Difference Between Data Mining and Data Profiling
One of the fundamental requirements before consuming datasets for any application is to understand the dataset at hand and its metadata. The process of discovering the metadata of a given dataset is known as “data profiling”, which encompasses a vast array of methods to examine datasets and produce metadata. Data mining is a broad concept that employs a wide range of methodologies and techniques to a host of problem sets. Data mining can be simply referred to as knowledge discovery which simply means to collect patterns from the available data. A clear, well-defined distinction between the two does not exist.
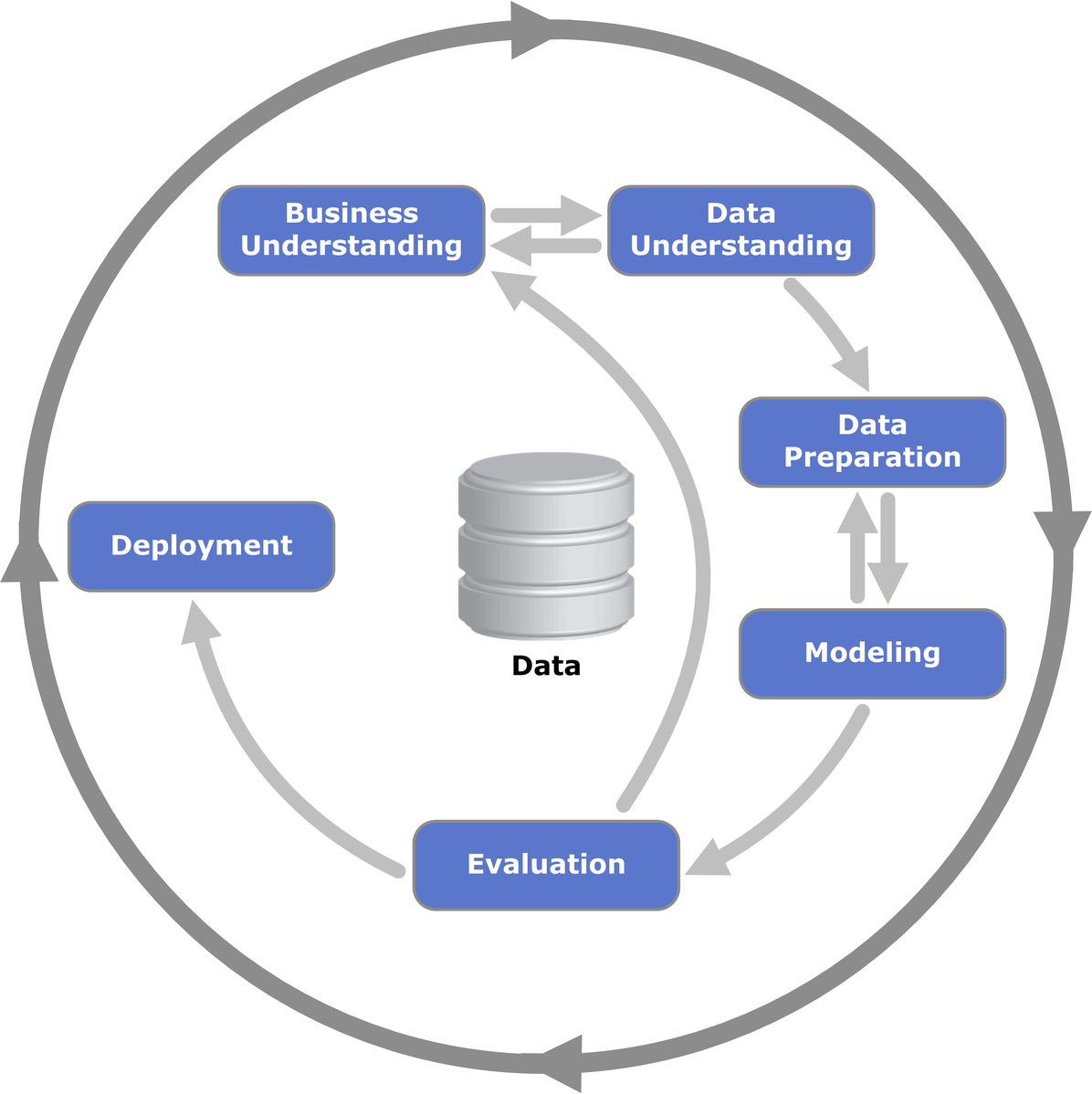
What is Data Mining?
Data Mining is a process of identifying patterns and correlations within large datasets to derive more useful bits of knowledge. These meaningful bits of knowledge can then be fed into the more general areas of Business Intelligence. The need to understand the large, complex datasets is common to virtually all fields of business, science and engineering. The whole process of applying computer-based methodologies, including new technologies, to extract useful information hidden in the data is called data mining. It simply evaluates a large collection of raw data and turns them into information. Data mining is a search for new, valuable and non-trivial knowledge in large datasets and then using the information to uncover relationships and hidden patterns in those datasets. Simply put, data mining is knowledge mining from data.
