Difference Between PCIe and NVMe
When it comes to solid state drives, or SSDs, and storage media in general, there is actually a lot to talk about and there are a lot of technical terms that are thrown around, from HCI to SATA to PCIe to NVMe. So, it creates a lot of confusion when it comes to understanding what the right choice for your storage solutions might be. The NVMe is a transfer protocol that runs on top of transfer interfaces, such as PCIe.
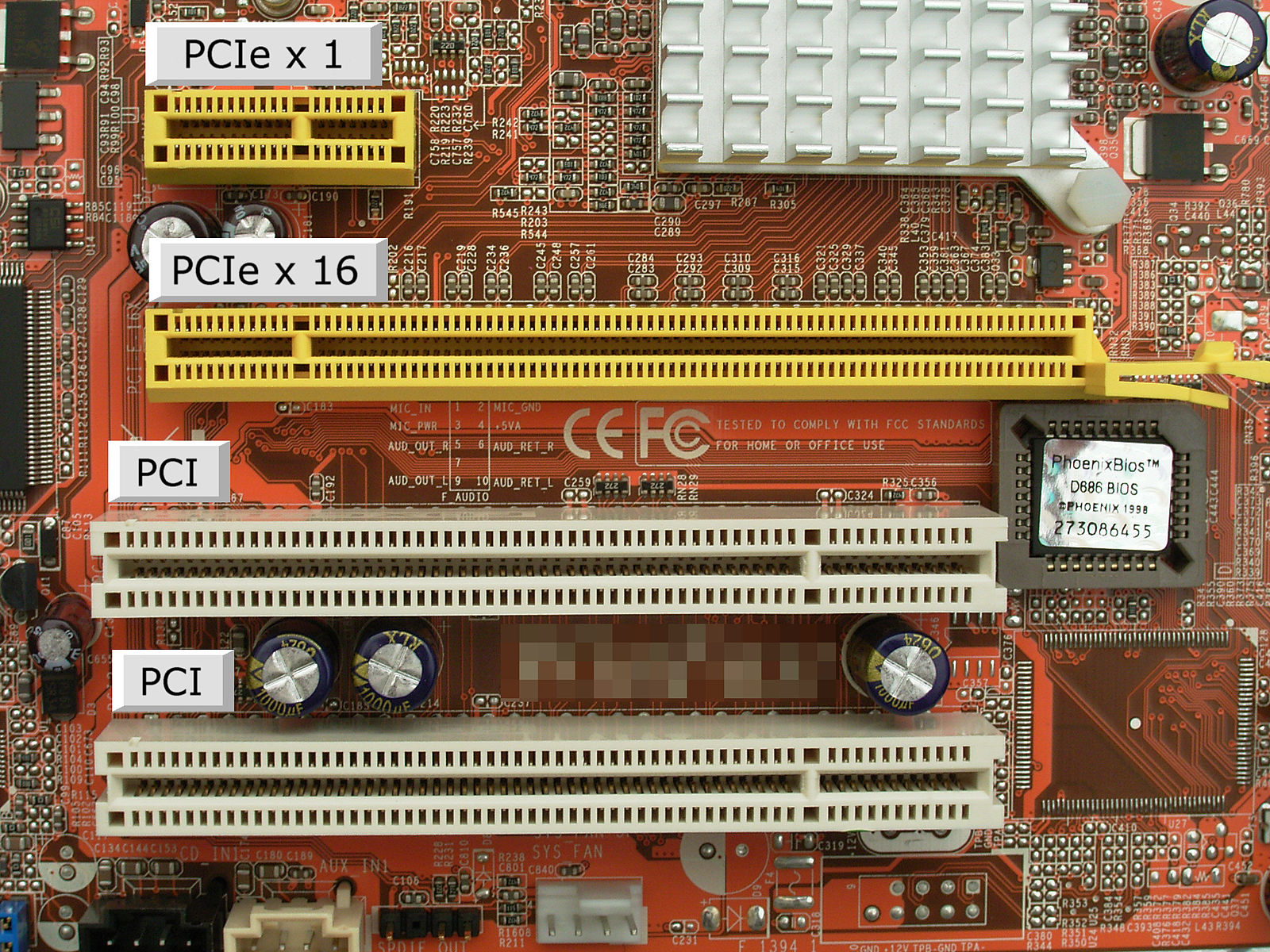
What is PCIe?
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, officially abbreviated as PCI Express or PCIe, is a high-speed standard bus interface for high-performance SSDs. It is the interface used to plug modern expansion cards into modern computers or motherboards. In fact, PCIe is at the heart of many server I/O and connectivity solutions. It is a standard bus interface that helps communicate with CPUs and the outside world of I/O networking devices. PCIe works with pretty much anything, including sound cards, video cards, Ethernet cards, raid cards, and solid-state drives (SSDs). It handles point-to-point connections for non-core components, unlike the older PCI bus topology which used shared parallel bus architecture.
Governed by the PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG), the PCIe speed is defined by its version and the number of lanes that are connected serially to form the physical connector. Each lane has two pairs of wires, one for receiving and the other one for transmitting. The PCIe link between two devices can have between 1 to 32 lanes. There are several different implementations of PCIe corresponding to generations that represent speed improvements plus physical packing options. The PCIe 5.0 is the latest standard that can reach absolutely insane speeds; we are talking about 32 gigatransfers per second (GT/s) against the 16 GT/s on the PCIe 4.0.

