Difference Between Adjustment Disorder and Anxiety
Adjustment disorder is a type of depression that is triggered by some type of stressful life event. Anxiety is a feeling of worry and nervousness that interferes with everyday life and that can be caused by several factors.
What is Adjustment Disorder?
Definition:
Adjustment disorder is a form of depression that only happens when there is a major life stress that acts as a trigger. The condition can be confused with major depression but it does not last for as long a period of time.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of adjustment disorder include feeling hopeless and sad. Patients may also struggle to get a good night’s sleep or sleep too much. There are also often marked changes in appetite which can cause patients to either eat too much or too little food. Patients may often also feel irritable and tearful and stop doing what they would normally do.
Causes:
In the case of adjustment disorder, the cause is always a major life stressor such as loss of income, loss of a job, severe physical illness, or a death in the family.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis can be made by psychologists or physicians who note the presence of the symptoms, which do not normally occur for longer than 6 months. A key part of the diagnosis is noting that the symptoms begin only after a large and major stressful life event has taken place.
Treatment:
Sometimes adjustment disorder goes away after a short period of time, but there are treatment options that can help; for instance, the temporary use of benzodiazepine medications and cognitive behavioral therapy. Benzodiazepines are very addictive and thus for many patients, they can only be used for a short period of time.
What is Anxiety?
Definition:
Anxiety is a condition in which a person feels worried and uneasy to such an extent that it interferes with their daily life. There are different types of anxiety including generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety disorder.
Symptoms:
People who suffer from anxiety often feel a general sense of worry that does not go away. This feeling of foreboding, nervousness and uneasiness can result in physical symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, dizziness, increased sweating and even shaking. In severe cases, a person may have a panic attack and feel like they are about to die.
Causes:
It can be difficult to pinpoint a single reason for a person having anxiety. Anxiety can be due to genetic factors, the type of personality and psychological constitution of a person, environmental stresses or even having a physical illness. Many factors may interact to make a person more vulnerable to developing chronic anxiety problems. Certain medical problems such as heart problems, hormonal changes, and even some medications can trigger anxiety.
Diagnosis:
A psychologist can diagnose anxiety by noting the symptoms and they may also classify the anxiety into a specific type. Social anxiety is when a person becomes anxious only in social situations while generalized anxiety is constant nervousness and worry.
Treatment:
Anxiety disorders can be treated by a combination of methods including psychotherapy, cognitive therapy, and medication. Medications such as benzodiazepines are very effective in helping to alleviate extreme anxiety in patients. For some situations, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are also used and may help with particular types of anxiety; for instance, paroxetine is commonly used to treat social anxiety disorder.
Difference between Adjustment Disorder and Anxiety
Definition
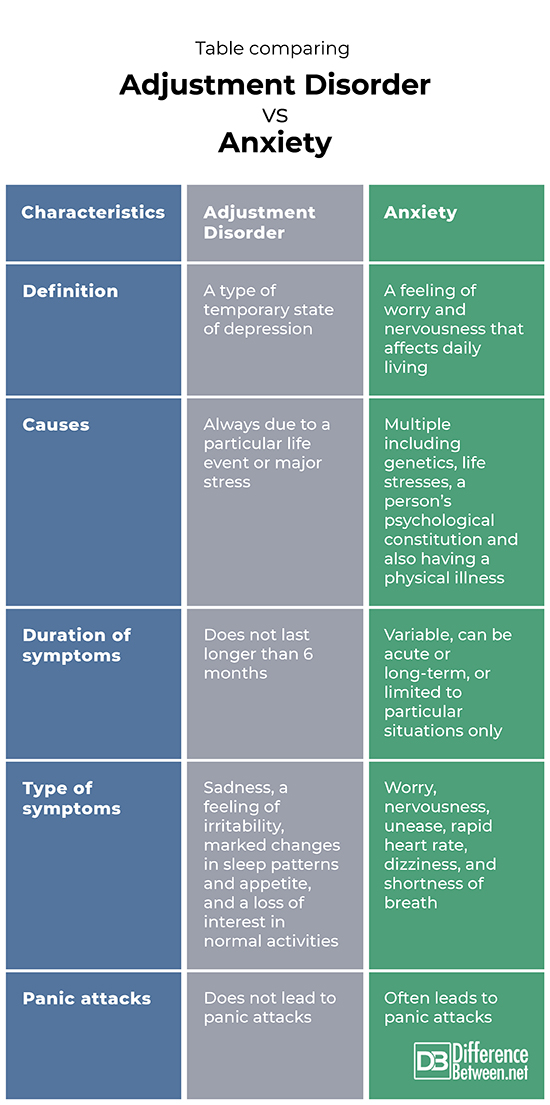
Adjustment disorder is a type of depression that is due to a major life stress or event and is temporary. Anxiety is worry and nervousness that often interferes with normal functioning and everyday life.
Causes
The cause of adjustment disorder is always an event that occurs which is stressful, such as, for instance, a death in a family. The causes of anxiety are many and can include genetics and environment or psychological constitution.
Duration of symptoms
Symptoms of adjustment disorder only last about half a year. Symptoms of anxiety vary depending on the type of anxiety and may be short-term or chronic.
Type of symptoms
Symptoms of adjustment disorder include sadness, irritability, changes in sleep patterns and appetite, and loss of interest in normal activities. Symptoms of anxiety include worry, nervousness, unease, rapid heart rate, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Panic attacks
Adjustment disorder does not generally lead to panic attacks. Anxiety disorders do often lead to panic attacks.
Table comparing Adjustment Disorder and Anxiety
Summary of Adjustment Disorder Vs. Anxiety
- Adjustment disorder is a form of depression that is caused by a major life stressor such as a death in the family.
- Anxiety can occur for a number of reasons including genetics, psychological makeup, and environmental factors.
- Both adjustment disorder and anxiety can be treated with a combination of cognitive therapy and medications such as benzodiazepines.
- Adjustment disorder does not last for more than 6 months.
- The duration of anxiety disorder varies depending on what type of disorder it is and may be a short-term condition or may be chronic.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/traumaanddissociation/14590708167
[1]Image credit: https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/O09dpGMEJYZHHs5RCyWTQrrEEdScgxF8g7I_y4Yb640QorDLrBxM80M43I2PT-0BimyqRx0OM40PVF5MJi9RsRHLuDI=s0
[2]Barnhill, John W. "Overview of anxiety disorders". Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/mental-health-disorders/anxiety-and-stress-related-disorders/overview-of-anxiety-disorders
[3]Carta, Mauro Giovanni, et al. "Adjustment Disorder: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment." Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health 5.1 (2009): 15.
[4]Snyder, Stephen, James J. Strain, and Dennis Wolf. "Differentiating major depression from adjustment disorder with depressed mood in the medical setting." General hospital psychiatry 12.3 (1990): 159-165.