Difference Between COPD and Asthma Treatment
What is COPD Treatment?
The treatment of COPD is driven by the need to control the symptoms. The aim of the treatment is to:
- Prevent the progression of the disease;
- Relieve the symptoms;
- Improve the patient’s health status;
- Prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations and complications;
- Improve the tolerance to physical activities;
- Reduce mortality.
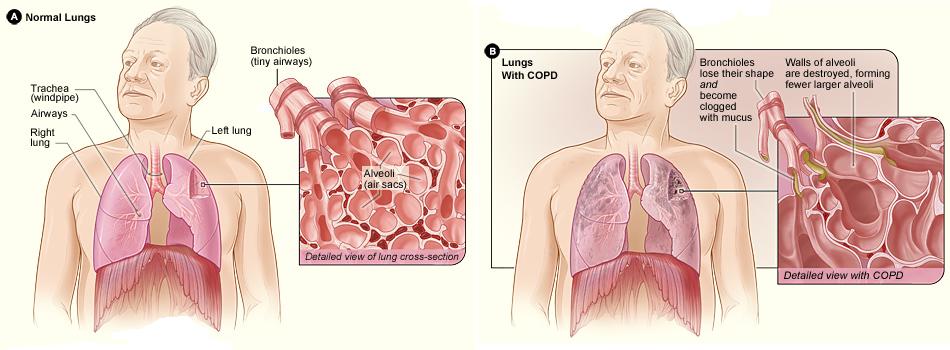
In COPD is very important to reduce the exposure to risk factors. These factors include tobacco smoke, occupational exposures, air pollution. The most important thing in case of COPD is to quit smoking. This may help prevent the lungs from further damage and slow the progression of the disease.
It is also important to avoid irritants that are worsening the symptoms, like air pollution, dust, chemicals, etc.
The following medications are used in COPD:
- Long-acting bronchodilators – preparations of the group of Methylxanthate and long-acting beta2-receptor agonists (Theophylline, Noviline, Formoterol, Salmeterol), providing prolonged dilatation of the bronchial tree.
- Inhaled corticosteroids – they are the “gold standard” in the treatment of asthma but are also used in COPD therapy. Despite their widespread use, the benefit of these drugs to COPD is controversial. They do not slow down the progress of the disease but reduce the frequency of exacerbations and improve the quality of life.
- Secretagogues – added upon exacerbation of the disease.
- Additional treatment – due to frequent exacerbations due to viral and bacterial infections, antibiotics have to be prescribed. Vaccines can be used to help prevent certain respiratory infections.
The surgery is the only definitive treatment of COPD. The possible surgical procedures are lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplantation.
COPD is a progressive condition, which typically gets worse over time. Lungs damaged by COPD can’t return to normal even with treatment.
What is Asthma Treatment?
The asthma treatment is driven by the need to avoid/minimize asthma attacks. The aim of the treatment is to:
- Prevent the progression of the disease;
- Relieve the symptoms;
- Improve the patient’s health status;
- Prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations;
- Maintain the function of the lungs as close to normal as possible;
- Maintain the physical activity levels as close to normal as possible;
- Prevent irreversible airflow limitations;
- Reduce mortality.
Factors, triggering asthma attacks, can be different for every patient. The attacks can be triggered by pets, pollen, dust, etc. For patients with asthma it is very important to avoid their personal triggers.
The medications used in asthma are:
- Inhaled corticosteroids – the “gold standard” in asthma treatment. They provide relieve of chronic inflammation and suppress the allergic reaction. In severe forms of asthma, as well as during a severe asthma attack, they may be administered orally or intravenously.
- Long-acting bronchodilators – preparations of the group of Methylxanthate and long-acting beta2-receptor agonists (Theophylline, Noviline, Formoterol, Salmeterol). They provide prolonged dilatation of the bronchial tree and prevent the night attacks.
- Anti-allergic stabilizers – used in the prophylaxis of asthma attacks – Cromoglycates, Ketotifen.
- Leukotriene antagonists – a relatively new class of drugs used in the therapy of asthma – Montelukast, etc.
