Difference Between Digital Certificate and Digital Signature
Both digital certificates and digital signatures play a significant part in the TLS/SSL ecosystem. They stand guard against forgery and tampering, especially when it comes to signing electronic documentation. So it’s important to understand the differences between the two. Let’s begin with digital signature first and then we can move to digital certificate, and then highlight the key differences between the two.
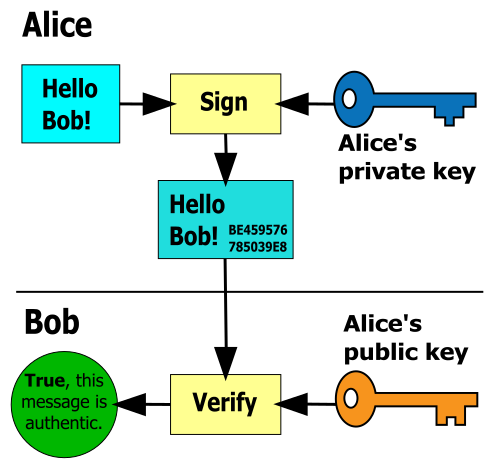
What is Digital Signature?
Let’s say Jason wants to send a digitally signed message to Ellie. First, Jason will create a pair of keys, a public key and a private key. He will keep the private key to himself and puts the public key in a public place. Then Jason will create a message and uses his private key to assign the message, and then send them to Ellie. When Ellie gets Jason’s digitally signed message she gets the public key and uses it to verify Jason’s digital signature. After she finished verifying Jason’s digital signature with the public key, then the credibility of the message was verified meaning it proves the message indeed was sent by Jason. So, digital signature is an electronic equivalent to a handwritten signature used to validate the authenticity of a digital document or a message. It is an electronic verification of the sender which proves the message or document was created and sent by the claimed sender.
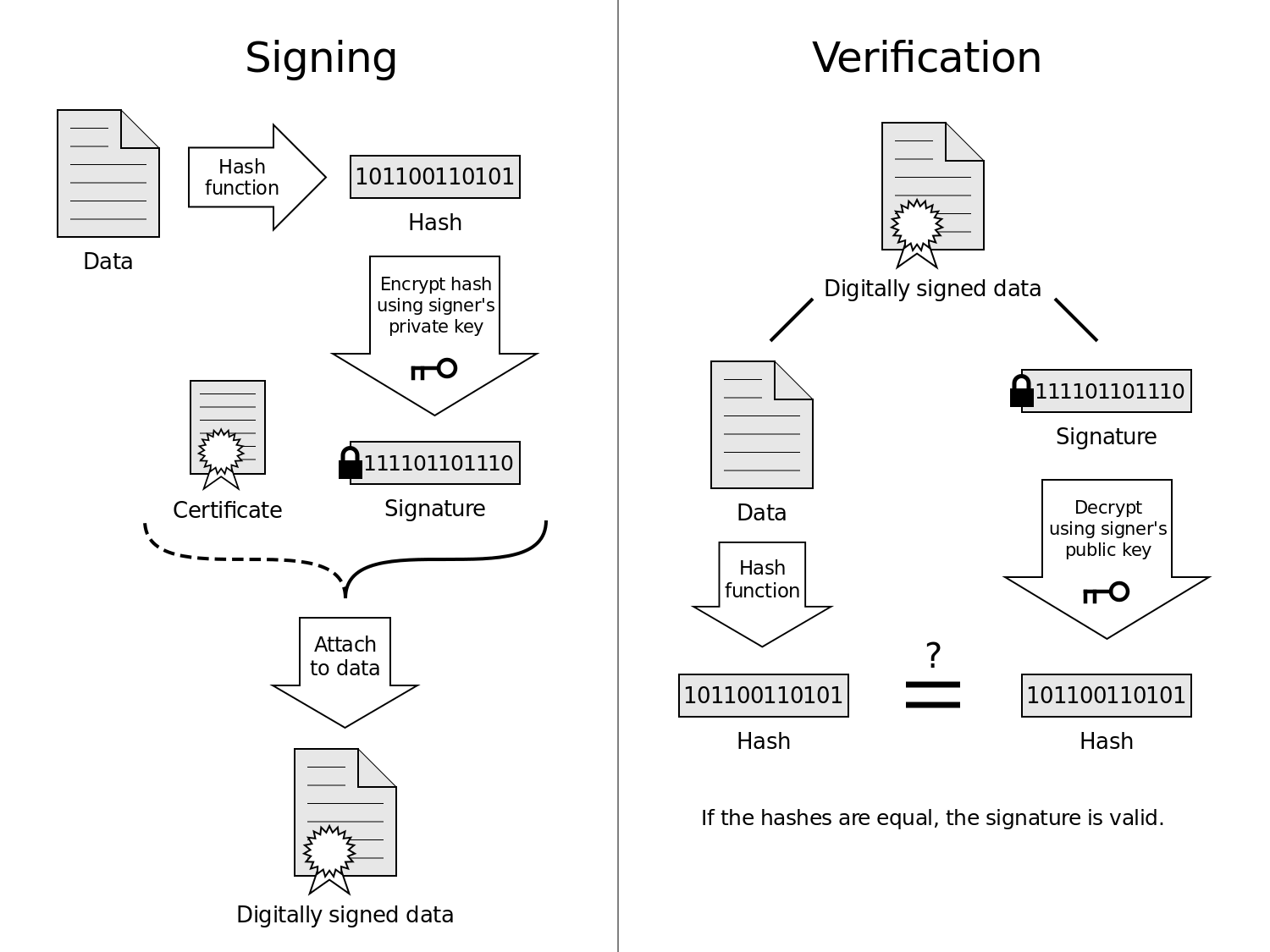
What is Digital Certificate?