What is NVMe?
Non-Volatile Memory Express, short for NVMe, is a communication transfer protocol specially designed for accessing high-speed storage media devices, such as flash and next-gen solid state drives. NVMe is a new technology standard purposely built for blazing fast access to PCIe SSDs. It is a new protocol alternative to AHCI/SATA and the SCSI protocol used by SAS. NVMe is an open collection of standards collectively developed by the NVM Express Workgroup, which consists of more than 90 companies. The standard was developed to assist in enabling the broad adoption of PCIe-based SSDs, and to give a scalable interface which will realize the true potential of the SSD technology in the coming future.
When SSDs first came to the picture, they used SATA and/or SAS protocols to be more in line with the existing hard drives we were so used to. So, to bring it up to the speed of SSDs, and to be closer to the CPU, PCIe was developed as the next logical interface for flash memory. But the early PCIe SSDs lacked industry standards and added features. So, the NVMe standard was developed specifically for non-volatile memory, especially high-speed SSDs. It is super fast, like 2 to 7 times faster than SATA SSDs. For example, traditional HDDs using the SCSI protocol had one queue for commands. The NVMe, on the other hand, is the first storage protocol to support up to 64,000 queues and 64,000 commands per queue.
Difference between PCIe and NVMe
Interface/Protocol of PCIe and NVMe
PCIe, short for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a standard bus interface for high-performance SSDs. PCIe works with pretty much anything, including sound cards, video cards, Ethernet cards, raid cards, and solid-state drives (SSDs). Non-Volatile Memory Express, short for NVMe, is a communication transfer protocol that runs on top of transfer interfaces such as PCIe. NVMe is a new technology standard purposely built for blazing fast access to high-speed storage media devices, such as flash and next-gen solid state drives.
Applications of PCIe and NVMe
– PCIe is a high-performance bandwidth interface used to plug modern expansion cards into modern computers or motherboards. It is used in all computer applications including personal computers, enterprise servers, communication systems, and industrial applications. PCIe is at the heart of many server I/O and connectivity solutions. NVMe SSDs are used in high-performance computing applications such as high-frequency trading. NVMe protocol was developed specifically for non-volatile memory, such as NAND flash and high-speed SSDs.
PCIe vs. NVMe: Comparison Chart
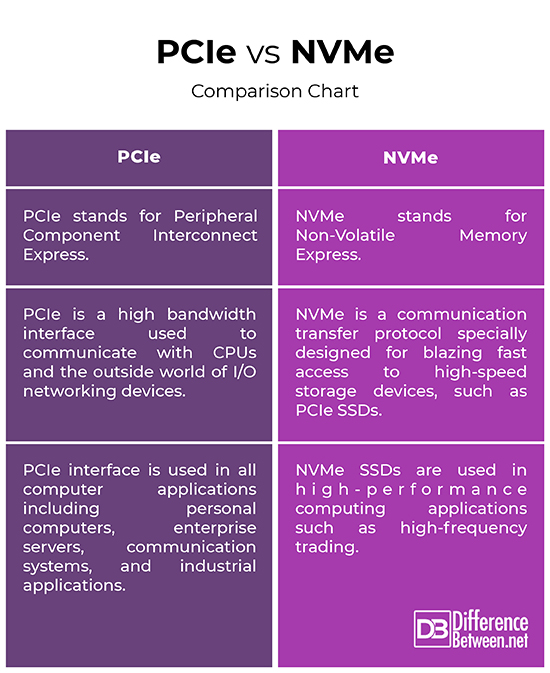
Summary of the difference between PCIe and NVMe
So, in a nutshell, PCIe is a standard bus interface that works with pretty much anything, including sound cards, video cards, Ethernet cards, raid cards, and solid-state drives (SSDs). PCIe is based on a point-to-point topology, unlike the older PCI bus topology which used shared parallel bus architecture. The PCIe specification is maintained by the PCI Special Interest Group. NVMe, on the other hand, is an interface specification for communication with NAND flash and next-gen solid state drives, and functionally, it is based on the same protocols as SATA and SAS. NVMe and PCIe are not contradictory technologies; in fact, NVMe SSDs are typically directly attached to a host system over a PCIe bus. So, basically, NVMe uses PCIe to enable modern applications to reach their potential. It leverages PCIe for accessing high-speed storage solutions, such as SSDs.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Herd, Jon. IBM FlashSystem 7200 Product Guide. New York, United States: IBM Redbooks, 2020. Print
[1]Schulz, Greg. Software-Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials: Cloud, Converged, and Virtual Fundamental Server Storage I/O Tradecraft. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2017. Print
[2]Vetter, Scott, et al. IBM Power Systems H922 and H924 Technical Overview and Introduction. New York, United States: IBM Redbooks, 2021. Print
[3]Micheloni, Rino, et al. Inside Solid State Drives (SSDs). Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. Print
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/1887/43274523795_81047bb405_b.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:PCI_und_PCIe_Slots.jpg
