Difference Between Autism and Down Syndrome
What is Autism and Down Syndrome?
Both autism and down syndrome are lifelong developmental conditions. Both disorders are totally different conditions with different causes, different symptoms, different manifestations and different medications and treatments.
What is Autism?
Autism, or autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a serious and complex neurobehavioral condition characterized by problems in interacting, non-verbal communication, verbal communication, speech, social and motor skills.
Autism is a lifelong developmental condition that affects how people recognize the world and interact with others. Autistic people look at others, hear, feel and interact with other people in an entirely different manner.
What is Down Syndrome?
Down syndrome (DS or DNS), is also termed as trisomy 2. It is a genetic disorder which is triggered by the third copy of chromosome 21. People with down syndrome show mental equivalent of an eight and nine-year-old. However, some individual can lead a very normal life.
The condition is usually characterized by delay in growth, a poor muscle tone and a lower IQ.
The disorder occurs by chance and can be detected in the womb itself.
Difference Between Autism and Down Syndrome
-
Definition
Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) A neurotype with causes most of which are not known (there exists a genetic factor though). The effects include weakened social cognition and interaction, sensitive power of sensation, and a restricted focus of interests. Some individuals even suffer a delay in cognitive development. Again, there are many more abnormal traits of autistic individuals, but it is not usually a result of physical health problems.
Down Syndrome
A genetic condition which is a result of altered chromosome setup. The typical effects include learning disability, delayed speech, upward slant to the eyes, delayed crawling and walking, delay in physical growth, mild to moderate issues with reasoning, thinking, and understanding intellectual disability, short stature and characteristic facial features. There are many other more symptoms and individuals with down syndrome often face physical health problems.
-
Types
Autism
There are 3 different types of Autism Spectrum Disorders namely;
- Autistic Disorder (also known as “classic” autism)
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder – (also known as “atypical autism”)
- Asperger Syndrome
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21
A common chromosome disorder, often termed as Down syndrome, due to an extra chromosome number 21 (trisomy 21). This variant accounts for 95% of Down syndrome cases. The rest of 5% of Down syndrome cases are because of conditions called Mosaicism Down Syndrome and Robertsonian translocation.
Mosaic Down syndrome
Mosaicism is usually described as a percentage. Twenty different cells are assessed in a chromosome study. A child is suffering from Mosaic Down Syndrome if:
- Five of the twenty cells possess typical number of forty-six chromosomes
- The remaining fifteen have a total of forty-seven chromosomes as a result of an extra chromosome twenty-one.
Robertsonian translocation (ROB)
This is the most common form of chromosomal rearrangement and takes place when the participating chromosomes break at their centromeres and the longer arm fuses to form a single, large chromosome with a single centromere. In this, a person possesses 45 chromosomes and are phenotypically normal. An individual with a translocation does not possess special physical features, but they are more likely to have a kid with an extra 21st chromosome.
-
Causes
Autism
There is no single cause for autistic spectrum disorder. It is mostly caused by certain abnormalities in the brain. However, autism is linked to several underlying medical conditions like:
- Absence of enzymes needed for metabolic activity – (untreated phenylketonuria [PKU])
- Congenital infections in the pregnant mother – German measles (Rubella), Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Toxoplasmosis
- Inflammation in brain – Encephalitis and bacterial meningitis) (Neurological disorders that happen after birth)
- Tuberous sclerosis and Fragile X Syndrome (rare genetic disorders)
- Influenza (flu) multidose preparations
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome disorder is caused when abnormal cell division takes place and you get an extra full or partial copy of genetic material from chromosome 21. The extra chromosome causes issues as the brain and physical features develop. This disorder is not linked to anything in the enternal environment or anything that parents did or did not do.
