Difference Between Hematoma and Seroma
Surgical complication is the term often used in the medical profession, but its true nature still remains inconsistent over the years. They are commonly referred to as operative complications that comprise both intra and post-operative complications. One such surgery related complication is associated with sutures. Sutures are a fundamental part of veterinary surgery. There are like over a dozen of complications associated with sutures alone. Dead space is one such surgery related complication created after tissue debridement or mass removal. This may result in the formation of seroma or hematoma which increases the risk of incisional infection. So, what are seroma and hematoma, and how they form? Let’s take a look.
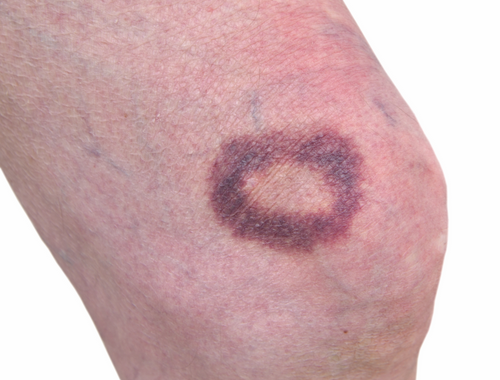
Hematoma
Hematoma is generally defined as a collection of hemat, which means blood. Often called blood suffusion, hematoma is a collection of blood outside of the larger blood vessels. Post trauma, injury or surgery sometimes large amount of blood is accumulated on the body part, much like a bruise. This is hematoma. It’s common when some injury to the wall of a blood vessel causes blood to collect and pool under the skin, resulting in the formation of hematoma. Depeding on the cause, location or the size, sometimes surgery is required to drain the blood. Hematoma increases the wound tension which many affect the wound healing process, thereby reducing the tissue perfusion. It can also happen inside the body when they cannot be seen clearly.
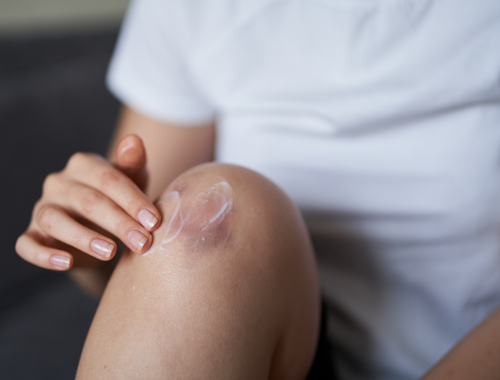
Seroma
Unlike hematoma which is a collection of blood, seroma is the collection of clear fluid under the surface of your skin, typically around the area of an incision. Seroma is a collection or blob of serous fluid that normally develops in the body post surgery, particularly following a breast surgery. It generally forms between the muscle layer and the fat layer of your body because those tissue layers haven’t healed together yet. What a seroma does is it pushes those layers apart so they can’t heal properly. It often develops as a complication of surgery but can also be formed after an injury. It is often not a high-risk thing, but can cause serious pain and discomfort. It looks like a soft, tender swollen lump like a large cyst that discharges clear fluid.
Difference between Hematoma and Seroma
Nature
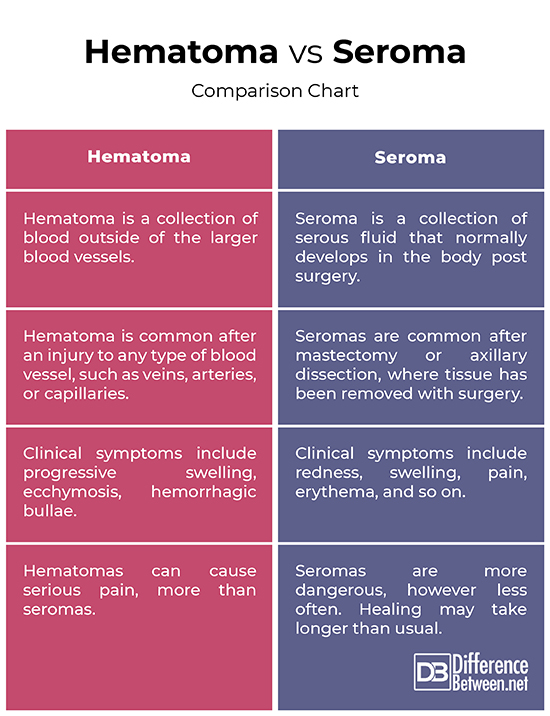
– Both hematoma and seroma are surgery related complications that develop in the body following a surgery, and they affect wound healing in patients. But a hematoma is not the same as a seroma. Hematoma is when a pool of blood collects under your skin after surgery and looks like a bruise or something. Seroma, on the other hand, is the collection of clear fluid under the surface of your skin, typically around the area of an incision. Besides the nature, both hematoma and seroma create a barrier between the skin flap and the soft tissue.
Cause
– Seromas are very distinct from hematomas as they contain almost no red blood cells. Seromas are basically serous fluid formations which look like a large cyst. Although some degree of ecchymosis is common after breast surgery, true hematomas occur in less breast biopsies or breast procedures. They are a common result of an injury to any type of blood vessel, such as veins, arteries, or capillaries. Seromas are common after mastectomy or axillary dissection. It develops in the body where tissue has been removed with surgery. When the surgical wound doesn’t heal properly, a dead space may form between the tissues.
Hematoma vs. Seroma: Comparison Chart
Summary
Clinically, both hematomas and seromas are the most common surgical complications that may develop within the first 24 hours after a surgery is performed. These complications present as extensive ecchymosis, which is like a collection of fluid beneath the incision site. Often a little pain in involved and may not present any immediate complications clinically. Extensive undermining increases the likelihood of formation of seroma, while failure to achieve meticulous hemostasis increases the risk of hematoma. Both are often not dangerous and can be treated with antibiotics prescribed by your healthcare professional.
What are the signs of a seroma?
Common signs of seroma include swollen lump, unevenness in the area, pain around the area, redness in the area, a feeling of liquid moving under the skin, and so on. The signs are often visible and the area surrounding it may become inflamed and red.
Is a seroma hard or soft?
Seroma is a soft, tender swollen lump like a large cyst that discharges clear fluid.
What is a hematoma?
Hematoma is a pool of blood formation under your skin after surgery and looks like a bruise.
What is a hematoma in an incision?
Hematoma represents a collection of blood beneath the incision site. When a pool of blood collects under your skin after surgery, it is hematoma.
Does compression help seroma?
Small seromas can be resolved with compressions alone. Doctors often recommend patients to wear compression garments for a couple of weeks after surgery. This massages the area gently to help move the fluid out.
When should I be concerned about a seroma?
Although often harmless, there are cases when seromas become extremely large and infected and turn into an abscess. If it gets very painful and you start experiencing some complications, you should go see a doctor.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
References :
[0]Eisele, David and Richard V. Smith. Complications in Head and Neck Surgery. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences, 2008. Print
[1]Eisele, David and Richard V. Smith. Complications in Head and Neck Surgery. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences, 2008. Print
[2]Rubio-Martinez, Luis M. and Dean A. Hendrickson. Complications in Equine Surgery. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2021. Print
[3]Gloster, Hugh M. Complications in Cutaneous Surgery. Berlin, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2010. Print
