Difference Between Alliteration and Assonance
Alliteration Vs. Assonance
Alliteration and assonance are among the many literary devices used in poetry and prose writing. They are meant to engage a reader’s auditory skills while also making the pieces they are used in blissful and fun to read. The two are mainly different in terms of what letter type is repeated and where.
Since poetry and prose use them heavily, they can be a little hard to distinguish to most people. As such, they have for long been used in place of each other, and unless a distinction line is drawn, the confusion will continue to be rife.
What is Alliteration?
Alliteration is a literary style that deals with the repetition of similar or identical consonant sounds. It makes a line fun to read and usually repeats the consonant sounds at the beginning of each word, but can also appear anywhere else where a word is stressed at. Such a line like ‘rubber baby buggy bumpers for anyone’ employs alliteration with the repetition of the consonant ‘b.’
Application
In Poetry:
One reference of the use of alliteration in poetry is in Edgar Allan Poe’s poem, The Raven. The third stanza on the poem employs alliteration on the first line with the repetition of the consonant and sound ‘s’ in what is known as sibilance, a more specific type of alliteration.
- And the silken, sad, uncertain rustling of ….
The second line in the same stanza:
- …filled me with fantastic terrors never felt before.
Other examples of alliteration include:
- We could hear their shouts and sibilant whispers.
- Listen to his sibilant whisper.
- English, Japanese, and Chinese share sounds that involve high rates of air flow from the mouth.
- She kept the constituents of consonantal clusters separate relishing fricatives and sibilants as much as liquids and plosives.
What is Assonance?
It is a literary device that employs the repetition of vowel sounds in quick succession and in more than two instances. The use of assonance is usually in a number of nearby words in a sentence, line, or phrase and can be anywhere in a word.
Application
In poetry:
We draw our reference from the same poem by Edgar Allan Poe, The Raven. In the poem, Edgar applies assonance in the first line of the last stanza:
- And the Raven, never flitting, still is sitting, still is sitting.
In the above line, there is a short ‘I’ sound that arrives with the word flitting and stays there until the end of that line. This is also along the ‘s’ and ‘t’ sounds that add more alliteration effects to the line and stanza.
In Robert Frost’s poem After Apple-Picking, assonance is also applied in different lines such as:
Stem end and blossom end,
And every fleck of russet showing clear.
Other examples of assonance include:
- He wants to try and light the fire.
- That’s hot and monotonous.
Difference Between Alliteration and Assonance
Meaning of Alliteration Vs. Assonance
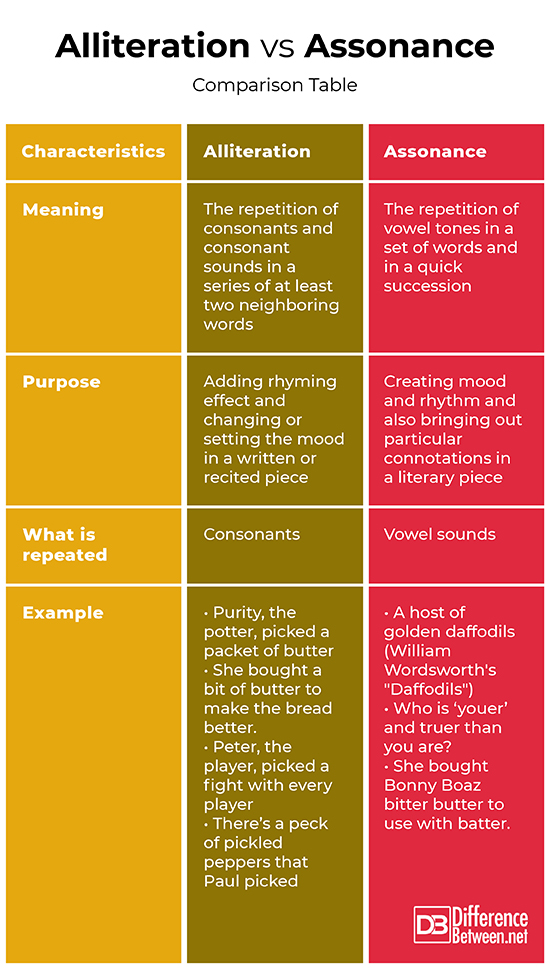
Alliteration is a literary device that employs the repetition of consonants sounds mainly at the beginning of close words and in a quick succession. Assonance, on the other hand, is a literary device employing the repetition of vowel sounds in two or more neighboring words and in a quick succession.
What is Repeated in Alliteration Vs. in Assonance
In alliteration, consonants sounds are repeated in a succession of neighboring words while in assonance, it is vowel sounds that are repeated in a quick succession of neighboring words.
Purpose of Alliteration Vs. Assonance
The main purpose of alliteration includes creating mood and rhythm in a written piece. It can also be applied to bring out particular connotations, like the repetition of consonant ‘s’ that can be used to suggest a snake-like quality, imply danger, or slyness.
The purposes of assonance include creating a rhyming effect within lines and changing the mood in a literary piece. As it enhances a musical effect, it consequently enhances the pleasure of reading the piece.
Examples of Alliteration Vs. Assonance
Alliteration examples:
- Paul, the possum, picked pecks of pickled peppers on a paper.
- She sells sea shells by the seashore.
- A good cook can cook cookies like a good cook can cook.
Assonance examples:
- William Blake’s “Tyger”: “Tyger, Tyger burning bright in the forest of the night.”
- Clapping your hands and stamping your feet creates a rhythm.
- The machine beats as it sweeps and cleans.
- Wear the dress here, there, and everywhere.
Alliteration Vs. Assonance: Comparison Table
Summary
The two, alliteration and assonance are literary devices that employ the repetition of sounds in a quick succession. Alliteration also falls under one of the many forms of consonance. They are both applied to add bliss to a written piece while also engaging the auditory skills of the consumers of such work. Their main difference is the letters whose sounds are repeated and where. With such differences, it is easier to interpret the meaning of a poem or prose and especially where the devices are used.
- Difference Between Minecraft and Terraria - August 7, 2020
- Difference Between Alliteration and Onomatopoeia Poems - July 25, 2019
- Difference Between Certification and Licensure - July 24, 2019
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rollenhagen-Froschmeuseler_II_241.gif
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ulalume-AmericanReview.gif
[2]"Alliteration Vs Assonance | Assonance Meaning | Grammarist – Grammarist". Grammarist.Com, 2019, https://grammarist.com/usage/alliteration-vs-assonance/.
[3]"Assonance Examples". Softschools.Com, 2019, http://www.softschools.com/examples/grammar/assonance_examples/120/.
[4]"Author's Craft - Literary Devices - Alliteration". Udleditions.Cast.Org, 2019, http://udleditions.cast.org/craft_ld_alliteration.html.