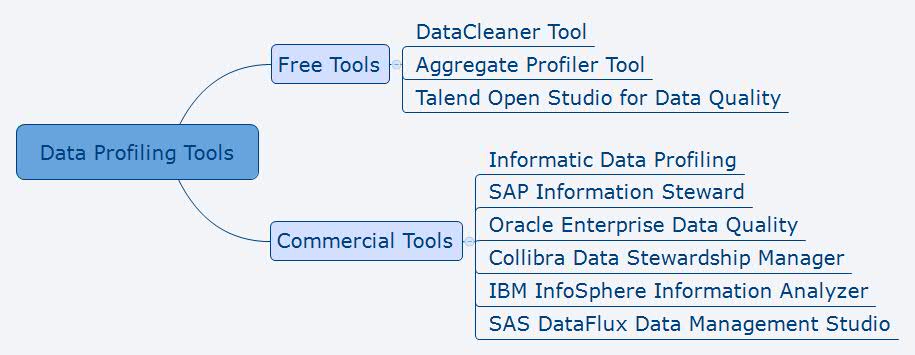
What is Data Profiling?
Data Profiling is a process of analyzing raw data from existing datasets for the purpose of collecting statistics or informative summaries about the data. It refers to a set of activities designed to determine the metadata of a given dataset when it is not available and to validate metadata when it is available within a dataset. These metadata, such as statistics about the data or dependencies among columns, can help understand and manage new datasets. Some data profiling can be applied to just any data type, while some are type-specific. This is very different from data analysis which is rather used to derive business information from data. Data profiling is used to derive information about the data itself and assess the quality of the data in order to discover anomalies in the dataset. Moreover, it helps understand and prepare data for subsequent cleansing, integration, and analysis.
Difference between Data Mining and Data Profiling
Definition
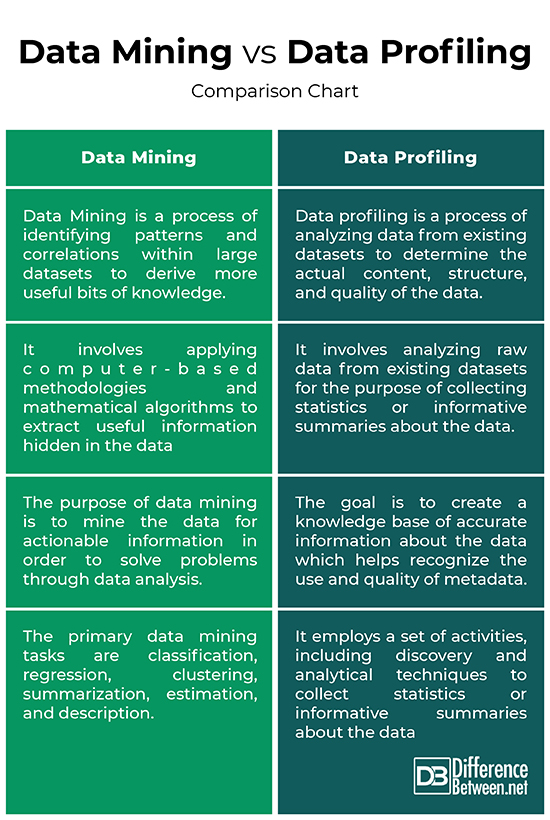
– Data Mining is a process of identifying patterns and correlations present in raw data and interpreting those patterns in their problem domains to turn them into useful information and knowledge. These meaningful bits of knowledge can then be fed into the more general areas of Business Intelligence. Data profiling, on the other hand, is a process of analyzing data from existing datasets to determine the actual content, structure, and quality of the data. Data profiling is a process which involves learning from the data.
Process
– Data profiling employs a set of activities, including discovery and analytical techniques to collect statistics or informative summaries about the data, which can then be analyzed by a business analyst to determine if the data matches the business intent. It helps understand and prepare data for subsequent cleansing, integration, and analysis. The data mining, on the other hand, can be put into one of two categories: Predictive data mining, which involves using some variables in the data set to predict unknown or future values of other variables of interest, and Descriptive data mining, which focuses on producing new, nontrivial information based on available dataset.
Purpose
– The purpose of data mining is to mine the data for actionable information. It involves effective data collection and processing and making use of sophisticated mathematical algorithms for segmenting the data and predicting future trends, so that it can be used into the more general areas of Business Intelligence. The purpose of data profiling is to derive information about the data and assessing the quality of the data in order to discover anomalies in the dataset. The goal is to create a knowledge base of accurate information about your data. The process needs to be repeated on critical data stores at times to make sure the information stays accurate.
Data Mining vs. Data Profiling: Comparison Chart
Summary
It is apparent that some of the techniques of data mining can be used for data profiling. Data profiling is used to collect statistics or informative summaries about the data, while data mining helps identify specific data patterns in large datasets. Data profiling collects technical metadata to support data management, while data mining discovers non-obvious results to support business management with new actionable insights. Data mining is a rather broad concept which is based on the fact that there’s a need to analyze massive volumes of data in almost every domain and data profiling adds value to that analysis.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Loshin, David. Business Intelligence: The Savvy Manager's Guide. Burlington, Massachusetts: Morgan Kaufmann, 2003. Print
[1]Loshin, David. Business Intelligence: The Savvy Manager's Guide. Burlington, Massachusetts: Morgan Kaufmann, 2003. Print
[2]Kantardzic, Mehmed. Data Mining: Concepts, Models, Methods, and Algorithms. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2019. Print
[3]Olson, Jack E.. Data Quality: The Accuracy Dimension. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2003. Print
[4]Abedjan, Ziawasch, et al. Data Profiling. Mountain View, California: Morgan & Claypool Publishers, 2018. Print
[5]Nong, Ye. Data Mining: Theories, Algorithms, and Examples. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2013. Print
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:CRISP-DM_Process_Diagram.png
[7]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Populated_Data_Profiling_Tools.jpg