-
Symptoms
Autism
- Restricted repertoire of interests, activities and behaviours
- Impaired communication
- Impaired reciprocal social interaction
- Abnormalities in eating or sleeping
- Ritualistic or compulsive behaviours
- Seizures
Down Syndrome
- Bulging tongue
- Flaccid muscles
- Loss of hearing
- Eyes that slant upward and short neck
- Obesity and Immune deficiency
- Vision disorder
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
- Polycythaemia
- Thickening of the skin of the palms and soles
-
Treatment and Medications
Autism
- Treatment
- Applied behaviour analysis
- Cognitive behavioural therapy
- Social skills training
- Sensory integration therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
- Medications
- Antipsychotics
- Antidepressants
- Stimulants
- Anticonvulsants
- Potential alternative treatments
- Gluten-free
- Melatonin
- Oxytocin
- Vitamin C
- Dimethylglycine
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- CBD Oil
- Vitamin B-6 and magnesium in combination
Down Syndrome
- Treatment
- Early Intervention and Educational Therapy
- Speech therapy
- Medical subspecialists depending on the requirements of the patient (for example, geneticist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, hearing and eye specialists)
- Occupational therapy
- Exercises to help improve motor skills
- Behavioural therapy to help manage the emotional challenges
- Medication
- Amino acid supplements
- A drug known as Piracetam
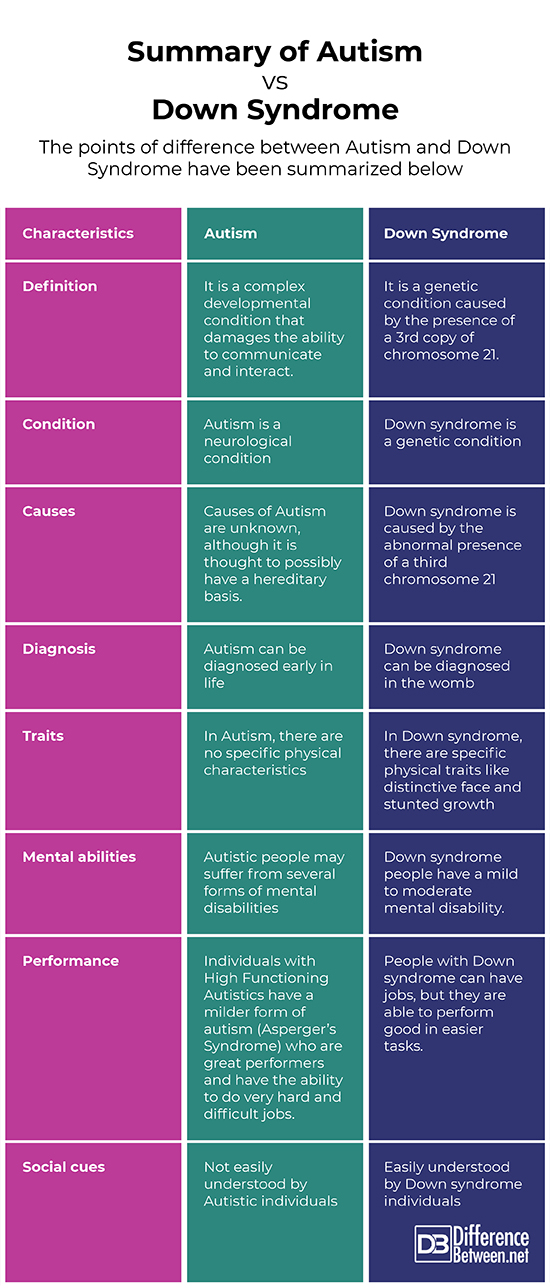
Summary of Autism Vs. Down Syndrome
The points of difference between Autism and Down Syndrome have been summarized below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/15/Down_syndrome_lg.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/heart-autism-awareness-support-love-3612853/
[2]Desai, S. S. (1997). Down syndrome: a review of the literature. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics, 84(3), 279-285.
[3]Dugger, C. E. (2012). The Effects of Early Intervention on Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research Papers.
[4]Lord, C., Cook, E. H., Leventhal, B. L., & Amaral, D. G. (2013). Autism spectrum disorders. Autism: The Science of Mental Health, 28(2), 217.


I really love this. It gave me clarification.