Difference Between Bandwidth and Broadband
Broadband is a term refers to the width of a band. It is simply a high-speed, always-on internet connection in terms of transmission capacity. Bandwidth is the maximum data transfer rate from one point to another at a given time period over a network.

What is Broadband?
In telecommunications, broadband is the most used form of high-speed internet access that brings internet signal to and from a device through a telephone line. The term has different meanings. Earlier, the term broadband referred to cable TV to homes. While CATV is still an option for residential broadband, the generally accepted meaning of the term is wider and less specific. It generally refers to an always-on, high-speed internet connection that often runs on cable, as opposed to the conventional narrowband and dial-up connection. However, the original narrative of the term ‘broadband’ has changed and it’s now simply referred to as shorthand for high speed Internet access. The term was originally defined by the ITU as the transmission capacity that is faster than primary rate ISDN. However, with the proliferation of Internet and the need for high-speed Internet access, the term broadband is defined exclusively in terms of transmission capacity and speed.
What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth is the maximum rate at which the data can be transferred from one point to another within a network over a specific period of time. Bandwidth is a performance metric of the capacity of network communications. Bandwidth determines the amount of information that can be transmitted across a given path in a given unit of time. This does not refer to data transfer speed, just the maximum capacity of data to be transferred. Recent developments in networking have skyrocketed the transmission capacity of computer networks used by individuals and businesses around the world. However, the communication rarely takes place at the fastest speed possible and this is because of the delay in completing the communication. Bandwidth is one of the key aspects of high-speed communication, the other being the latency. Bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps) which was quite low in the 1980s, but in the 1990s, bandwidth would be recorded in gigabits per second (Gbps).
Difference between Bandwidth and Broadband
Meaning
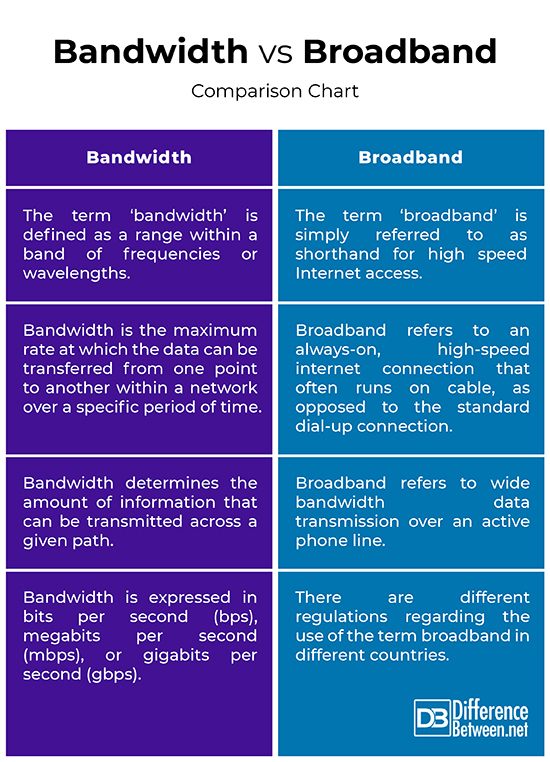
– The term ‘broadband’ simply referred to as shorthand for high speed Internet access. Broadband is the most used form of high-speed internet access that brings internet signal to and from a device through a telephone line. The term broadband is defined exclusively in terms of transmission capacity and speed. Bandwidth, on the other hand, is a performance metric of the capacity of network communications which is described as the maximum rate at which the data can be transferred from one point to another within a network over a specific period of time.
Technology
– Broadband technology refers to a high-speed, always-on connection to the Internet with higher bandwidth, as opposed to the Internet connection offered by a standard dial-up line. It refers to wide bandwidth data transmission over an active phone line. The medium of transmission can be twisted pair copper wires, optical fibers, and coaxial cables. Similarly, wireless broadband can be identified as mobile, fixed and satellite. One or more of these technologies can be used to provide broadband telecommunication services. Bandwidth, on the other hand, refers to the capacity of an Internet connection which determines the amount of information that can be transmitted in a specific period of time across a given path.
Measure
– OECD defines a broadband service with a baseline speed of at least 256 kbps. In practice, broadband measurements provide other data than the access speed. The broadband speed is the measure of how quickly users can upload or download data using their internet connection. However, the speed may vary for wireline and wireless Internet access. There are different regulations regarding the use of the term broadband in different countries. The FCC, for example, defines broadband as a minimum of 25 mbps download and 3 mbps upload. Bandwidth, on the other hand, refers to the data transfer rate in a given time period and is expressed in bits per second (bps), megabits per second (mbps), or gigabits per second (gbps).
Bandwidth vs. Broadband: Comparison Chart
Summary of Bandwidth Vs. Broadband
Broadband is basically a high-speed, always-on internet connection in which a single cable carries a huge amount of data at once. The medium of transmission can be twisted pair copper wires, optical fibers, and coaxial cables. Broadband is generally offered in four different forms, DSL, fiber-optic, cable and satellite. Bandwidth, on the other hand, is the primary performance metric governing interapplication delay. The bandwidth is a constantly changing number as it is relative to the network and end system technology at a given time. Previously, kbps applications were considered high speed, but with the proliferation of Internet and the need for high-speed access, the speeds are now up to mbps and gbps.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:D-Link_DIR-600_Broadband_Modem.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Coherence_bandwidth.png
[2]Maldoom, Dan, et al. Broadband in Europe: How Brussels Can Wire the Information Society. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2005. Print
[3]Chlamtac, Imrich, et al. Broadband Services: Business Models and Technologies for Community Networks. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print
[4]French, Deanie. Internet Based Learning: An Introduction and Framework for Higher Education and Business. Sterling, Virginia: Stylus Publishing, LLC., 1999. Print
[5]Sterbenz, James P.G. and Joseph D. Touch. High-Speed Networking: A Systematic Approach to High-Bandwidth Low-Latency Communication. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2002. Print
[6]Esmailzadeh, Riaz. Broadband Telecommunications Technologies and Management. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2016. Print
[7]Haidine, Abdelfatteh and Abdelhak Aqqal. Broadband Communications Networks: Recent Advances and Lessons from Practice. London, United Kingdom: IntechOpen, 2018. Print