- Additional treatment– treatment of the prerequisites for the onset of asthma and its complications – antibiotics, mucolytics, secretolytics, treatment of reflux disease, etc.
There is a relatively new surgical procedure which can be applied to relieve the symptoms of asthma. It is called bronchial thermoplasty and consists in the reduction of the ability of some muscles from the airway to constrict by burning them off.
Asthma can be well controlled with a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In children, it is possible to outgrow the disease as they get older.
Difference Between COPD and Asthma Treatment
-
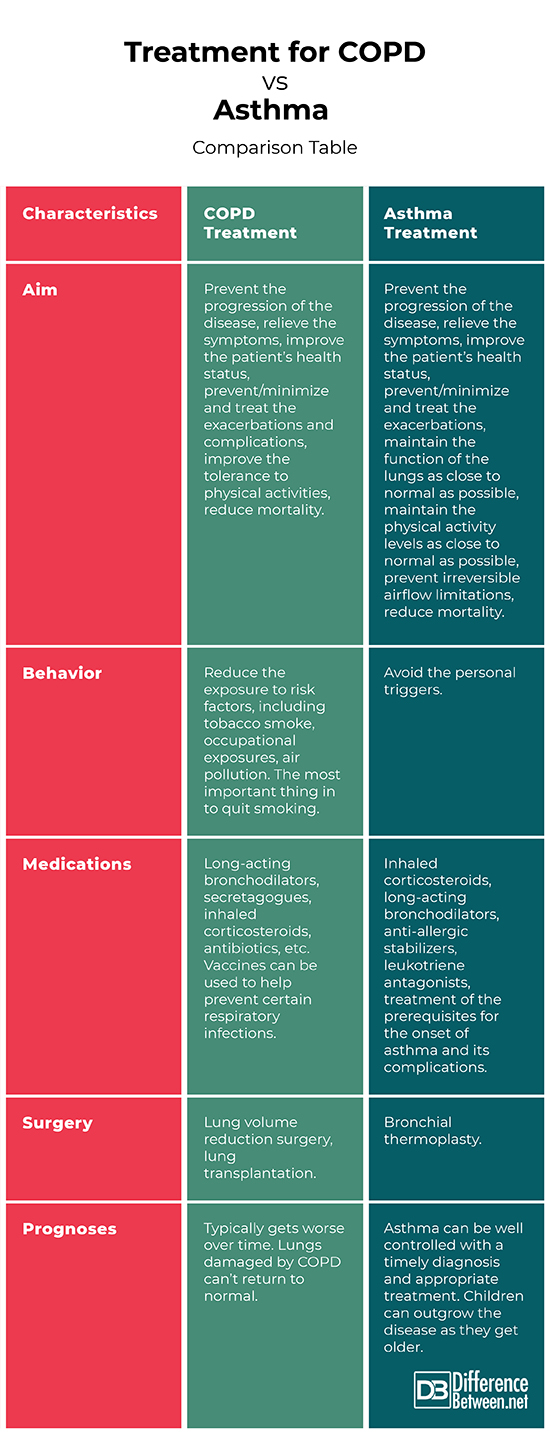
Aim
COPD Treatment: The treatment of COPD is driven by the need to control the symptoms. Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations and complications, improve the tolerance to physical activities, reduce mortality.
Asthma Treatment: The treatment of asthma is driven by the need to avoid/minimize asthma attacks. Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations, maintain the function of the lungs as close to normal as possible, maintain the physical activity levels as close to normal as possible, prevent irreversible airflow limitations, reduce mortality.
-
Behavior
COPD Treatment: In COPD it is important to reduce the exposure to risk factors, including tobacco smoke, occupational exposures, air pollution. The most important thing is to quit smoking.
Asthma Treatment: For patients with asthma it is important to avoid their personal triggers.
-
Medications
COPD Treatment: The medications used in COPD are long-acting bronchodilators, secretagogues, inhaled corticosteroids, antibiotics, etc. Vaccines can be used to help prevent certain respiratory infections.
