Difference Between Internal and External Environment
What are internal and external environments?
The sum total of life-sustaining fluid, metabolic activities inside a living organism and surrounding objects outside its body cells, conditions, or impacts, ecology, air, water, minerals etc form the internal and the external environments of an organism.
The internal life-sustaining fluid that allows sustaining exchanges and encompassing the cells, form the internal environment. The internal environment is important for normal cell function. The surrounding environment in which a living organism lives forms the external environment.
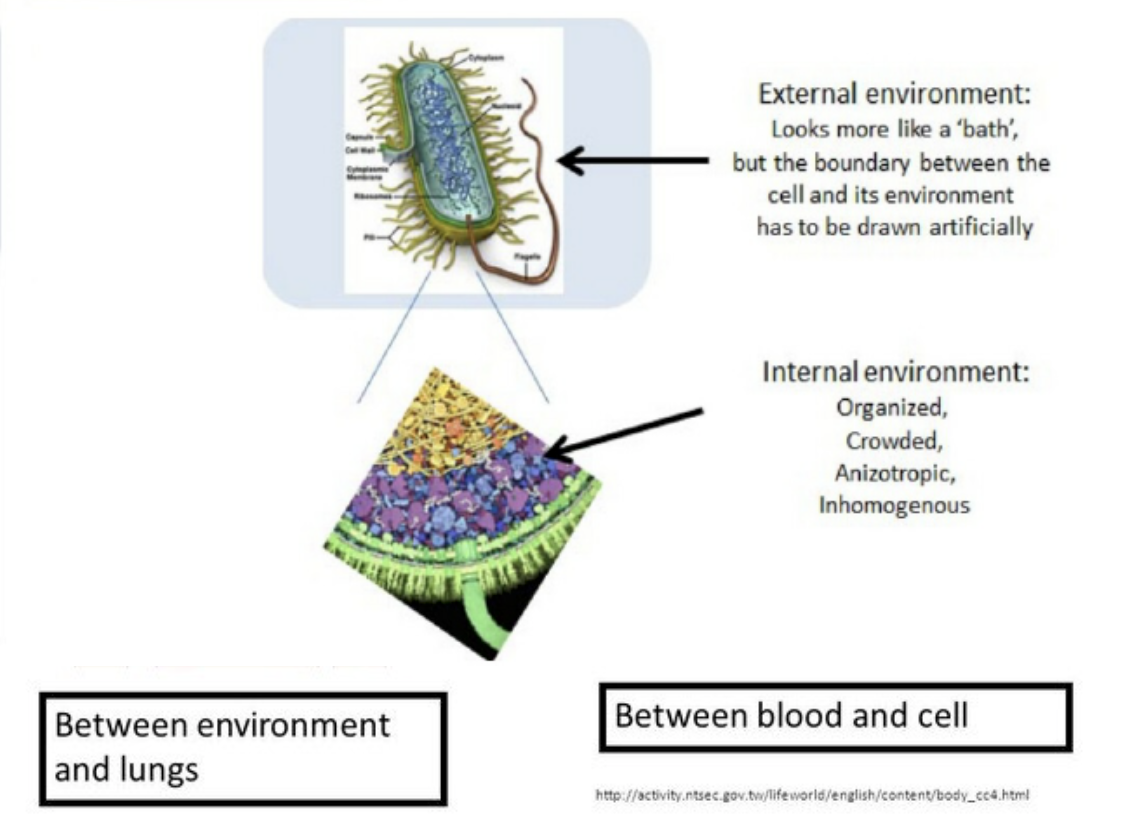
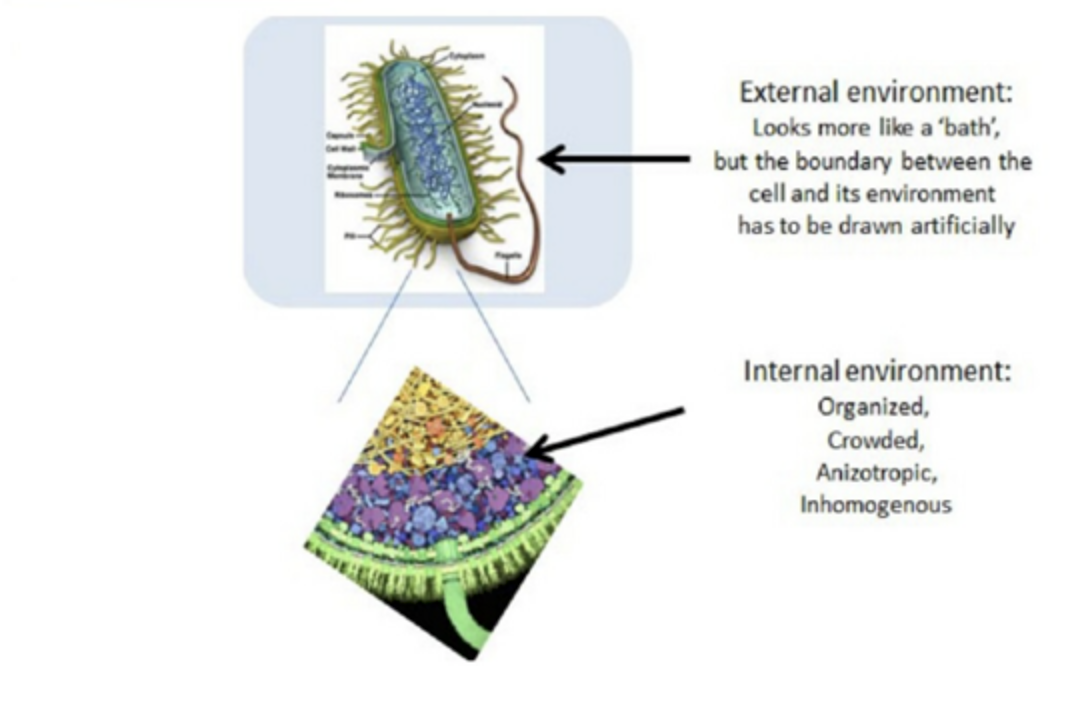
The association between the internal and external environments of a living organism is quite significant. While talking about unicellular organisms like Amoeba, algae and Paramecium, all the things to the inner side of its cell sheath comprise the internal environment.
What is Internal Environment?
The conception of the internal environment was first given by the French physiologist named Claude Bernard (1813–78), who said that conservation of an unchanging inside environment was mandatory for a living organism to survive and endure the varying outside environment.
Selective assimilation of matter traversing the cell walls play a significant role in controlling the inside environment of both flora and fauna. Animals, additionally are proficient in regulating their bodily fluids by the hormonal stimulation and also the nervous system. The conditions prevailing inside the body of an organism especially with respect to the anatomy of the tissue fluid are known as internal environment of an organism.