Similarly, digital certificate is a new form of electronic identification that establishes a digital identity for an individual or an organization and guarantees the authenticity of the message or information received over the web. Digital certificates are electronic credentials that assert the online identities of computers and other entities on a network. For example, digital certificates are used in digital communications, particularly SSL communications which are used between web clients and web servers. SSL is a means of providing encrypted security between a client and a web. They are an integral part of website security and the ultimate sign of trust. It’s a digital form of identification, like a driver’s license or passport, issued by a Certification Authority (CA) which contains the public key for a digital signature and verifies that the public key belongs to the specific individual or organization.
Difference between Digital Certificate and Digital Signature
Definition
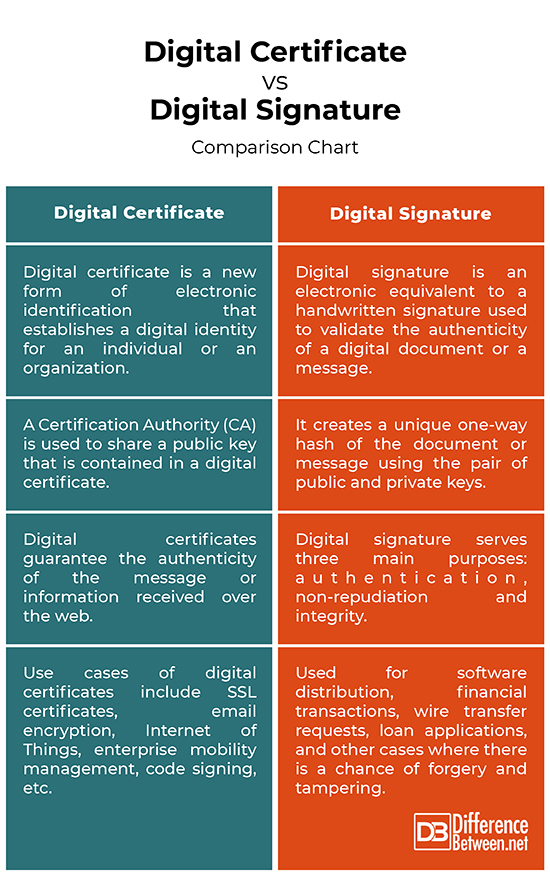
– A digital certificate is a form of electronic identification used to establish a digital identity of the sender and guarantees the authenticity of the message received over the web. This lets the recipient of the message know that the message in fact comes from a trusted source or the sender who claims to be the one who sent the message. A digital signature is an electronic equivalent of a handwritten signature used to verify the authenticity and integrity of the message or any digital document.
Process
– A digital signature is a cryptographic code like a numeric string affixed to documents, emails and digital certificates. It is a process that guarantees that the original contents of the message have not been altered with when in transit. It creates a unique one-way hash of the document or message using the pair of public and private keys. A digital certificate is issued by a Certification Authority (CA) which contains the public key for a digital signature and a variety of other identification information, and verifies that the public key belongs to the specific individual or organization.
Purpose
– Digital signature serve three main purposes: authentication, non-repudiation and integrity. A digital signature guarantees the recipient that the message was created and sent by the claimed sender, who cannot deny having sent the message after. A digital signature also ensures that the original contents of the message have not been altered with during transit. Similarly, digital certificates guarantee the authenticity of the message or information received over the web. Digital certificate basically creates trustworthiness between the sender and the receiver.
Use Cases
– Digital signatures are used by individuals and businesses alike for various purposes, most commonly for software distribution, financial transactions, wire transfer requests, loan applications, and other cases where there is a chance of forgery and tampering. Digital signatures come in quite handy with email users. One of the best examples of digital certificates is SSL certificates which ensure safe and secure connection from a web server to a browser. Other use cases include email encryption, Internet of Things, enterprise mobility management, code signing, and so on.
Digital Certificate vs. Digital Signature: Comparison Chart
Summary
Digital certificates are a kind of identification document that you can use to prove your identity in messages or electronic transactions over the Internet. A digital certificate can be obtained from a trusted third-party or you can setup a locally trusted Certification Authority (CA) server within your own organization to provide digital certificates. Digital certificates are a new form of electronic identification. Digital signature, on the other hand, is an electronic equivalent to a handwritten signature used to validate the authenticity of a digital document or a message. Digital signatures use cryptographic hash algorithm to efficiently detect message forgery and tampering.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Thorsteinson, Peter and G. Gnana Arun Ganesh. NET Security and Cryptography. New Jersey, United States: Prentice Hall, 2004. Print
[1]Thorsteinson, Peter and G. Gnana Arun Ganesh. NET Security and Cryptography. New Jersey, United States: Prentice Hall, 2004. Print
[2]Brassard, Gilles. Advances in Cryptology - CRYPTO '89: Proceedings. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 1995. Print
[3]Feghhi, Jalal et al. Digital Certificates: Applied Internet Security. Massachusetts, United States: Addison-Wesley, 1999. Print
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4d/Illustration_of_digital_signature.svg/500px-Illustration_of_digital_signature.svg.png
[5]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/Digital_Signature_diagram.svg/1500px-Digital_Signature_diagram.svg.png
