Difference Between Briefing and Debriefing
Briefing and debriefing are both critical in several settings such as in military missions and conducting research. These processes may also involve meetings or conversations which aim to facilitate information. However, briefing generally entails giving information while debriefing is more concerned with obtaining details. The following discussions further delve into their distinctions.

What is Briefing?
Briefing basically means giving information; it is synonymous with orientation, meeting, and rundown. It is used in several settings such as in the military, in press conferences, and in conducting or presenting research.
- Military Briefs (United States Marine Corps, 2017)
These are designed to clearly, concisely, and expediently present information. There are four types: information brief, decision brief, staff briefing, and mission brief.
- Information brief
This only deals with facts and no conclusion needs to be drawn from it. It is usually utilized when information of high priority is being passed like in after-action reports.
- Decision brief
This information is presented to a commander who will make a decision. It usually presents pertinent choices and their respective pros and cons.
- Staff briefing
This type is the most widely used since it is applicable in every command level. It aims to secure a unified effort and to rapidly disseminate information.
- Mission brief
This is designed to give specific instructions for a mission’s completion. It provides more details and is often conducted with the efforts of a joint staff.
- Press Briefing
-This is also known as a press conference in which an individual or an organization makes public statements.
-It also pertains to a document which contains an official statement.
- Research Briefing
-This features a succinct summary of evidences which aims to introduce main findings to a varied audience. It may be presented through a webpage, written document, podcast, video, poster, seminar, etc.
-This is also a part of the research process in which a prospective participant will be informed of the aim of the study, duration of the process, confidentiality, and related details. At the end of the briefing, the prospective participant will either agree or refuse to take part.

What is Debriefing?
Debriefing has several meanings; it may pertain to obtaining useful information, interrogating an individual, reviewing a process upon completion, disclosing the purpose of an experiment, or providing psychological support.
- Military Debriefing
-This refers to a meeting which questions someone such as a spy.
-This is also used to receive information from a soldier or a pilot after a mission. It aims to analyze if mission objectives were met, the encountered challenges, and any valuable information. Military debriefing is also designed to instruct which information can be made public and censored. It is also a session which can help assess if an individual is ready to go back to work.
- Psychological Debriefing
This is a conversational session (1 to 3 hours) which provides emotional and psychological support after a traumatic experience. It aims to prevent post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health concerns (Society of Clinical Psychology, 2016).
- Research Debriefing
In this phase the researchers express their gratitude and explain that the information gathered from the participant will remain confidential. It aims to identify if the participants were harmed in any way and to address such issues if present. In this part of the experiment, the participants are given the chance to ask questions. The researchers share more details about the study’s objectives, hypotheses, and probable indications of findings.
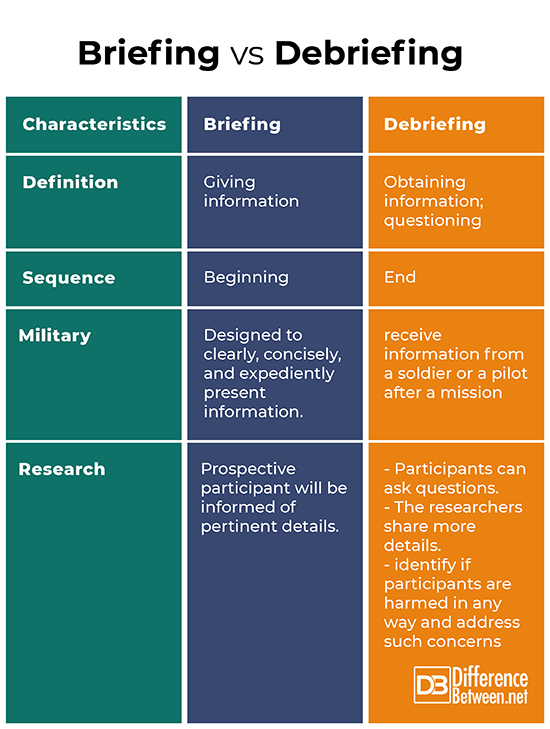
Difference between Briefing and Debriefing
Definition
Briefing basically means giving information; its synonyms include orientation, meeting, and rundown. In comparison, debriefing is popularly defined as questioning someone; its synonyms include examine, interrogate, and cross-examine.
Sequence
Briefing is generally done in the beginning while debriefing is conducted at the end. For instance, during the briefing phase in conducting research, a prospective participant will be informed of the aim of the study, duration of the process, confidentiality, and related details during the briefing phase. The prospective participant will then either agree or refuse to take part. On the contrary, during the debriefing phase, the researchers express their gratitude and explain that the information gathered from the participant will remain confidential.
Military
Military briefs are designed to clearly, concisely, and expediently present information. There are four types: information brief (only deals with facts and no conclusion needs to be drawn), decision brief (presented to a commander who will make a decision), staff briefing (to secure a unified effort and to rapidly disseminate information), and mission brief (give specific instructions for a mission’s completion). On the other hand, military debriefing is used to receive information from a soldier or a pilot after a mission. It aims to analyze if mission objectives were met, the encountered challenges, and any valuable information. Military debriefing is also designed to instruct which information can be made public and censored. It also refers to the cross-examination of a spy.
Research
The research brief features a succinct summary of evidences which aims to introduce main findings to a varied audience. It may be presented through a webpage, written document, podcast, video, poster, seminar, etc. Moreover, in the briefing phase, the prospective participant will be informed of pertinent details and he or she will either accept or deny the researcher’s request. In comparison, the debriefing involves giving the participants the chance to ask questions. Also, the researchers share more details about the study’s objectives, hypotheses, and probable indications of findings.
Briefing vs Debriefing
Summary
- Briefing basically means giving information and is conducted at the beginning while debriefing is popularly defined as questioning someone and is generally done at the end.
- Military briefs are designed to clearly, concisely, and expediently present information while debriefing is done to receive information from a soldier or a pilot after a mission.
- In the briefing phase, the prospective participant will be informed of pertinent details and he or she will either accept or deny the researcher’s request while the debriefing involves sharing more information about the study’s objectives, hypotheses, and probable indications of findings.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Society of Clinical Psychology. Psychological Debriefing for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder. https://www.div12.org/treatment/psychological-debriefing-for-post-traumatic-stress-disorder/#:~:text=Psychological%20debriefing%20is%20a%20formal,disorder%20and%20other%20negative%20sequelae.
[1]United States Marine Corps. Military Briefing Student Handout. The Basic School Marine Corps Training Command, 2017. https://www.trngcmd.marines.mil/Portals/207/Docs/TBS/W3S0005%20-%20MILITARY%20BRIEFING.pdf?ver=2017-01-24-150014-960#:~:text=Military%20briefs%20are%20designed%20to,brief%2C%20and%20the%20mission%20brief.
[2]Warshawsky, D. Briefing, Debriefing, and Reporting. Ready for Sea Handbook. https://fas.org/irp/doddir/navy/rfs/part07.htm
[3]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2015/Jan/20/2001002175/780/780/0/150120-F-TN449-026.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/da/photos/debriefing-skrivning-papir-pen-5113960/