The internal body conditions that need to be controlled include temperature, water concentration, blood sugar content, CO2 level. These are controlled to offer a constant inside environment and that is called homeostasis.
What is External Environment?
The environment surrounding the organism from the outside, that involve physical, social, chemical and biological conditions encompassing the living organism. The external environment is utilized in contradiction to the inside environment of the living organism.
Living organisms discover and react to alteration in the conditions of their outside environment. In responding to any perils and opportunities, living organisms may act or change their actions. For e.g. floral stems show growth towards the sunlight. With time, the branches of trees become strong when they are tightened by the wind. Faunal species, react towards stimulus with a wide range of behaviours resulting due to hibernation activity of a bear to your own experience of Goosebumps on a cold and chilly night.
Figure 1. Internal and External environment.
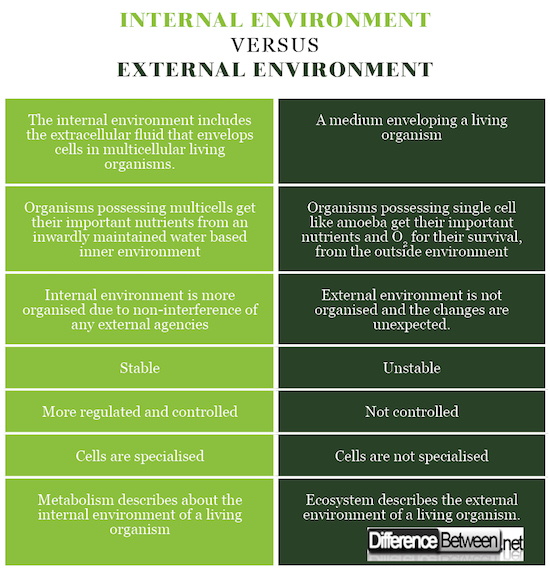
Difference Between Internal and External Environments
Definition
Internal environment
It is the extracellular fluid (literally, fluid outside the cells) environment surrounding each cell.
External environment
It is the air surrounding the living organism.
