit history.
Difference between AI in Cybersecurity and AI in Financial Services
Primary Objective
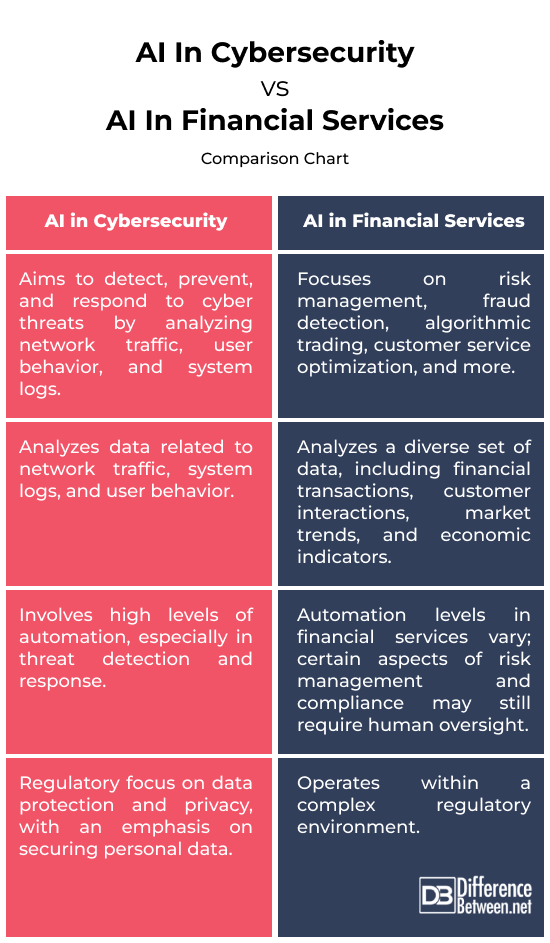
AI systems in cybersecurity analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify anomalies or malicious activities, aiming to secure digital assets and protect against cyberattacks. The primary objective of AI in cybersecurity is to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats.
AI serves a broader range of purposes in financial services. It includes risk management, fraud detection, algorithmic trading, customer service optimization, and personalized financial advice.
Nature of Data
AI in cybersecurity primarily analyzes data related to network traffic, system logs, and user behavior to identify patterns indicative of cyber threats. The emphasis is on recognizing abnormal activities and potential security breaches.
AI in financial services analyzes a diverse set of data, including financial transactions, customer interactions, market trends, and economic indicators. The goal is to extract insights for risk assessment, fraud prevention, investment decisions, and personalized customer services.
Automation Level
AI in cybersecurity often involves high levels of automation, especially in threat detection and response. Automated systems can analyze and respond to potential threats in real-time, minimizing the need for manual intervention.
While there is automation in financial services, the level varies across different applications. Algorithmic trading and robo-advisors are highly automated, executing trades or providing investment advice without direct human involvement. In contrast, certain aspects of risk management and compliance may still require human oversight.
Regulatory Landscape
Regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) emphasize the importance of securing personal data and imposing penalties for data breaches.
Financial services operate within a complex regulatory environment that includes oversight related to financial transactions, consumer protection, and market integrity. Compliance with regulations such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) is crucial.
AI in Cybersecurity vs. AI in Financial Services: Comparison Chart
Summary
While both AI applications share some common themes, such as the use of machine learning algorithms, their specific goals, data considerations, levels of automation, and regulatory challenges set them apart. Understanding these differences is essential for designing and implementing effective AI solutions tailored to the unique requirements of cybersecurity and financial services.
FAQs
What is difference between AI and cyber security?
AI is a broad field of computer science focused on creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Cybersecurity is a specific application of technologies and practices designed to protect computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage.
How is AI used in financial services?
AI is used in financial services for various purposes, including risk management, fraud detection, algorithmic trading, customer service optimization, and personalized financial advice.
How can AI be used in cyber security in banking?
In banking, AI can be used in cybersecurity for threat detection, rapid incident response, behavioral analysis, and adaptive learning. AI systems can analyze vast datasets, identify patterns indicative of cyber threats, and automate responses to minimize the impact of security incidents.
What are the challenges of AI in financial services?
Challenges may include interpretability of complex models, data privacy concerns, regulatory compliance, integration with existing systems, and addressing biases in algorithms. Ensuring transparency and ethical use of AI is crucial.
What is an example of AI in financial services?
One example is ZestFinance, which uses machine learning for credit underwriting.
What type of AI is used in finance?
In finance, both narrow AI (also known as weak AI) and general AI (strong AI) can be used. Narrow AI is designed for specific tasks, such as algorithmic trading or fraud detection. General AI, which possesses human-like cognitive abilities, is more theoretical and not widely implemented in finance.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Parisi, Alessandro. Hands-On Artificial Intelligence for Cybersecurity: Implement Smart AI Systems for Preventing Cyber Attacks and Detecting Threats and Network Anomalies. Packt Publishing Ltd, 2019.
[1]Das, Ravi. Practical AI for Cybersecurity. CRC Press, 2021.
[2]Boobier, Tony. AI and the Future of Banking. John Wiley and Sons, 2020.
[3]Sastry, V. V. L. N. Artificial Intelligence in Financial Services and Banking Industry. Idea Publishing, 2020.
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADZH_nqcGA-concept-augmented-analytics-business-analytics-and-financial-technology-concept-ai-artificial-intelligence-and-smart-analytics-data-science-learning-machine/
[5]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAFmVmZMy8E-inside-shield-cpu-concept-cybersecurity-technology/
