Difference Between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics
In today’s technology-driven world, companies sit on a massive pool of data that they generate from their several different business activities. Indeed, many businesses now have more data than they can handle. But the data are usually meaningless until they are analyzed for patterns, trends, relationships and other useful information. In the business context, data analysis is only the first step in the solution of a problem. And acting on the solution to make better decisions is a critical next step. Business intelligence and analytics are two of the hottest topics in today’s business world.
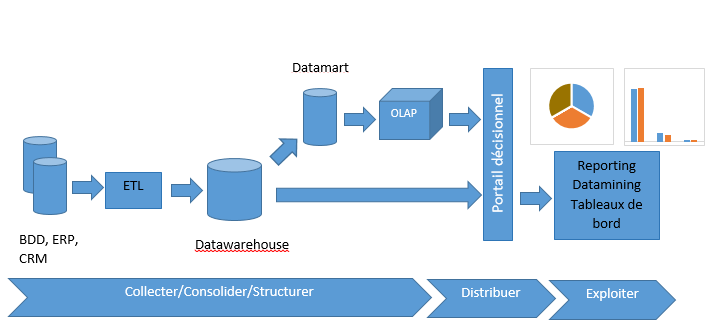
What is Business Intelligence?
There are several different definitions of Business Intelligence (or BI) that vary dramatically from user to user based on their role within the enterprise. But to simply put, BI is about delivering relevant and actionable information to the right people at the right time in order to make better and informed business decisions. BI is not a product or a system. It is architecture of integrated operational and decision-support applications and databases that make it possible to create value from big data. BI is about harnessing the full potential of data that your business generates in all of its daily activities, and analyzing this data to gain valuable insights into making informed decisions. The goal is to boost productivity and improve performance of your business using those insights. BI can be used to discover trends and information that would not have disclosed otherwise.
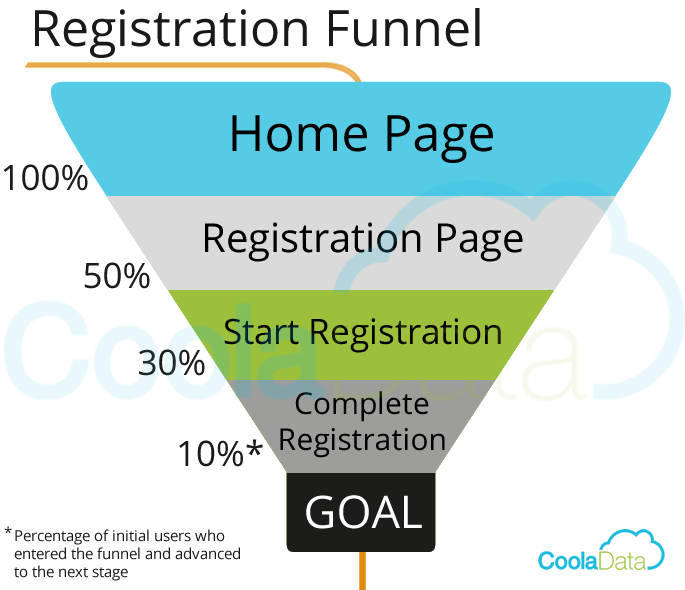
What is Business Analytics?
Analytics, at its basic level, is about turning data, and sometimes lots of data, into meaningful business insights that help your business grow and flourish. But in reality, analytics is never quite this simple. Let’s say you work at a credit card company and you could analyze data of your customers to determine who is more likely to subscribe to a credit card offer. In fact, from cyber security to finance, marketing, education, healthcare and energy, all of these sectors could benefit from applying and improving their analytics. Business analytics is any data-driven process that provides insights to create value. It is about understanding the value of insights and convincing an organization to change the way it does business. Understanding the value of business analytics requires a blend of technical, domain and soft skills. BA is the methodical exploration of data with an emphasis on statistical analysis that focuses on providing actionable insights.
Difference between Business Intelligence and Business Analytics
Definition
– Business Intelligence (BI) is architecture of integrated operational and decision-support applications and databases that make it possible to create value from big data. BI is about harnessing the full potential of data that your business generates, and analyzing this data to gain valuable insights into making informed decisions. Business analytics is about understanding the value of insights and convincing an organization to change the way it does business. Business analytics is any data-driven process that provides insights to drive tangible and intangible value.