Asthma Treatment: The medications used in asthma are inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting bronchodilators, anti-allergic stabilizers, leukotriene antagonists, medications for treatment of the prerequisites for the onset of asthma and its complications.
-
Surgery
COPD Treatment: The surgery is the only definitive treatment of COPD. The possible surgical procedures are lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplantation.
Asthma Treatment: Bronchial thermoplasty can be applied to relieve the symptoms of asthma. It consists in the reduction of the ability of some muscles from the airway to constrict by burning them off.
-
Prognoses
COPD Treatment: COPD is a progressive condition, which typically gets worse over time. Lungs damaged by COPD can’t return to normal even with treatment.
Asthma Treatment: Asthma can be well controlled with a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Children can outgrow the disease as they get older.
Treatment for COPD verses Asthma : Comparison Table
Summary of COPD vs. Asthma Treatment:
- The treatment of COPD is driven by the need to control the symptoms. Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations and complications, improve the tolerance to physical activities, reduce mortality.
- Asthma’s treatment is driven by the need to avoid/minimize asthma attacks. Its aim is to prevent the progression of the disease, relieve the symptoms, improve the patient’s health status, prevent/minimize and treat the exacerbations, maintain the function of the lungs as close to normal as possible, maintain the physical activity levels as close to normal as possible, prevent irreversible airflow limitations, reduce mortality.
- In COPD it is important to reduce the exposure to risk factors, in asthma, it is important to avoid the personal triggers.
- The medications used in COPD are long-acting bronchodilators, secretagogues, inhaled corticosteroids, antibiotics, etc. Vaccines can be used to help prevent certain respiratory infections. The medications used in asthma are inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting bronchodilators, anti-allergic stabilizers, leukotriene antagonists, medications for treatment of the prerequisites for the onset of asthma and its complications.
- Inhaled corticosteroids are the “gold standard” in the treatment of asthma. They are also used in COPD therapy but with controversial results.
- The surgery is the only definitive treatment of COPD. The possible surgical procedures are lung volume reduction surgery and lung transplantation. In case of asthma bronchial thermoplasty can be applied.
- COPD is a progressive condition, which typically gets worse over time. Asthma can be well controlled with a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Haas, F., S. Haas, R. Human. The Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema Handbook. 1st Edition. New York, Toronto: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 2000. Print.
[1]Warrell, D., T. Cox, J. Firth. Oxford Textbook of Medicine, Vol. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2010. Print.
[2]Yankova, Z. New Guide to Pulmonary Diseases and Tuberculosis. Sofia: Medical University Press. 2012. Print.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Copd_2010Side.JPG
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Asthma_comorbidities_2.PNG

I’m 59 years old and female. I was diagnosed a couple of years ago with COPD and I was beyond scared! My lung function test indicated 49% capacity. After having had flu a year ago, the shortness of breath, coughing and chest pains continued even after being treated with antibiotics. I’ve been smoking two packs a day for 36 years. Being born without a sternum caused my ribs to be curled in just one inch away from my spine, resulting to underdeveloped lungs. At age 34 I had surgery and it was fixed. Unfortunately my smoking just caused more damage to my already under developed lungs. The problem was having is that I enjoy smoking and don’t want to give up! Have tried twice before and nearly went crazy and don’t want to go through that again. I saw the fear in my husband and children’s eyes when I told them about my condition then they start to find solution on their own to help my condition.I am an 59 now who was diagnose COPD emphysema which I know was from my years of smoking. I started smoking in school when smoking was socially acceptable. I remember when smoking was permitted in hospitals. It was not known then how dangerous cigarettes were for us, and it seemed everybody smoked but i was able to get rid of my COPD lung condition through the help of total cure herbal foundation my husband bought, totalcureherbsfoundation .c om has the right herbal formula to help you get rid and repair any lung conditions and cure you totally with their natural organic herbs,it class products at affordable prices. Purchase these medicines and get the generic medicines delivered in USA, UK & Australia,I wish anybody who starts smoking at a young age would realize what will eventually happen to their bodies if they continue that vile habit throughout their life.