Difference Between Hematoma and Pseudoaneurysm
A hematoma is a pool of blood found somewhere in the body. A pseudoaneurysm is a section of an artery wall that is damaged.
What is Hematoma?
Definition:
A hematoma is an area of blood that has formed and collected somewhere in the body.
Causes and risk factors:
The cause of a hematoma is injury to a blood vessel. Any type of trauma or injury can cause a hematoma. How severe the problem is, depends on where the hematoma is and how big it is. For instance, hitting your toe may cause a small hematoma but a hard hit to the head may cause a more dangerous subdural hematoma. Anybody who is taking blood thinning medication is at increased risk of a hematoma. An aneurysm that starts to bleed can also result in a hematoma forming.
Symptoms and complications:
A hematoma under the skin may show as a purple spot on the skin. It may also be sore. A hematoma in the brain can produce severe symptoms like dizziness, vomiting, confusion, and headache. An intracranial hematoma is dangerous as it can lead to brain damage and death.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of a hematoma is by physical examination and imaging tests. Brain hematomas can be detected using MRI or CT scans.
Treatment:
Treatment methods depend on the type, size, and location of the hematoma. A small hematoma under the skin does not need to be treated. A hematoma in the brain often does require treatment, usually surgery, to remove the blood and alleviate pressure placed on the brain tissue.
What is Pseudoaneurysm?
Definition:
A pseudoaneurysm is when part of a blood vessel wall is damaged, sometimes causing blood leakage but definitely some blood accumulation between the walls of the blood vessel.
Causes and risk factors:
There are a couple of reasons you can develop a pseudoaneurysm. It is a complication of a catheter placement during angiography. Other causes include infection and surgery or some type of trauma. Risk factors include being on antiplatelet medicines and undergoing angiography.
Symptoms and complications:
The signs of a pseudoaneurysm include pain and the area where the problem is will be swollen and there will often be a lump present under the skin. The complication with a pseudoaneurysm is that it can burst, causing blood loss. It can also increase the chance of clots forming that could move and lodge in an artery causing further damage. For example, a pseudoaneurysm in a carotid artery could result in a clot that goes to the brain and causes a stroke.
Diagnosis:
A pseudoaneurysm is diagnosed by using an ultrasound and visualizing the blood vessel where the problem is thought to be.
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the size of the pseudoaneurysm. If it is small, less than 2 cm, nothing may be done. A large pseudoaneurysm can be treated with medicine under the guidance of ultrasound, or else by surgery or ultrasound-guided compression.
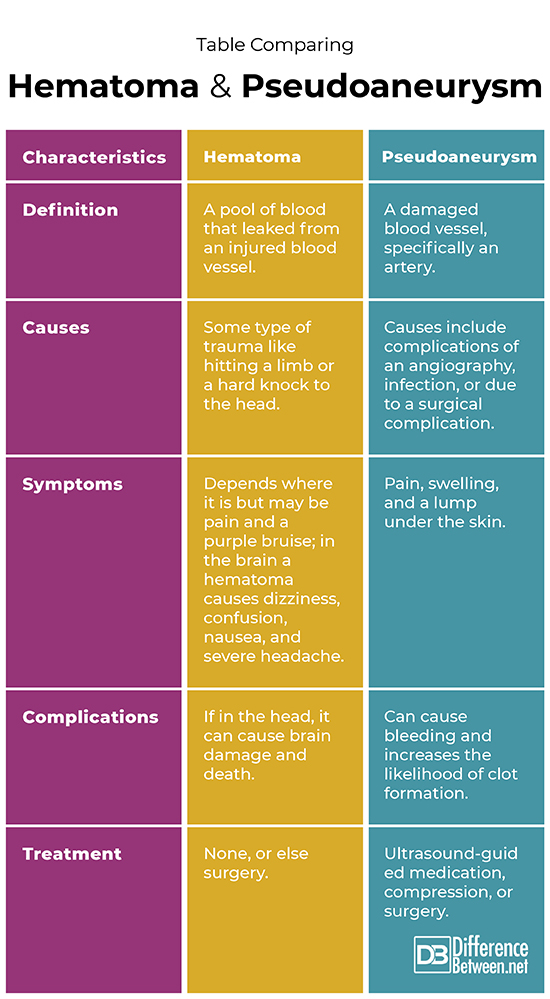
Difference between Hematoma and Pseudoaneurysm?
Definition
A hematoma is defined as a pool of blood that leaked from an injured blood vessel. A pseudoaneurysm is the damaged part of an artery.
Causes
A hematoma is caused by some type of trauma. The causes of a pseudoaneurysm are complications of an angiography or surgery, or infection.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a hematoma depend on its location and size but may include pain and a purple bruise; in the brain a hematoma causes dizziness, confusion, nausea, and severe headache. Symptoms of a pseudoaneurysm include pain, swelling, and the presence of a lump.
Complications
Complications of a hematoma are more likely if it is in the head; this can lead to brain damage and death. Complications of a pseudoaneurysm include bleeding and an increased chance of a clot forming.
Treatment
A hematoma may not need treatment but one in the brain usually requires surgery. A pseudoaneurysm can be treated with ultrasound-guided compression, medicine, or surgery.
Table comparing Hematoma and Pseudoaneurysm
Summary of Hematoma Vs. Pseudoaneurysm
- A hematoma and pseudoaneurysm are both related to the blood vessels.
- A hematoma is when blood pools under the skin because of an injury.
- A pseudoaneurysm is a specific area of damage in an artery.
FAQ
Is a pseudoaneurysm a hematoma?
A pseudoaneurysm is sometimes considered to be a type of hematoma because blood collects, but it collects between the walls of the blood vessel.
What exactly is a pseudoaneurysm?
A pseudoaneurysm is a damaged section of an artery, usually a tear in the blood vessel walls.
How do you rule out pseudoaneurysm?
Imaging tests like ultrasounds are a way to see if a pseudoaneurysm is present or not.
What is a hematoma?
A hematoma is when blood pools under the skin or in the brain.
Is pseudoaneurysm an emergency?
The only time a pseudoaneurysm is an emergency is if it bursts, causing bleeding.
What is the most common cause of pseudoaneurysm?
The most common cause of a pseudoaneurysm is a complication of placing a catheter, specifically during angiography.
What is recovery time for a pseudoaneurysm?
It can take about a month to recover from a pseudoaneurysm.
Can a pseudoaneurysm heal on its own?
A small pseudoaneurysm often heals on its own after 4 weeks.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cleveland Clinic. “Subdural hematoma”. Cleveland Clinic, 2022, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21183-subdural-hematoma
[1]Koc, R. Kemal, et al. "Acute subdural hematoma: outcome and outcome prediction." Neurosurgical review 20.4 (1997): 239-244.
[2]Mayo Clinic. “Pseudoaneurysm: What causes it”. Mayo Clinic, 2022, https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cardiac-catheterization/expert-answers/pseudoaneurysm/