Stability
Internal environment
There is more stability in case of the internal environment. The reason for this is because living beings cannot endure extreme changes to aspects like water accessibility and temperature. If these aspects change too extremely, the biochemical reactions that take place within living cells that are requisite for maintaining life will be interrupted. This will cause death of the living organism
External environment
The external environment of a living organism is unstable.
Examples
Internal environment
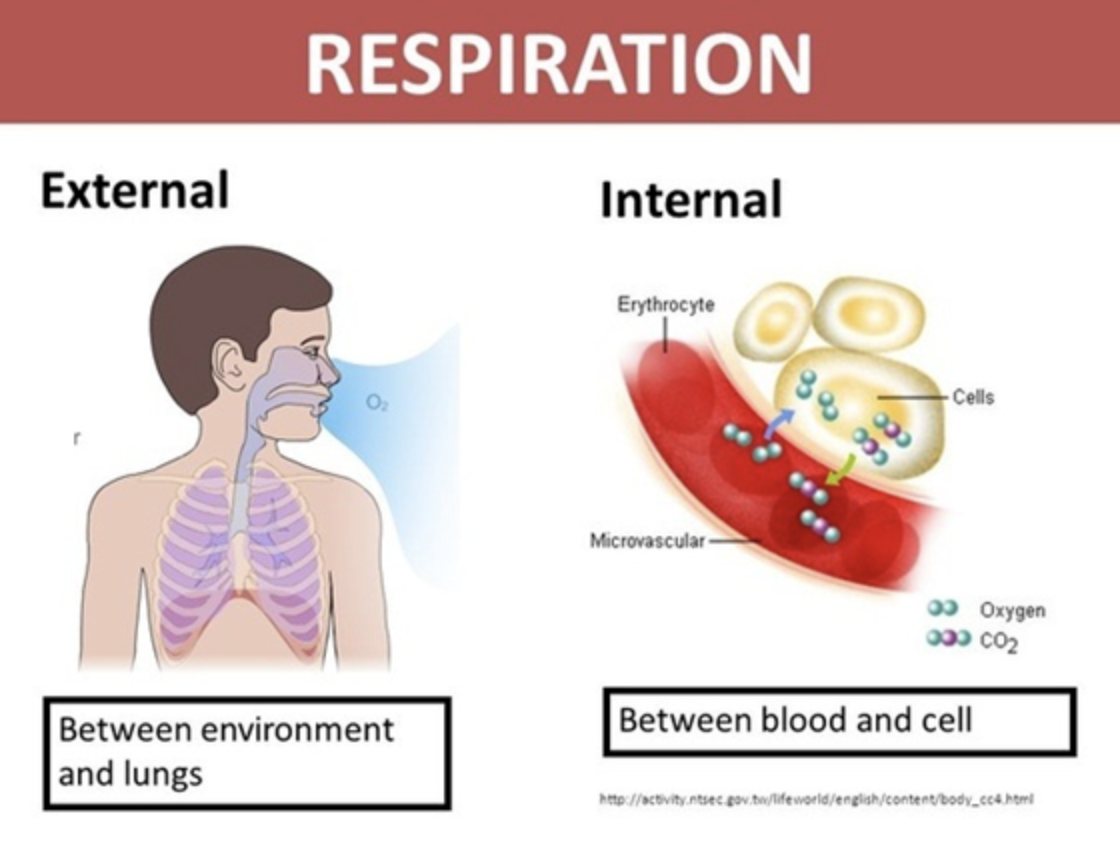
The concentration of Carbon dioxide (CO2), oxygen (O2) and water (H2O) around cells/organs/ tissues inside the body of a living organism.
External environment
Bacteria, changes in light, sound, temperature, heat, and chemical and mechanical contact.
Figure 2. Difference between Internal and External environment.
Tolerance
Internal environment
The internal environment is constant and maintenance of a constant interior environment is called homeostasis.
External environment
The external environment is too extreme for continued survival.
Summary of Internal and External Environment
The points of difference between internal environment and external environment have been summarized below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
2 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hammel, H. T., & Pierce, J. B. (1968). Regulation of internal body temperature. Annual review of physiology, 30(1), 641-710.
[1]Walsberg, G. E. (2001). Physiological diversity and its ecological implications. The Auk, 118(1), 279-280.
[2]Withers, P. C. (1992). Comparative physiology. Saunders College, Fort Worth Google Scholar.

This is good way to get ful infomatio n about education
This is really helpful