Approach
– BI helps you make informed, strategic, and operational decisions based on the historical data all the way up to the present. BI involves technology, people, tools, processes, and applications that help you organize and enable access to data and analyze information. BI filters through existing data to discover trends and patterns in the past and present to make better informed business decisions. Business analytics combines advances statistical analysis and predictive modeling to interpret data to discover future trends and patterns based on the current data. BA helps businesses to augment their operations and performance to make better decisions in the future.
Tools
– Business intelligence leverages a plethora of tools that fall under the umbrella of four key capabilities of BI solutions – organizational memory, information integration, insight creation, and presentation capability. Several important tools and technologies that enable organization to implement BI solutions include transactional systems, ERP systems, data warehousing, data mining or knowledge discovery, business analytics, real-time decision support, etc. Business analytics is the methodical exploration of data with an emphasis on statistical analysis that focuses on providing actionable insights. BA makes extensive use of numerical analysis and analytical modeling, including predictive and prescriptive modeling to make better business decisions.
Business Intelligence vs. Business Analytics: Comparison Chart
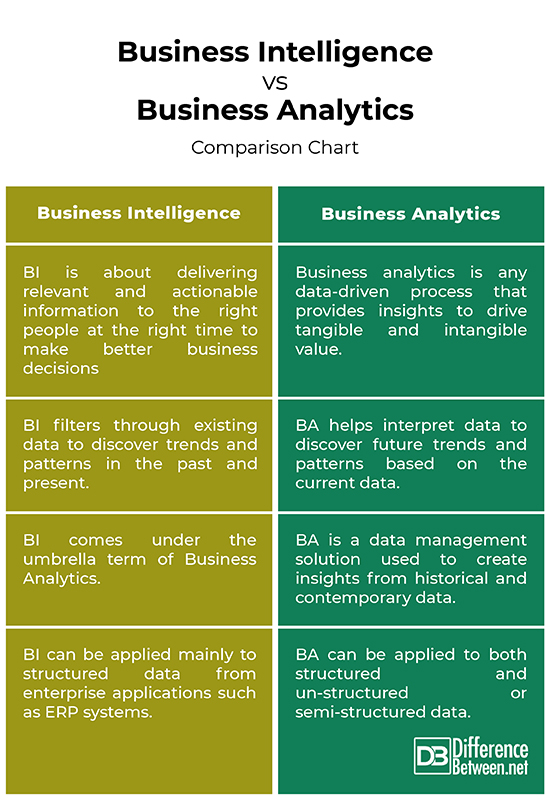
Summary
In a nutshell, BI and BA are a set of methodologies, architectures and technologies that give some meaningful insights to the existing data in different kinds of organization, making them relevant for decision-making. They are data management solutions implemented by businesses around the world with the goal of achieving better decision-making through collection and analysis of historical and present data. BI identifies the trends, patterns and relationships from the past data leading all the way to the present without predicting the future. BA is about harnessing the power of BI to its full potential in order to predict future trends based on the historical data that may be of tangible or intangible value. While two are very different terms, they are not contradictory; in fact, they work towards a common goal – that is to increase organizational productivity and improve performance.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Biere, Mike. Business Intelligence for the Enterprise. New Jersey, United States: Prentice Hall, 2003. Print
[1]Moss, Larissa Terpeluk and S. Atre. Business Intelligence Roadmap: The Complete Project Lifecycle for Decision-Support Applications. Massachusetts, United States: Addison-Wesley, 2003. Print
[2]Kudyba, Stephen and Richard Hoptroff. Data Mining and Business Intelligence: A Guide to Productivity. Pennsylvania, United States: Idea Group Publishing, 2001. Print
[3]Albright, Christian S. and Wayne L. Winston. Business Analytics: Data Analysis & Decision Making. Massachusetts, United States: Cengage, 2016. Print
[4]Sabherwal, Rajiv and Irma Becerra-Fernandez. Business Intelligence: Practices, Technologies, and Management. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2013. Print
[5]Melo, Pedro Novo and Carolina Machado. Business Intelligence and Analytics in Small and Medium Enterprises. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2019. Print
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Composants_du_Business_Intelligence.png
[7]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Business_Analytics_Funnel_Visualization.png
